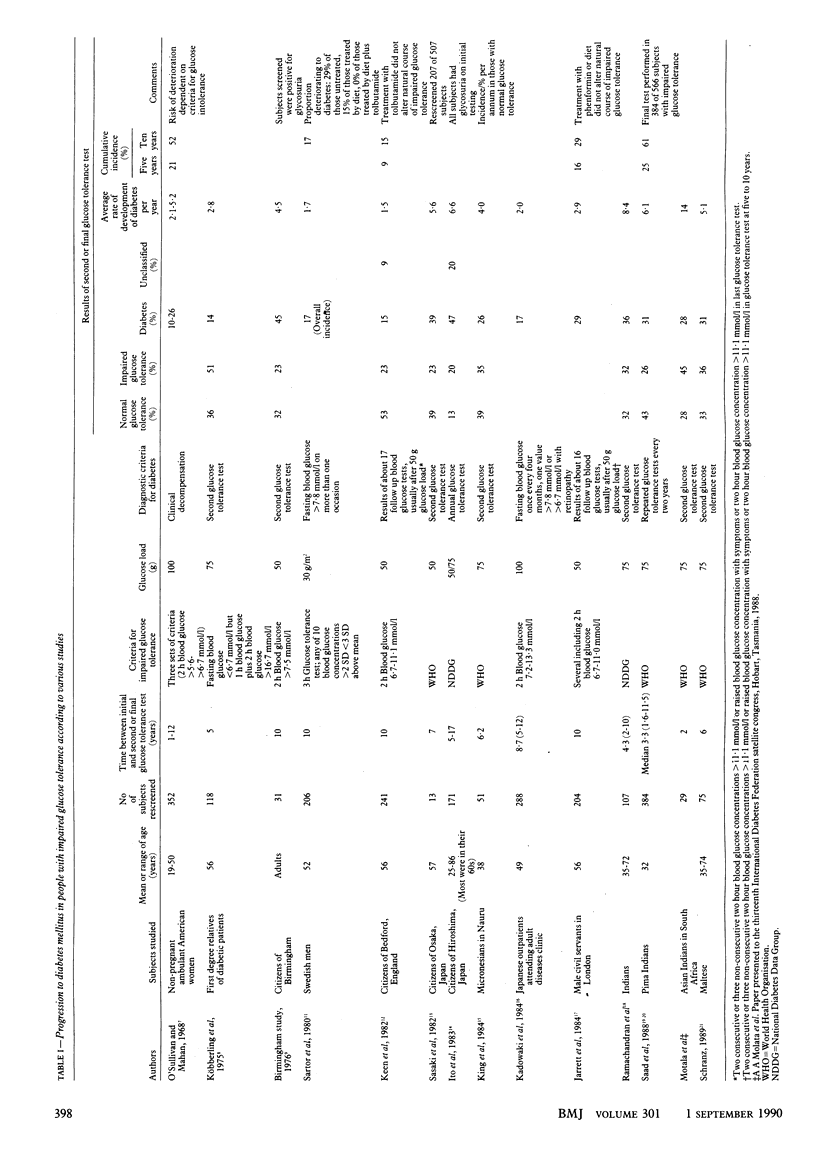
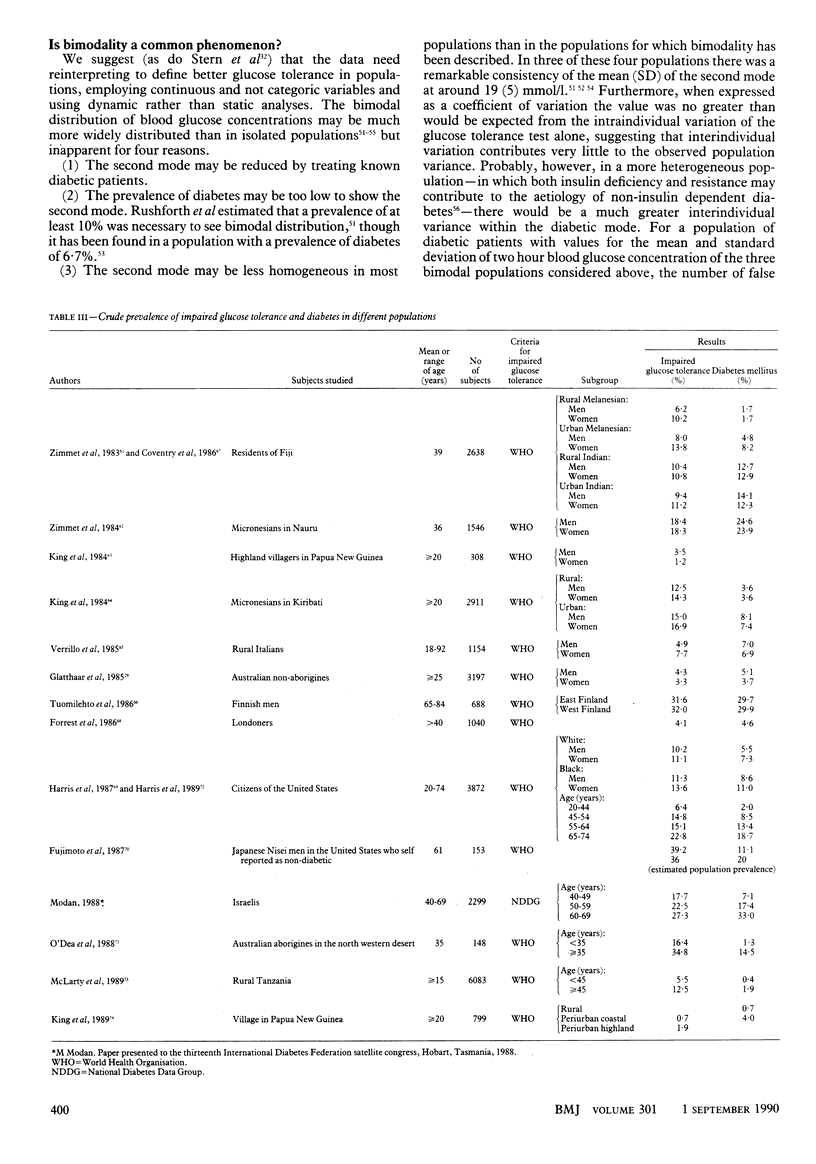
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albutt E. C., Nattrass M., Northam B. E. Glucose tolerance test and glycosylated haemoglobin measurement for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus--an assessment of the criteria of the WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus 1980. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(Pt 1):67–73. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers D. G. Blood pressures that fall on rechecking. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 9;284(6309):71–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6309.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coventry J., King H., Zimmet P., Raper L. R., Sicree R. Impaired glucose tolerance in the biethnic (Melanesian and Indian) populations of Fiji. Diabetes Res. 1986 Oct;3(8):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest R. D., Jackson C. A., Gould B. J., Casburn-Budd M., Taylor J. E., Yudkin J. S. Four assay methods for glycated hemoglobin compared as screening tests for diabetes mellitus: the Islington Diabetes Survey. Clin Chem. 1988 Jan;34(1):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest R. D., Jackson C. A., Yudkin J. S. Glucose intolerance and hypertension in north London: the Islington Diabetes Survey. Diabet Med. 1986 Jul-Aug;3(4):338–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest R. D., Jackson C. A., Yudkin J. S. The abbreviated glucose tolerance test in screening for diabetes: the Islington Diabetes Survey. Diabet Med. 1988 Sep;5(6):557–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest R. D., Jackson C. A., Yudkin J. S. The abbreviated glucose tolerance test in screening for diabetes: the Islington Diabetes Survey. Diabet Med. 1988 Sep;5(6):557–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto W. Y., Leonetti D. L., Kinyoun J. L., Newell-Morris L., Shuman W. P., Stolov W. C., Wahl P. W. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance among second-generation Japanese-American men. Diabetes. 1987 Jun;36(6):721–729. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.6.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Coronary-heart-disease risk and impaired glucose tolerance. The Whitehall study. Lancet. 1980 Jun 28;1(8183):1373–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to degree of glycaemia: the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganda O. P., Day J. L., Soeldner J. S., Connon J. J., Gleason R. E. Reproducibility and comparative analysis of repeated intravenous and oral glucose tolerance tests. Diabetes. 1978 Jul;27(7):715–725. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.7.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatthaar C., Welborn T. A., Stenhouse N. S., Garcia-Webb P. Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. A prevalence estimate based on the Busselton 1981 survey. Med J Aust. 1985 Nov 11;143(10):436–440. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb123131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabauskas V. J. Glucose intolerance as contributor to noncommunicable disease morbidity and mortality. WHO integrated program for community health in noncommunicable diseases. Diabetes Care. 1988 Mar;11(3):253–257. doi: 10.2337/diacare.11.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding P. E., Oakley N. W., Wynn V. Reproducibility of oral glucose tolerance data in normal and mildly diabetic subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1973 Oct;2(4):387–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1973.tb01725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. I., Hadden W. C., Knowler W. C., Bennett P. H. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance and plasma glucose levels in U.S. population aged 20-74 yr. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):523–534. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. I. Impaired glucose tolerance in the U.S. population. Diabetes Care. 1989 Jul-Aug;12(7):464–474. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.7.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito C., Mito K., Hara H. Review of criteria for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus based on results of follow-up study. Diabetes. 1983 Apr;32(4):343–351. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.4.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J. Do we need IGT? Diabet Med. 1987 Nov-Dec;4(6):544–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1987.