Abstract
1. We have examined the accumulation by human blood platelets of amino acids that are believed to be involved in neurohumoral transmission in the central nervous system.
2. Platelets were incubated in Ca++-free Krebs solution at 37° C with radio-active amino acids for various times and then the platelets were analysed for the radioactive substance and its metabolites.
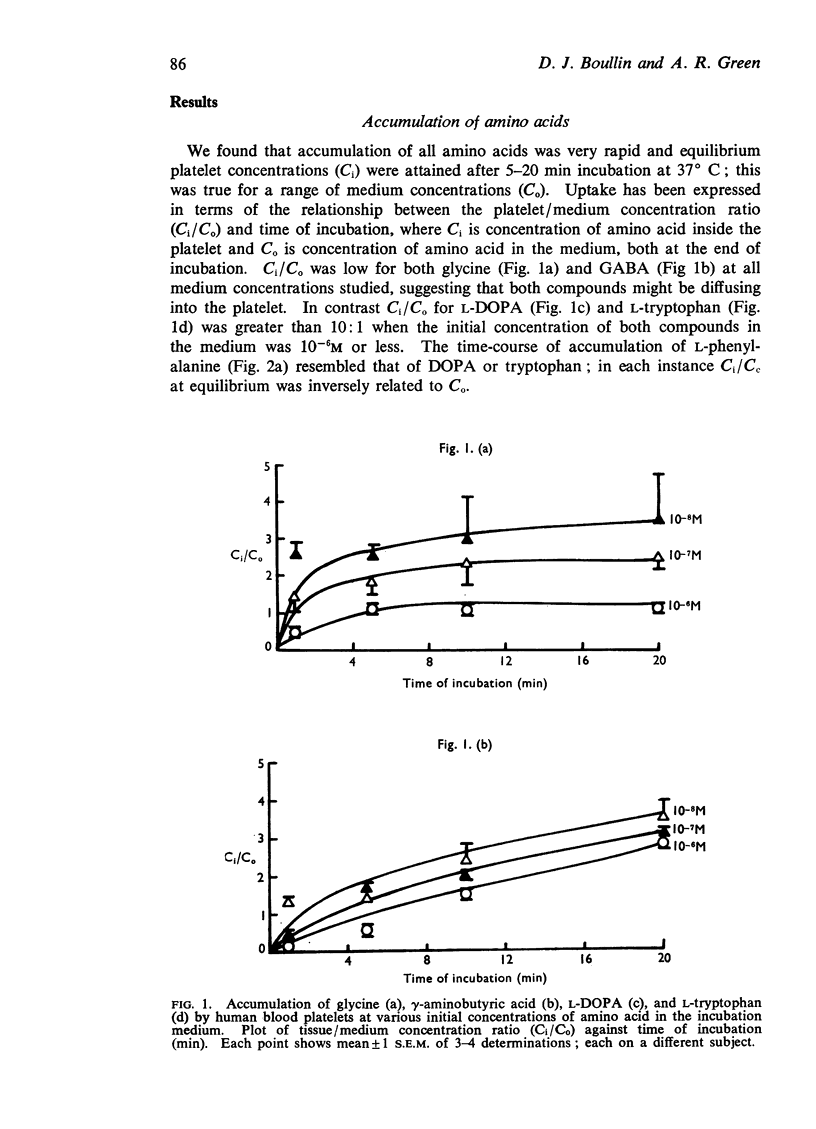
