Abstract
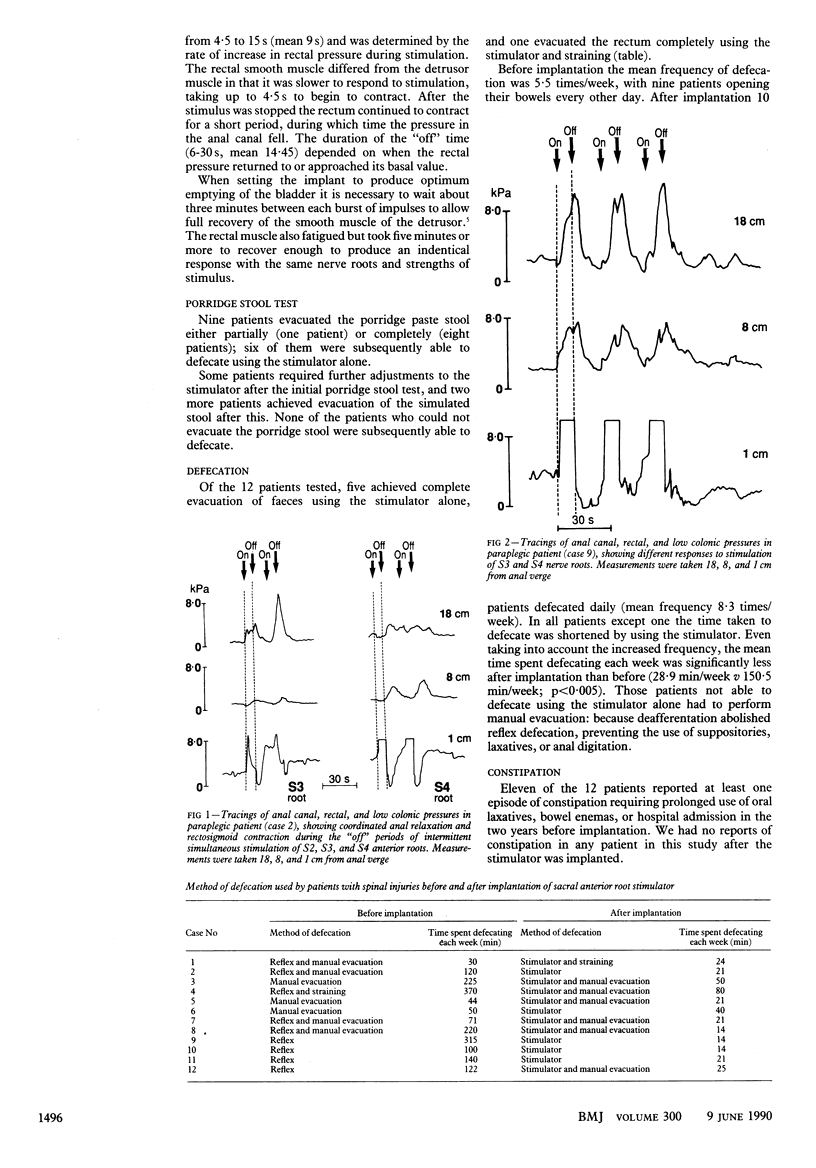
OBJECTIVE--To observe the effects of stimulation of the sacral anterior roots on anorectal and low colonic pressures and to programme implanted stimulators to produce defecation. DESIGN--Prospective study of 12 consecutive patients. SETTING--Spinal injuries unit and university gastrointestinal physiology department. PATIENTS--12 Patients with complete supraconal spinal cord lesions. Their injuries had been sustained at least two years before the study. INTERVENTIONS--A Brindley-Finetech intradural sacral anterior root stimulator was implanted in all patients. Three months postoperatively the stimulator settings were adjusted after measurement of simultaneous anorectal and low colonic pressures. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Full defecation. RESULTS--Six patients achieved complete rectal evacuation of faeces using the implant and subsequently did not require manual help for defecation. For all but one of the patients the total time taken to complete defecation was reduced, and all were free from constipation, the most prevalent gastrointestinal symptom in patients with spinal injuries. CONCLUSIONS--Sacral anterior root stimulators can be programmed to achieve complete unassisted defecation and can considerably improve the quality of life of patients with spinal injuries.
Full text
PDF