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., Fuller J. H., McCartney M. Worsening to diabetes in men with impaired glucose tolerance ("borderline diabetes"). Diabetologia. 1979 Jan;16(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00423146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Hyperglycaemia and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Nov 6;2(7993):1009–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90844-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., McCartney P. The Whitehall Study: ten year follow-up report on men with impaired glucose tolerance with reference to worsening to diabetes and predictors of death. Diabet Med. 1984 Nov;1(4):279–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1984.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., McCartney P., Keen H. The Bedford survey: ten year mortality rates in newly diagnosed diabetics, borderline diabetics and normoglycaemic controls and risk indices for coronary heart disease in borderline diabetics. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00254833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Miyake Y., Hagura R., Akanuma Y., Kajinuma H., Kuzuya N., Takaku F., Kosaka K. Risk factors for worsening to diabetes in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 1984 Jan;26(1):44–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00252262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen H., Jarrett R. J., McCartney P. The ten-year follow-up of the Bedford survey (1962-1972): glucose tolerance and diabetes. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00254832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H., Finch C., Collins A., Koki G., King L. F., Heywood P., Zimmet P. Glucose tolerance in Papua New Guinea: ethnic differences, association with environmental and behavioural factors and the possible emergence of glucose intolerance in a highland community. Med J Aust. 1989 Aug 21;151(4):204–210. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb115991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H., Heywood P., Zimmet P., Alpers M., Collins V., Collins A., King L. F., Raper L. R. Glucose tolerance in a highland population in Papua New Guinea. Diabetes Res. 1984 May;1(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H., Taylor R., Zimmet P., Pargeter K., Raper L. R., Beriki T., Tekanene J. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM) in a newly independent Pacific nation: the Republic of Kiribati. Diabetes Care. 1984 Sep-Oct;7(5):409–415. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.5.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H., Zimmet P., Raper L. R., Balkau B. The natural history of impaired glucose tolerance in the Micronesian population of Nauru: a six-year follow-up study. Diabetologia. 1984 Jan;26(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00252261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Savage P. J., Bennett P. H. Diabetes incidence in Pima indians: contributions of obesity and parental diabetes. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Feb;113(2):144–156. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köbberling J., Kattermann R., Arnold A. Follow-up of "non-diabetic" relatives of diabetics by retesting oral glucose tolerance after 5 years. Diabetologia. 1975 Oct;11(5):451–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00429915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Mott D. M., Howard B. V., Bennett P. H., Yki-Järvinen H., Freymond D., Nyomba B. L., Zurlo F., Swinburn B., Bogardus C. Impaired glucose tolerance as a disorder of insulin action. Longitudinal and cross-sectional studies in Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 12;318(19):1217–1225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805123181901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONALD G. W., FISHER G. F., BURNHAM C. REPRODUCIBILITY OF THE ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST. Diabetes. 1965 Aug;14:473–480. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.8.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancia G., Bertinieri G., Grassi G., Parati G., Pomidossi G., Ferrari A., Gregorini L., Zanchetti A. Effects of blood-pressure measurement by the doctor on patient's blood pressure and heart rate. Lancet. 1983 Sep 24;2(8352):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney P., Keen H., Jarrett R. J. The Bedford Survey: observations on retina and lens of subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and in controls with normal glucose tolerance. Diabete Metab. 