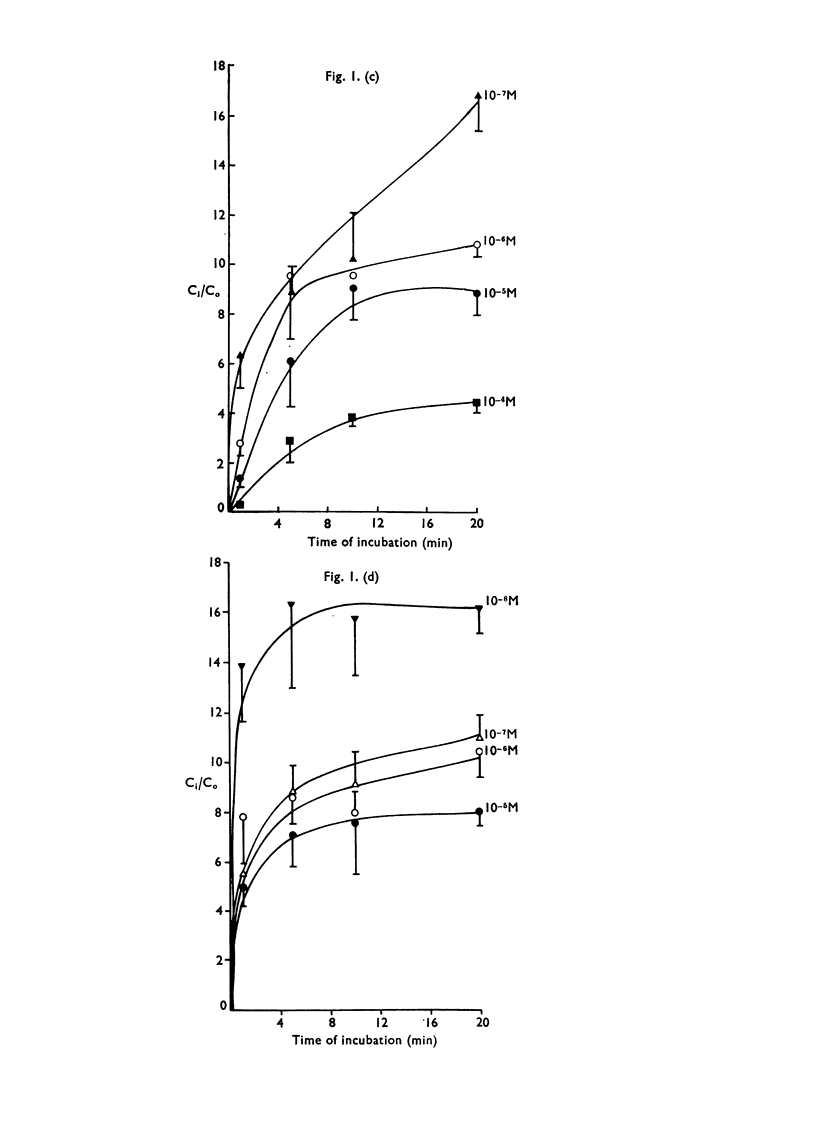
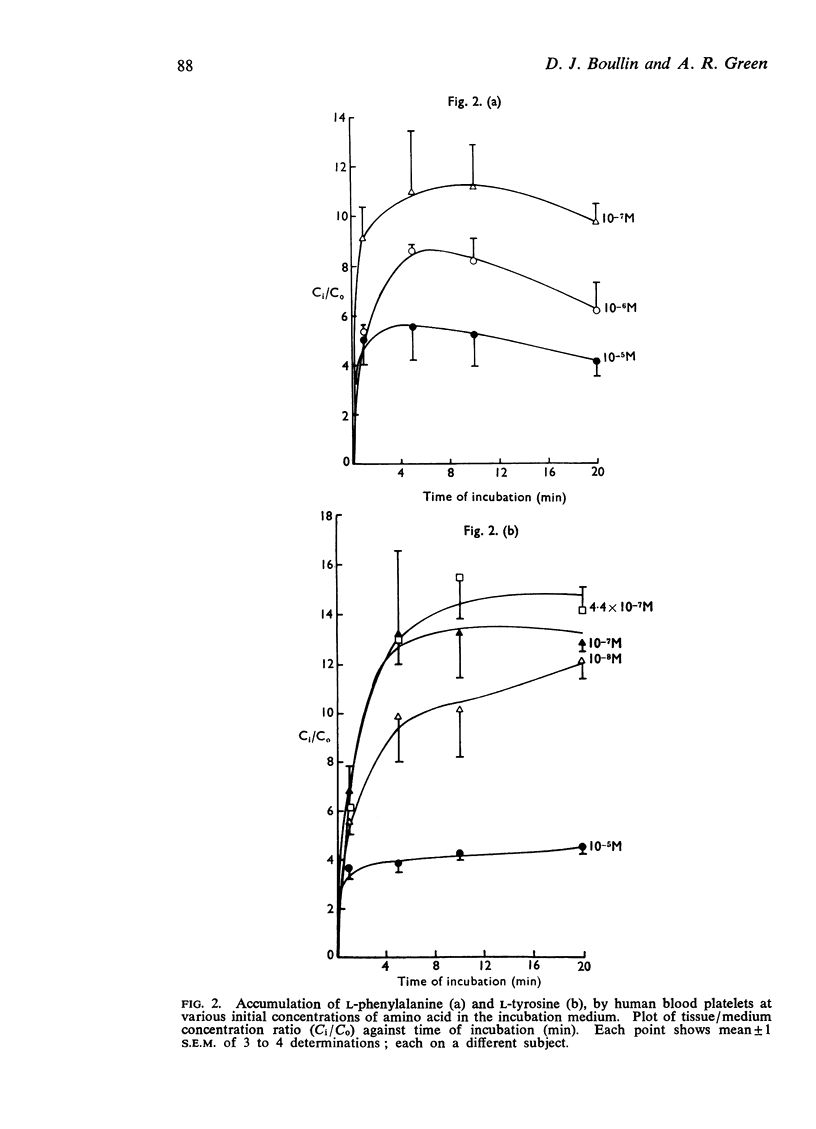
3. L-Phenylalanine, L-DOPA, L-tryptophan and L-tyrosine were rapidly accumulated, the equilibrium tissue/medium concentration ratio (Ci/C0) being greater than 10:1 when the concentration of amino acid in the medium was 10-7M or lower. Glycine and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulation was less, Ci/C0 being lower than 3:1 when C0 was 10-7M.
