Abstract
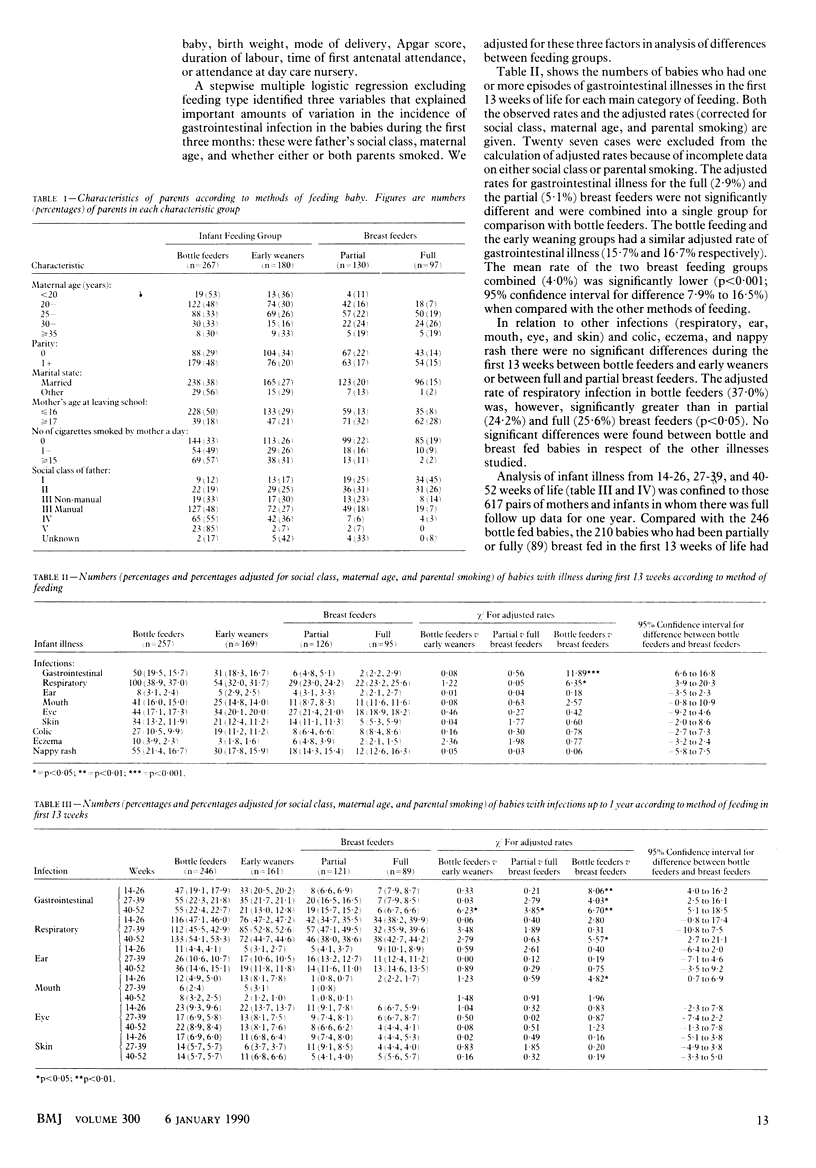
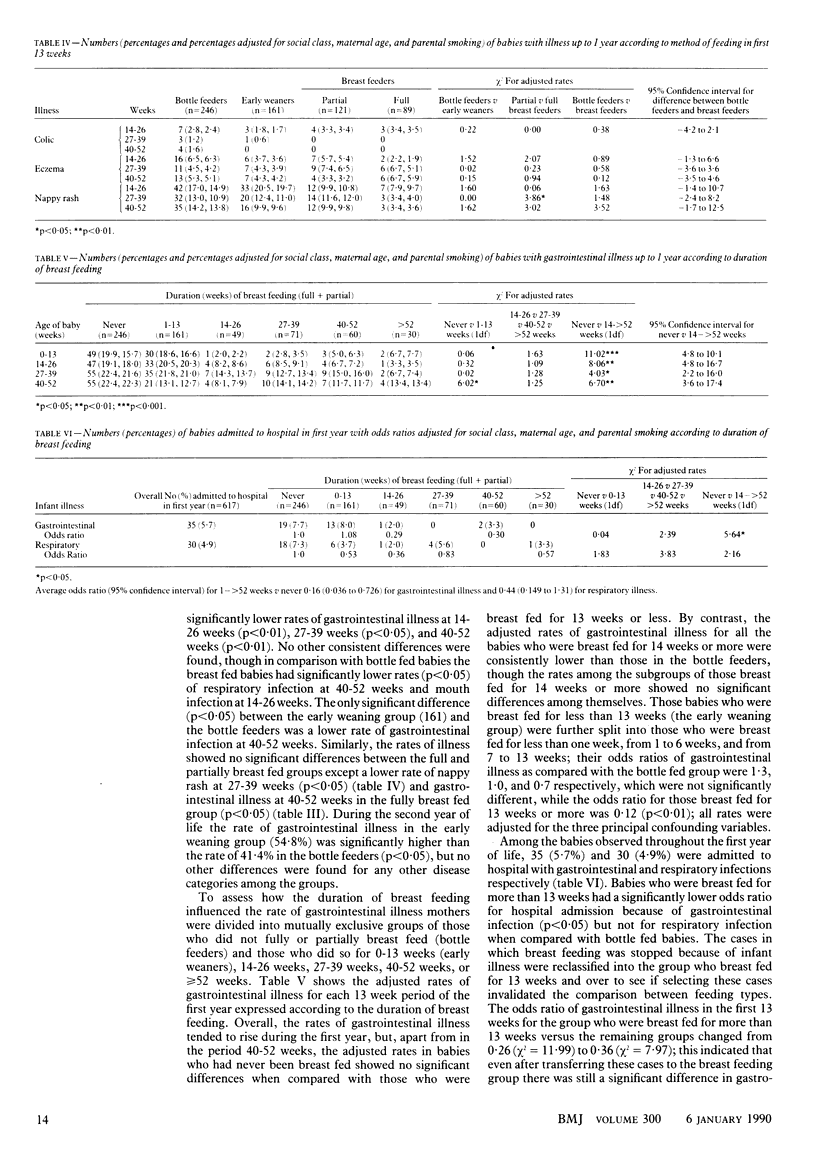
OBJECTIVE--To assess the relations between breast feeding and infant illness in the first two years of life with particular reference to gastrointestinal disease. DESIGN--Prospective observational study of mothers and babies followed up for 24 months after birth. SETTING--Community setting in Dundee. PATIENTS--750 pairs of mothers and infants, 76 of whom were excluded because the babies were preterm (less than 38 weeks), low birth weight (less than 2500 g), or treated in special care for more than 48 hours. Of the remaining cohort of 674, 618 were followed up for two years. INTERVENTIONS--Detailed observations of infant feeding and illness were made at two weeks, and one, two, three, four, five, six, nine, 12, 15, 18, 21, and 24 months by health visitors. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE--The prevalence of gastrointestinal disease in infants during follow up. RESULTS--After confounding variables were corrected for babies who were breast fed for 13 weeks or more (227) had significantly less gastrointestinal illness than those who were bottle fed from birth (267) at ages 0-13 weeks (p less than 0.01; 95% confidence interval for reduction in incidence 6.6% to 16.8%), 14-26 weeks (p less than 0.01), 27-39 weeks (p less than 0.05), and 40-52 weeks (p less than 0.05). This reduction in illness was found whether or not supplements were introduced before 13 weeks, was maintained beyond the period of breast feeding itself, and was accompanied by a reduction in the rate of hospital admission. By contrast, babies who were breast fed for less than 13 weeks (180) had rates of gastrointestinal illness similar to those observed in bottle fed babies. Smaller reductions in the rates of respiratory illness were observed at ages 0-13 and 40-52 weeks (p less than 0.05) in babies who were breast fed for more than 13 weeks. There was no consistent protective effect of breast feeding against ear, eye, mouth, or skin infections, infantile colic, eczema, or nappy rash. CONCLUSION--Breast feeding during the first 13 weeks of life confers protection against gastrointestinal illness that persists beyond the period of breast feeding itself.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauchner H., Leventhal J. M., Shapiro E. D. Studies of breast-feeding and infections. How good is the evidence? JAMA. 1986 Aug 15;256(7):887–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K. Prospective studies of the effect of breast feeding on incidence of infection and allergy. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Sep;68(5):691–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb18439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. S. Morbidity in breast-fed and artificially fed infants. II. J Pediatr. 1979 Nov;95(5 Pt 1):685–689. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80711-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Shannon F. T., Taylor B. Breast-feeding, gastrointestinal and lower respiratory illness in the first two years. Aust Paediatr J. 1981 Sep;17(3):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1981.tb01937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovar M. G., Serdula M. K., Marks J. S., Fraser D. W. Review of the epidemiologic evidence for an association between infant feeding and infant health. Pediatrics. 1984 Oct;74(4 Pt 2):615–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Wyatt R. G. The uniqueness of human milk. Host resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Aug;24(8):976–986. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.8.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plank S. J., Milanesi M. L. Infant feeding and infant mortality in rural Chile. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(2):203–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B., Wadsworth J., Golding J., Butler N. Breast-feeding, bronchitis, and admissions for lower-respiratory illness and gastroenteritis during the first five years. Lancet. 1982 May 29;1(8283):1227–1229. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