1983 Dec;9(4):303–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLarty D. G., Swai A. B., Kitange H. M., Masuki G., Mtinangi B. L., Kilima P. M., Makene W. J., Chuwa L. M., Alberti K. G. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in rural Tanzania. Lancet. 1989 Apr 22;1(8643):871–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92866-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Karasik A., Halkin H., Fuchs Z., Lusky A., Shitrit A., Modan B. Effect of past and concurrent body mass index on prevalence of glucose intolerance and type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes and on insulin response. The Israel study of glucose intolerance, obesity and hypertension. Diabetologia. 1986 Feb;29(2):82–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00456115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dea K., Traianedes K., Hopper J. L., Larkins R. G. Impaired glucose tolerance, hyperinsulinemia, and hypertriglyceridemia in Australian aborigines from the desert. Diabetes Care. 1988 Jan;11(1):23–29. doi: 10.2337/diacare.11.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J. B., Mahan C. M. Glucose tolerance test. Variability in pregnant and nonpregnant women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1966 Nov;19(5):345–351. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/19.5.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J. B., Mahan C. M. Prospective study of 352 young patients with chemical diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 9;278(19):1038–1041. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805092781904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Insulin and glucose responses to identical oral glucose tolerance tests performed forty-eight hours apart. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):449–453. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro R. E., Koepsell T. D., Chen M. S., Lipsky B. A., Belcher D. W., Inui T. S. Comparative clinical reliability of fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1986 Jul-Aug;9(4):370–375. doi: 10.2337/diacare.9.4.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering G. Hypertension. Definitions, natural histories and consequences. Am J Med. 1972 May;52(5):570–583. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran A., Snehalatha C., Naik R. A., Mohan V., Shobana R., Viswanathan M. Significance of impaired glucose tolerance in an Asian Indian population: a follow-up study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1986 Jun;2(3):173–178. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(86)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper L. R., Taylor R., Zimmet P., Milne B., Balkau B. Bimodality in glucose tolerance distributions in the urban Polynesian population of Western Samoa. Diabetes Res. 1984 May;1(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Hollenbeck C. B., Chen Y. D. Relationship between glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin action in non-obese individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 1989 Jan;32(1):52–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00265404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G., Miller R. Study of the relationship between glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose load in man. Diabetes. 1968 Sep;17(9):560–569. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.9.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi G., Vaccaro O., Rivellese A., Pignalosa S., Tutino L., Mancini M. Reproducibility of the new diagnostic criteria for impaired glucose tolerance. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Mar;121(3):422–429. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal M., McMahan C. A., Stern M. P., Eifler C. W., Haffner S. M., Hazuda H. P., Franco L. J. Evidence of bimodality of two hour plasma glucose concentrations in Mexican Americans: results from the San Antonio Heart study. J Chronic Dis. 1985;38(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(85)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushforth N. B., Bennett P. H., Steinberg A. G., Burch T. A., Miller M. Diabetes in the Pima Indians. Evidence of bimodality in glucose tolerance distributions. Diabetes. 1971 Nov;20(11):756–765. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.11.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. F., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Nelson R. G., Bennett P. H. Transient impaired glucose tolerance in Pima Indians: is it important? BMJ. 1988 Dec 3;297(6661):1438–1441. