Abstract
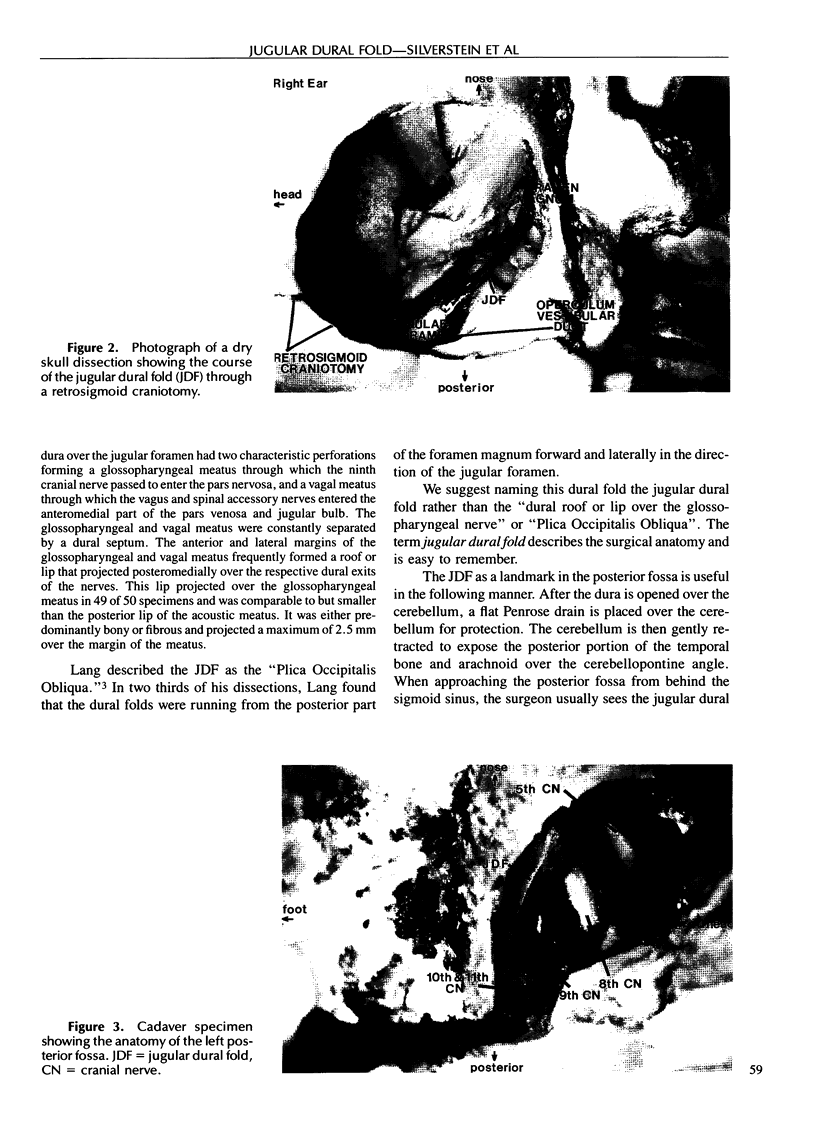
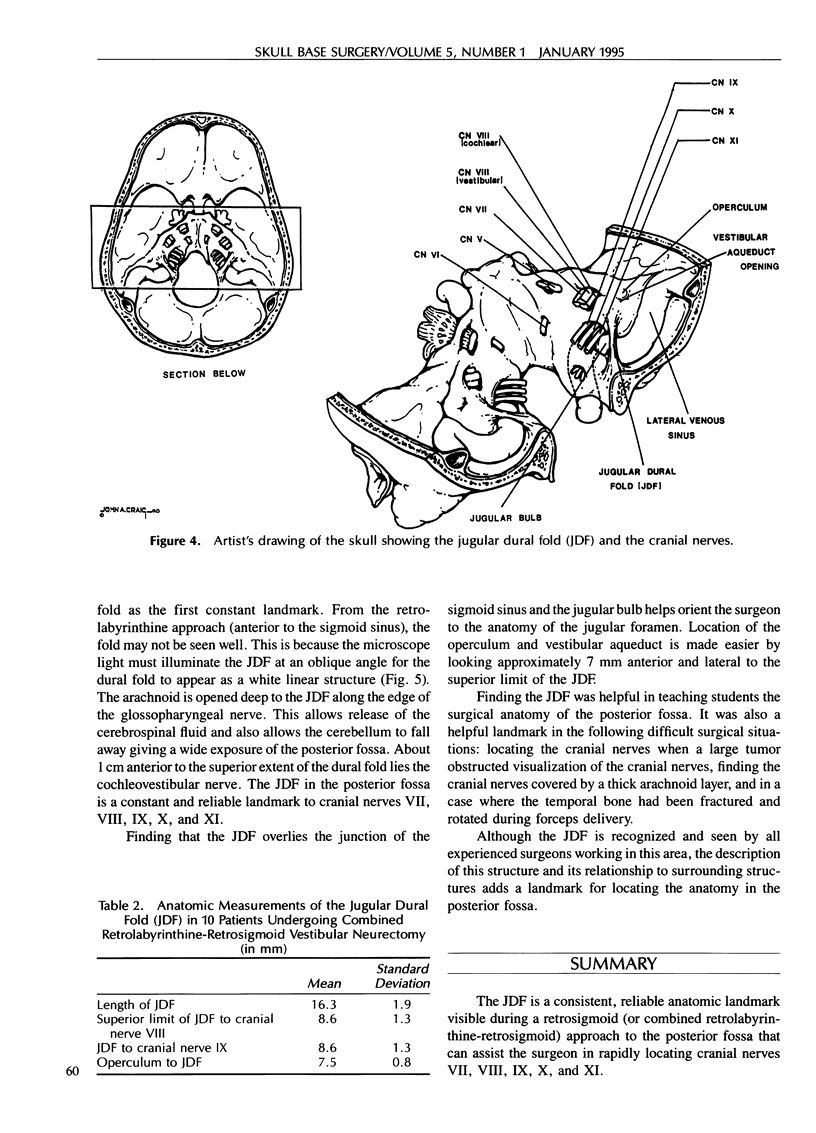
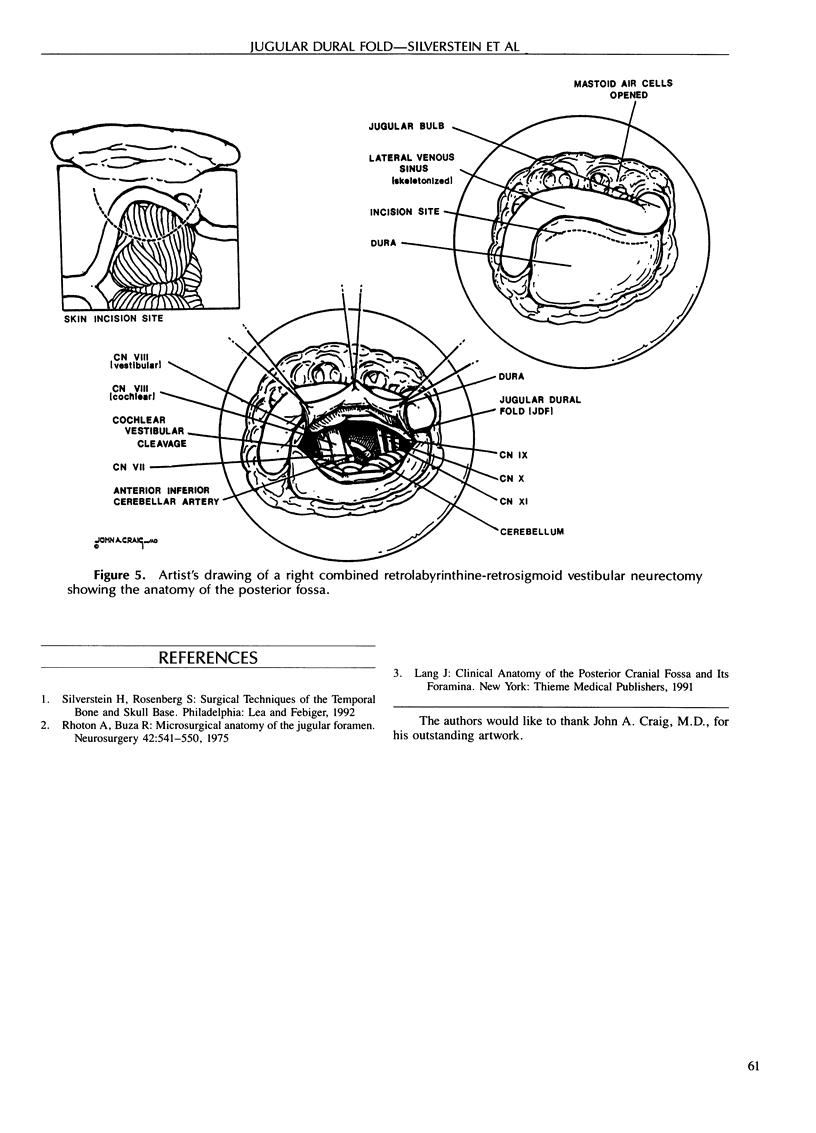
During a retrosigmoid (or combined retrolabyrinthine-retrosigmoid) approach to the posterior fossa for vestibular neurectomy or removal of small acoustic neuromas, a white dural fold is a consistent landmark to cranial nerves VII through XII. This fold of dura appears as a white linear structure extending from the foramen magnum across the sigmoid sinus, attaching to the posterior aspect of the temporal bone, anterior to the vestibular aqueduct. The name “jugular dural fold” is suggested for this landmark. The jugular dural fold overlies the junction of the sigmoid sinus and the jugular foramen. As measured in formalin-fixed cadaver heads, the overall length of the jugular dural fold is 20.8 mm (± 2.9 mm). The cochleovestibular nerve lies 9.9 mm (± 1.5 mm) anterior to the superior aspect of the jugular dural fold, the glossopharyngeal nerve lies 9.5 mm (± 1.6 mm) anterior to the midpoint of the jugular dural fold, and the operculum of the vestibular aqueduct lies 6.6 mm (± 0.7 mm) posterior to the jugular dural fold. Intraoperative measurements in patients undergoing combined retrolabyrinthine-retrosigmoid vestibular neurectomy show an overall length of the jugular dural fold of 16.3 mm (± 1.9 mm). The cochleovestibular nerve lies 8.6 mm (± 1.3 mm) anterior to the superior aspect of the jugular dural fold, the glossopharyngeal nerve lies 8.6 mm (± 1.3 mm) anterior to the midpoint of the jugular dural fold, and the operculum lies 7.5 mm (± 0.8 mm) posterior to the jugular dural fold. The jugular dural fold can be used as a reliable landmark for rapidly locating cranial nerves in the posterior fossa.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Rhoton A. L., Jr, Buza R. Microsurgical anatomy of the jugular foramen. J Neurosurg. 1975 May;42(5):541–550. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.42.5.0541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]