Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To determine whether signs of illness reported by parents can be used to identify babies at risk from the sudden infant death syndrome. DESIGN--A two year prospective case-controlled study based in a geographically defined area. SETTING--Four health districts in Avon and north Somerset. SUBJECTS--Babies who had died suddenly and unexpectedly aged between 1 week and 2 years (index babies) and two control babies for each index baby selected from the same health visitor's list and matched for age, time of year of the interview, and area of residence. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Major and minor signs of illness during two weeks before the index babies' death, or before the interview for control babies, and consultations with the general practitioner during the same period. RESULTS--Parents reported major and minor signs of illness in the previous week in 66 of the 95 index babies compared with 77 of the 190 controls. No significant difference was found in the incidence of major signs reported (34 out of 95 index babies and 44 out of 190 controls), but a higher proportion of the index babies had been seen by their general practitioner during the previous week (17/95 v 11/190). CONCLUSION--Major and minor signs of illness are neither a sensitive nor a specific indicator of sudden unexpected death of infants and have no predictive value. Better understanding of the reasons why a higher proportion of parents of babies who died took them to their general practitioners may help to identify babies at risk before death.
Full text
PDF
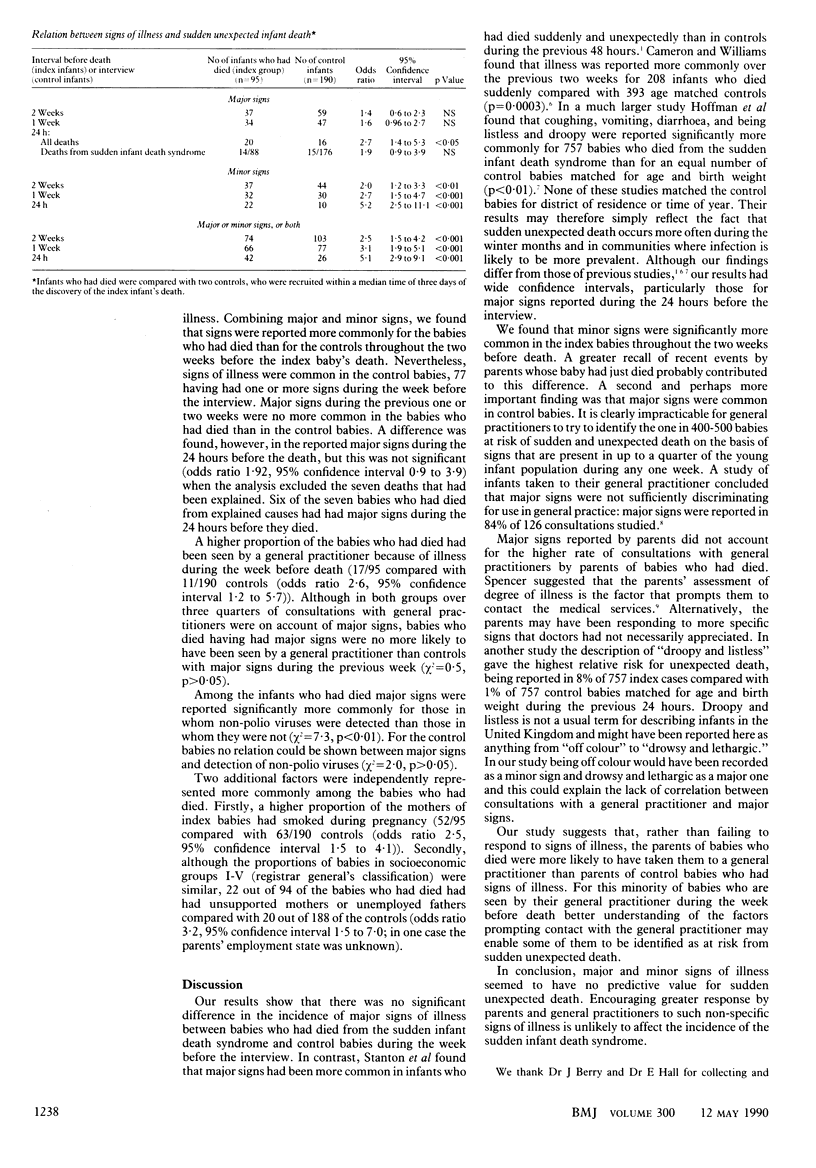
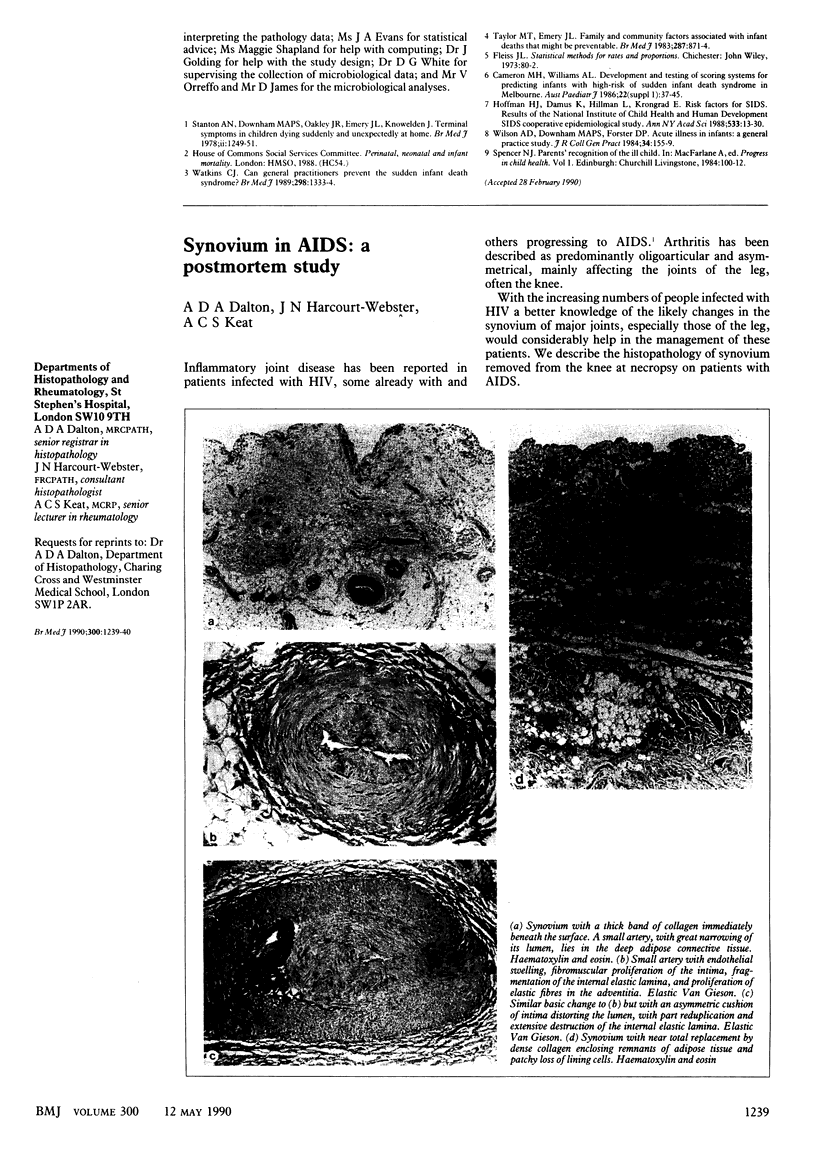
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron M. H., Williams A. L. Development and testing of scoring systems for predicting infants with high-risk of sudden infant death syndrome in Melbourne. Aust Paediatr J. 1986;22 (Suppl 1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman H. J., Damus K., Hillman L., Krongrad E. Risk factors for SIDS. Results of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development SIDS Cooperative Epidemiological Study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;533:13–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb37230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton A. N., Downham M. A., Oakley J. R., Emery J. L., Knowelden J. Terminal symptoms in children dying suddenly and unexpectedly at home. Preliminary report of the DHSS multicentre study of postneonatal mortality. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 4;2(6147):1249–1251. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6147.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. M., Emery J. L. Family and community factors associated with infant deaths that might be preventable. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):871–874. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C. J. Can general practitioners prevent the sudden infant death syndrome? BMJ. 1989 May 20;298(6684):1333–1334. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6684.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Downham M. A., Forster D. P. Acute illness in infants: a general practice study. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1984 Mar;34(260):155–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]