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6661.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. F., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Nelson R. G., Mott D. M., Bennett P. H. Sequential changes in serum insulin concentration during development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1989 Jun 17;1(8651):1356–1359. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. F., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Nelson R. G., Mott D. M., Bennett P. H. The natural history of impaired glucose tolerance in the Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 8;319(23):1500–1506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812083192302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor G., Scherstén B., Carlström S., Melander A., Nordén A., Persson G. Ten-year follow-up of subjects with impaired glucose tolerance: prevention of diabetes by tolbutamide and diet regulation. Diabetes. 1980 Jan;29(1):41–49. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki A., Suzuki T., Horiuchi N. Development of diabetes in Japanese subjects with impaired glucose tolerance: a seven year follow-up study. Diabetologia. 1982 Mar;22(3):154–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00283743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schranz A. G. Abnormal glucose tolerance in the Maltese. A population-based longitudinal study of the natural history of NIDDM and IGT in Malta. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1989 Jun 20;7(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(89)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicree R. A., Zimmet P. Z., King H. O., Coventry J. S. Plasma insulin response among Nauruans. Prediction of deterioration in glucose tolerance over 6 yr. Diabetes. 1987 Feb;36(2):179–186. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke I. D., Donnelly P., Catovsky D., Darrell J., Johnson S. A., Goldman J. M., Galton D. A. Co-trimoxazole alone for prevention of bacterial infection in patients with acute leukaemia. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):5–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P., Rosenthal M., Haffner S. M. A new concept of impaired glucose tolerance. Relation to cardiovascular risk. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):311–314. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.4.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P. Type II diabetes mellitus. Interface between clinical and epidemiological investigation. Diabetes Care. 1988 Feb;11(2):119–126. doi: 10.2337/diacare.11.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple R. C., Carrington C. A., Luzio S. D., Owens D. R., Schneider A. E., Sobey W. J., Hales C. N. Insulin deficiency in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):293–295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toeller M., Knussmann R. Reproducibility of oral glucose tolerance tests with three different loads. Diabetologia. 1973 Apr;9(2):102–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01230688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto J., Nissinen A., Kivelä S. L., Pekkanen J., Kaarsalo E., Wolf E., Aro A., Punsar S., Karvonen M. J. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in elderly men aged 65 to 84 years in eastern and western Finland. Diabetologia. 1986 Sep;29(9):611–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00869258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrillo A., de Teresa A., La Rocca S., Giarrusso P. C. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in a rural area of Italy. Diabetes Res. 1985 Nov;2(6):301–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmet P., King H., Taylor R., Raper L. R., Balkau B., Borger J., Heriot W., Thoma K. The high prevalence of diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance and diabetic retinopathy in Nauru--the 1982 survey. Diabetes Res. 1984 May;1(1):13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmet P., Taylor R., Ram P., King H., Sloman G., Raper L. R., Hunt D. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in the biracial (Melanesian and Indian) population of Fiji: a rural-urban comparison. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Nov;118(5):673–688. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmet P., Whitehouse S. Bimodality of fasting and two-hour glucose tolerance distributions in a Micronesian population. Diabetes. 1978 Aug;27(8):793–800. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.8.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



