Abstract
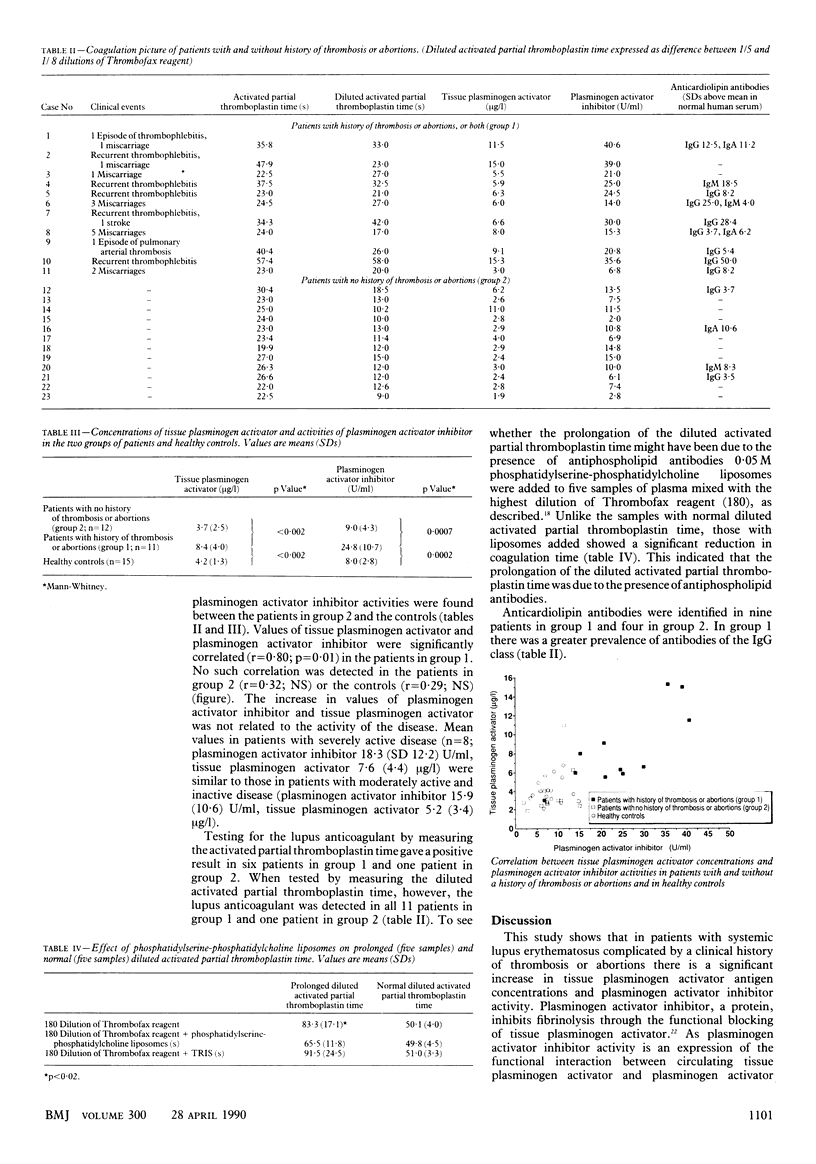
OBJECTIVE--To examine the relations among tissue plasminogen activator antigen, plasminogen activator inhibitor, the lupus anticoagulant, and anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. DESIGN--Prospective study of blood samples (a) from selected patients with systemic lupus erythematosus whose disease was and was not complicated by a history of thrombosis or recurrent abortions, or both, and (b) from a series of healthy controls with a similar age and sex distribution. SETTING--University based medical clinic. SUBJECTS--23 Patients with definite systemic lupus erythematosus (American Rheumatism Association criteria), of whom 11 (eight women) aged 26-51 had a history of thrombosis or recurrent abortions, or both, and 12 (10 women) aged 23-53 had no such history. 15 Healthy subjects (10 women) aged 25-58 served as controls. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Tissue plasminogen activator concentrations, plasminogen activator inhibitor activities, detection of the lupus anticoagulant, and values of anticardiolipin antibodies in the two groups of patients and in the patients with a history of thrombosis or abortions compared with controls. Other measurements included concentrations of proteins that are known to change during the acute phase of systemic lupus erythematosus--namely, fibrinogen, C3 and C4, and C reactive protein. RESULTS--Patients with a history of thrombosis or abortions, or both, had significantly higher values of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor than patients with no such history. A significant correlation between tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor (r = 0.80) was found only in the patients with a history of complications of their disease. The lupus anticoagulant was detected in six of the 11 patients with a history of thrombosis or abortions when tested by measuring the activated partial thromboplastin time but was found in all 11 patients when tested by measuring the diluted activated partial thromboplastin time. Nine of these 11 patients had raised values of anticardiolipin antibodies. The findings showed no relation to the activity of the disease. CONCLUSIONS--A significant correlation between tissue plasminogen activator concentrations and plasminogen activator inhibitor activities was found only in patients whose systemic lupus erythematosus was complicated by a history of thrombosis or recurrent abortions. The findings show that these patients have raised plasminogen activator inhibitor activities, and the frequent association between these raised activities and the presence of the lupus anticoagulant suggests that the two may be linked.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving B. M., Baldwin P. E., Richards R. L., Jackson B. J. The dilute phospholipid APTT: a sensitive assay for verification of lupus anticoagulants. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):709–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordova C., Violi F., Alessandri C., Ferro D., Saliola M., Musca A., Balsano F. Prekallikrein and factor VII as prognostic indexes of liver failure. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 May;85(5):579–582. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glueck H. I., Kant K. S., Weiss M. A., Pollak V. E., Miller M. A., Coots M. Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relation to the presence of circulating anticoagulants. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Aug;145(8):1389–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Anti-phospholipid antibodies. Clin Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;11(3):591–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Valadier J., Alessi M. C., Aillaud M. F., Ansaldi J., Philip-Joet C., Holvoet P., Serradimigni A., Collen D. Deficient t-PA release and elevated PA inhibitor levels in patients with spontaneous or recurrent deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow W. J., Isenberg D. A., Todd-Pokropek A., Parry H. F., Snaith M. L. Useful laboratory measurements in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1982 Spring;51(202):125–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Páramo J. A., Alfaro M. J., Rocha E. Postoperative changes in the plasmatic levels of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its fast-acting inhibitor--relationship to deep vein thrombosis and influence of prophylaxis. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):713–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semble E. L., Agudelo C. A., Challa V. R., Heise E. R., Pisko E. J. Temporal arteritis in Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Oct-Dec;3(4):345–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valesini G., Tincani A., Harris E. N., Mantelli P. G., Allegri F., Palmieri G., Hughes G. R., Balsano F., Balestrieri G. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify shared idiotypes on anticardiolipin and anti-DNA antibodies in human sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):18–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violi F., Valesini G., Ferro D., Tincani A., Balestrieri G., Balsano F. Anticoagulant activity of anticardiolipin antibodies. Thromb Res. 1986 Nov 15;44(4):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violi F., Valesini G., Iuliano L., Ghiselli A., Falco M., Balsano F. Anticardiolipin antibodies and prostacyclin synthesis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Jun 3;57(3):374–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



