Abstract
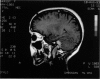
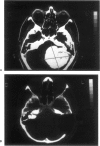
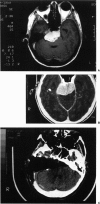
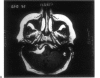
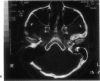
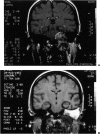
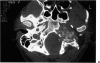
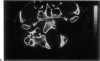
Posterior fossa meningioma is the second most common tumor in the cerebellopontine angle. It has a higher rate of postoperative morbidity and mortality compared to acoustic neuroma. Forty posterior fossa meningioma patients managed in our centers were reviewed. Thirty-nine patients were managed surgically with 42 surgical procedures. The approaches used were the translabyrinthine approach in 18 patients (43%), the modified transcochlear in 11 cases (26%), the petro-occipital transsigmoid in 5 cases (12%), the suboccipital in 4 cases (10%), the petro-occipital trassigmoid transcervical in 2 cases (5%), the petro-occipital transsigmoid transtentorial in 1 case (2%), and a subtemporal transtentorial for another case (2%). Facial nerve anatomical integrity was preserved in 87% of procedures but was interrupted in 5 cases, with 4 of the latter subsequently repaired. Total tumor removal was accomplished in 38 cases. A second-stage total tumor removal is planned for the remaining case. There was only one case of perioperative death and no cases of radiological recurrence so far.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Mefty O., Fox J. L., Smith R. R. Petrosal approach for petroclival meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1988 Mar;22(3):510–517. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198803000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriaga M., Shelton C., Nassif P., Brackmann D. E. Selection of surgical approaches for meningiomas affecting the temporal bone. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):738–744. doi: 10.1177/019459988910700605.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs M. T., Fagan P. A., Sheehy J. P., Bentivoglio P. J., Doust B. D., Tonkin J. Meningioma of the posterior skull base. Skull Base Surg. 1991;1(1):43–50. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1056978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricolo A. P., Turazzi S., Talacchi A., Cristofori L. Microsurgical removal of petroclival meningiomas: a report of 33 patients. Neurosurgery. 1992 Nov;31(5):813–828. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199211000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTELLANO F., RUGGIERO G. Meningiomas of the posterior fossa. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1953;104:1–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitselberger W. E., Horn K. L., Hankinson H., Brackmann D. E., House W. F. The middle fossa transpetrous approach for petroclival meningiomas. Skull Base Surg. 1993;3(3):130–135. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1060575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javed T., Sekhar L. N. Surgical management of clival meningiomas. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1991;53:171–182. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9183-5_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäskeläinen J., Haltia M., Servo A. Atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: radiology, surgery, radiotherapy, and outcome. Surg Neurol. 1986 Mar;25(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(86)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallio M., Sankila R., Hakulinen T., Jäskeläinen J. Factors affecting operative and excess long-term mortality in 935 patients with intracranial meningioma. Neurosurgery. 1992 Jul;31(1):2–12. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199207000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird F. J., Harner S. G., Laws E. R., Jr, Reese D. F. Meningiomas of the cerebellopontine angle. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985 Apr;93(2):163–167. doi: 10.1177/019459988509300207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg M. R., Symon L. Meningiomas of the clivus and apical petrous bone. Report of 35 cases. J Neurosurg. 1986 Aug;65(2):160–167. doi: 10.3171/jns.1986.65.2.0160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirimanoff R. O., Dosoretz D. E., Linggood R. M., Ojemann R. G., Martuza R. L. Meningioma: analysis of recurrence and progression following neurosurgical resection. J Neurosurg. 1985 Jan;62(1):18–24. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.1.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molony T. B., Brackmann D. E., Lo W. W. Meningiomas of the jugular foramen. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992 Feb;106(2):128–136. doi: 10.1177/019459989210600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nager G. T., Heroy J., Hoeplinger M. Meningiomas invading the temporal bone with extension to the neck. Am J Otolaryngol. 1983 Sep-Oct;4(5):297–324. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(83)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif P. S., Shelton C., Arriaga M. Hearing preservation following surgical removal of meningiomas affecting the temporal bone. Laryngoscope. 1992 Dec;102(12 Pt 1):1357–1362. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199212000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Feb;20(1):22–39. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samii M., Ammirati M. The combined supra-infratentorial pre-sigmoid sinus avenue to the petro-clival region. Surgical technique and clinical applications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1988;95(1-2):6–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01793075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samii M., Tatagiba M. Experience with 36 surgical cases of petroclival meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1992;118(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01400723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekhar L. N., Jannetta P. J. Cerebellopontine angle meningiomas. Microsurgical excision and follow-up results. J Neurosurg. 1984 Mar;60(3):500–505. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.3.0500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen C. N., Sekhar L. N. An extreme lateral approach to intradural lesions of the cervical spine and foramen magnum. Neurosurgery. 1990 Aug;27(2):197–204. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199008000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spetzler R. F., Daspit C. P., Pappas C. T. Combined approach for lesions involving the cerebellopontine angle and skull base: experience with 30 cases. Skull Base Surg. 1991;1(4):226–234. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1057102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thedinger B. A., Glasscock M. E., 3rd, Cueva R. A. Transcochlear transtentorial approach for removal of large cerebellopontine angle meningiomas. Am J Otol. 1992 Sep;13(5):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]