Abstract
The registration accuracy of skin- and bone-implanted fiducials using a frameless stereotactic system were analyzed prospectively.
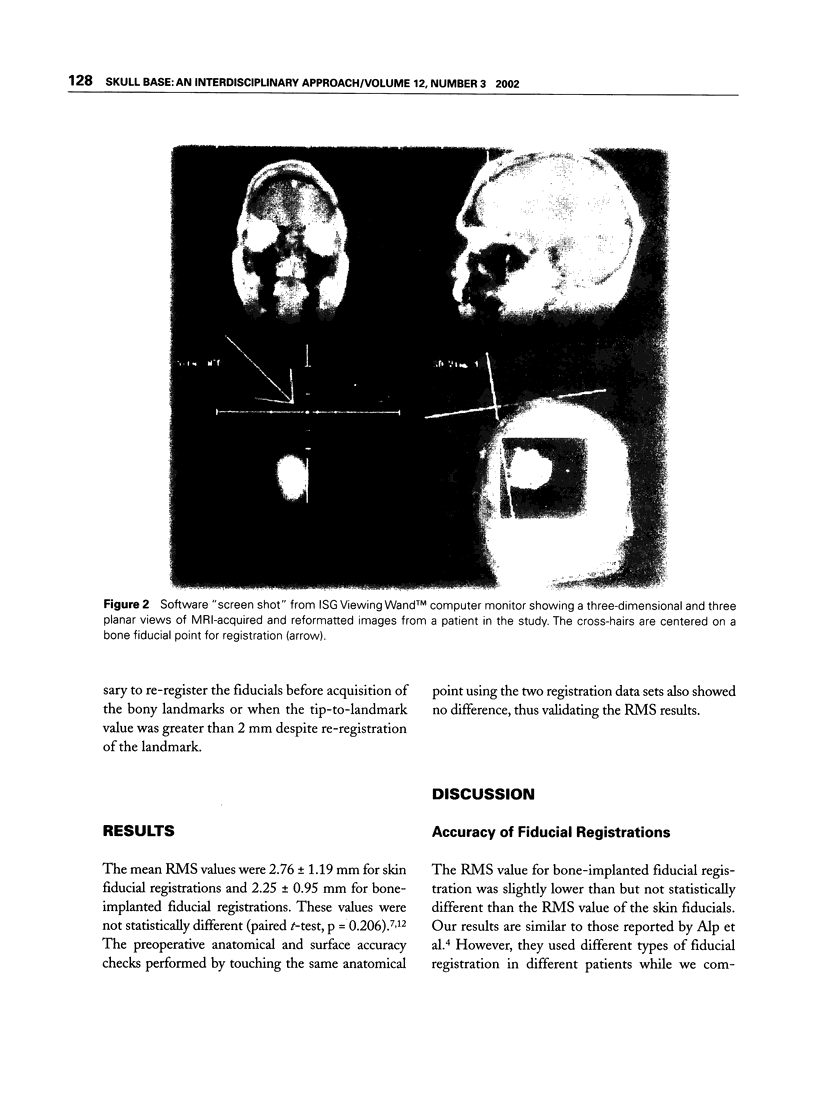
Twenty-eight patients underwent resection of intra-axial neoplasmas after both skin- and bone-implantable fiducial markers were placed. Both sets of fiducials were independently co-registered to a magnetic resonance imaging data set acquired preoperatively using the ISG Viewing Wand™. Root mean square errors were recorded as an objective measure of registration accuracy of the two types of fiducials.
Root mean square errors of bone-implanted fiducials registration were lower than those of skin fiducials; however, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.206).
The registration accuracy of skin- and bone-implanted fiducials appears to be similar. Still, bone-implanted fiducials may be advantageous compared to skin fiducials when re-registration of the patient-image space is desired intraoperatively such as during major drift in the patient's position or after surgical repositioning.
Keywords: Fiducial markers, frameless stereotaxis, registration accuracy
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alp M. S., Dujovny M., Misra M., Charbel F. T., Ausman J. I. Head registration techniques for image-guided surgery. Neurol Res. 1998 Jan;20(1):31–37. doi: 10.1080/01616412.1998.11740481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. S., Lustgarten J. H., Miller E., Khandji A. G., Goodman R. R. Effects of coregistration of MR to CT images on MR stereotactic accuracy. J Neurosurg. 1995 May;82(5):772–779. doi: 10.3171/jns.1995.82.5.0772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R., Heilbrun M. P., Koehler S., McDonald P., Peters W., Siemionow V. Three-point transformation for integration of multiple coordinate systems: applications to tumor, functional, and fractionated radiosurgery stereotactic planning. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1994;63(1-4):76–79. doi: 10.1159/000100296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golfinos J. G., Fitzpatrick B. C., Smith L. R., Spetzler R. F. Clinical use of a frameless stereotactic arm: results of 325 cases. J Neurosurg. 1995 Aug;83(2):197–205. doi: 10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbrun M. P., Koehler S., MacDonald P., Siemionow V., Peters W. Preliminary experience using an optimized three-point transformation algorithm for spatial registration of coordinate systems: a method of noninvasive localization using frame-based stereotactic guidance systems. J Neurosurg. 1994 Nov;81(5):676–682. doi: 10.3171/jns.1994.81.5.0676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm P. A., Eckel T. S. Accuracy of registration methods in frameless stereotaxis. Comput Aided Surg. 1998;3(2):51–56. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1998)3:2<51::AID-IGS1>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler P. F., Napel S., Sumanaweera T. S., Pichumani R., van den Elsen P. A., Martin D., Drace J., Adler J. R., Perkash I. Registration error quantification of a surface-based multimodality image fusion system. Med Phys. 1995 Jul;22(7):1049–1056. doi: 10.1118/1.597591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. M., Smith K. R., Bucholz R. D. An accurate and ergonomic method of registration for image-guided neurosurgery. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1994 Jul-Aug;18(4):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0895-6111(94)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaus M., Steinmeier R., Sporer T., Ganslandt O., Fahlbusch R. Technical accuracy of a neuronavigation system measured with a high-precision mechanical micromanipulator. Neurosurgery. 1997 Dec;41(6):1431–1437. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199712000-00046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney J., Roberts D. W. Frameless stereotaxy of the brain. Mt Sinai J Med. 2000 Sep;67(4):300–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimsky C., Ganslandt O., Cerny S., Hastreiter P., Greiner G., Fahlbusch R. Quantification of, visualization of, and compensation for brain shift using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery. 2000 Nov;47(5):1070–1080. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200011000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipos E. P., Tebo S. A., Zinreich S. J., Long D. M., Brem H. In vivo accuracy testing and clinical experience with the ISG Viewing Wand. Neurosurgery. 1996 Jul;39(1):194–204. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199607000-00048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. K., Grzeszczuk R., Levin D. N., Pelizzari C. A., Chen G. T., Erickson R. K., Johnson D., Dohrmann G. J. A frameless stereotactic approach to neurosurgical planning based on retrospective patient-image registration. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1993 Aug;79(2):296–303. doi: 10.3171/jns.1993.79.2.0296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. B., Fitzpatrick J. M., Toms S. A., Maurer C. R., Jr, Maciunas R. J. Fiducial point placement and the accuracy of point-based, rigid body registration. Neurosurgery. 2001 Apr;48(4):810–817. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200104000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]