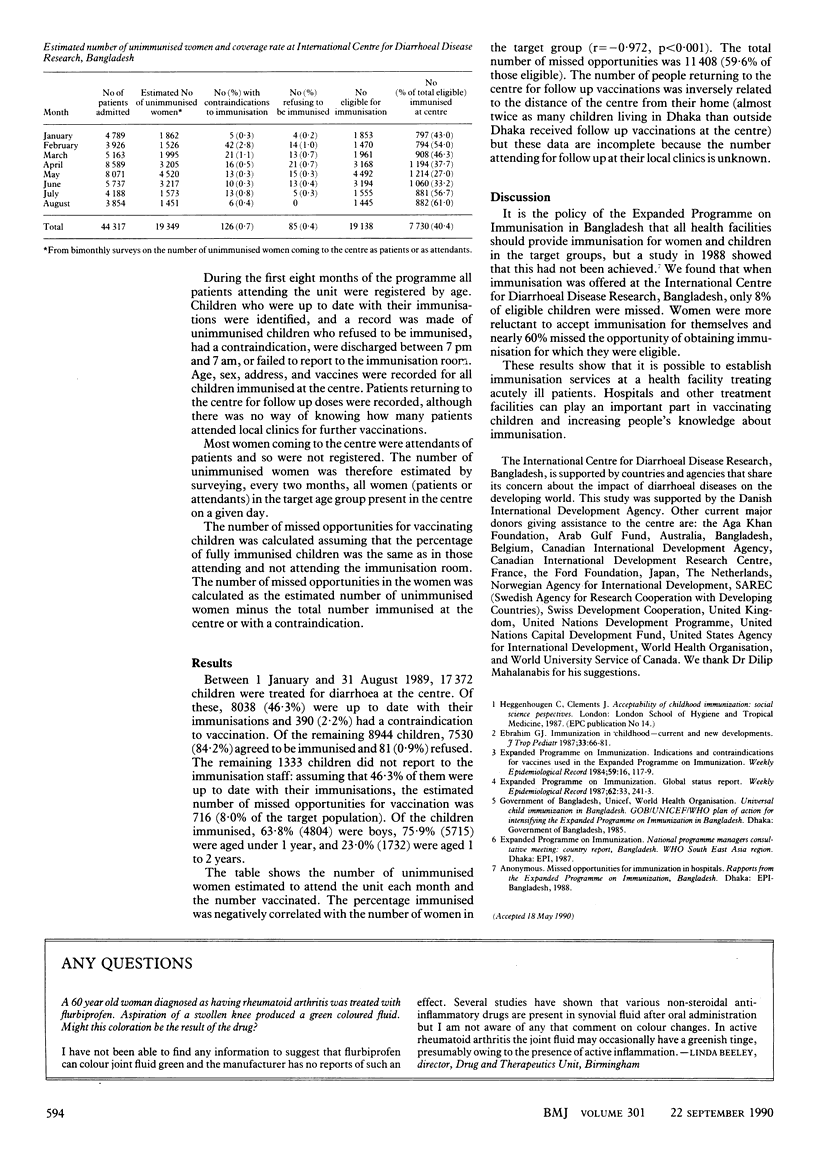
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To study the uptake of vaccination offered to women and children attending a curative health facility. DESIGN--Prospective survey over eight months of the uptake of vaccination offered to unimmunised women and children attending a diarrhoeal treatment centre as patients or attendants. SETTING--The International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Dhaka, Bangladesh. SUBJECTS--An estimated 19,349 unimmunised women aged 15 to 45 and 17,372 children attending the centre for treatment or accompanying patients between 1 January and 31 August 1989. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--The number of women and children who were unimmunised or incompletely immunised was calculated and the percentage of this target population accepting vaccination was recorded. RESULTS--7530 (84.2%) Of 8944 eligible children and 7730 (40.4%) of 19,138 eligible women were vaccinated. Of the children, 63.8% were boys, 75.9% were aged under 1 year, and 23.0% were aged 1 to 2 years. The estimated number of missed opportunities for vaccination was 716 among the children (8.0% of the target population) and 11,408 among the women (59.6% of those eligible). CONCLUSION--It is possible to establish immunisation services at a health facility treating acutely ill patients.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ebrahim G. J. Immunization in childhood--current trends and new developments. J Trop Pediatr. 1987 Apr;33(2):66–68. doi: 10.1093/tropej/33.2.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