4. Uptake of L-phenylalanine, L-DOPA and L-tryptophan were all decreased or abolished by incubation at 4° C, or with metabolic inhibitors or by disruption of the platelet membrane prior to incubation, while L-tyrosine accumulation was not affected.
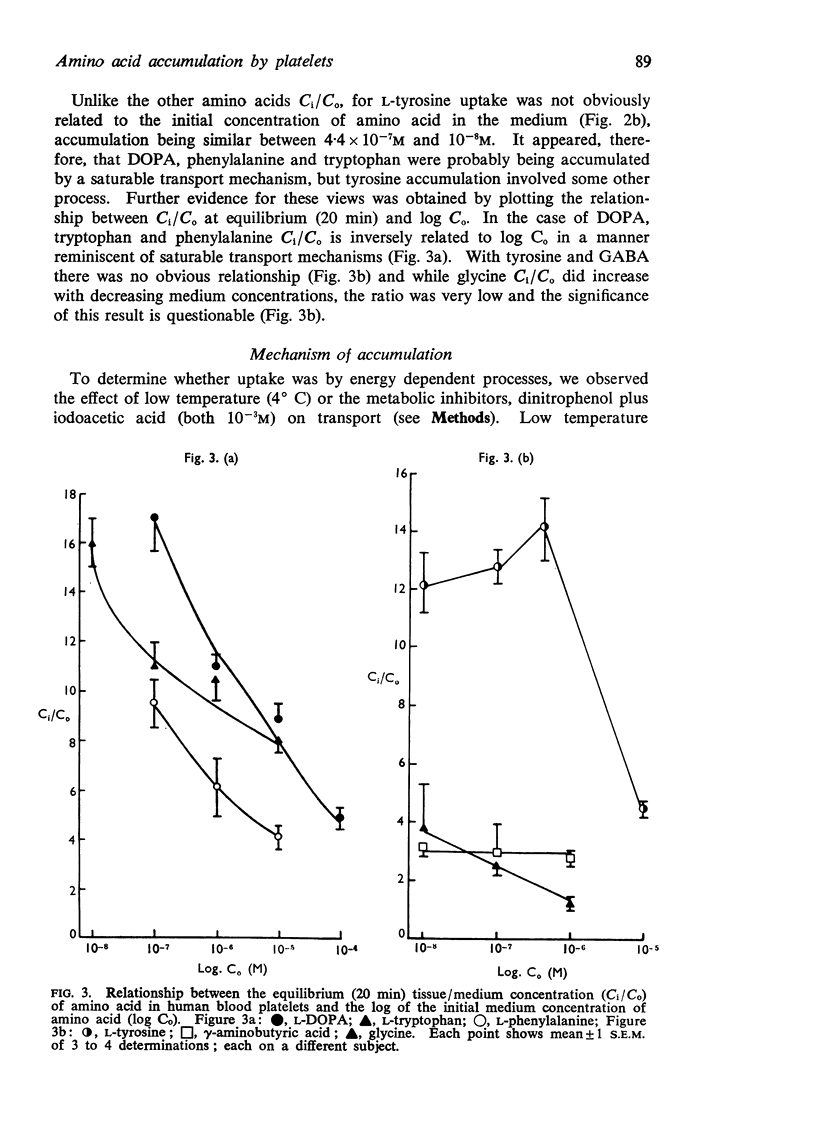
5. It is considered that L-phenylalanine, L-DOPA and L-tryptophan are accumulated by saturable, energy-dependent processes; that glycine and GABA diffuse into the platelet, and L-tyrosine accumulates as a result of diffusion and intracellular binding.
6. None of the amino acids examined showed any significant metabolism during a 20 min incubation. However, some evidence for tyrosine binding to soluble protein was obtained.
7. Results are compared to reports of accumulation of these amino acids by the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V., HORNYKIEWICZ O., STAFFORD A. The uptake of adrenaline and noradrenaline by blood platelets of the pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Dec;13(4):411–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. J., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6357–6365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R. G. Specificity of cerebral amino acid transport: a kinetic analysis. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:245–258. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F., Rafelson M. E., Jr In vitro incorporation of amino-acids into the contractile protein of human blood platelets. Nature. 1967 Jul 15;215(5098):283–284. doi: 10.1038/215283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., Coleman M., O'Brien R. A. Abnormalities in platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine efflux in patients with infantile autism. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):371–372. doi: 10.1038/226371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., O'Brien R. A. Abnormalities of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and binding by blood platelets from children with Down's syndrome. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):287–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., O'Brien R. A. Accumulation of dopamine by blood platelets from normal subjects and parkinsonian patients under treatment with L-DOPA. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Aug;39(4):779–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., O'Brien R. A. The accumulation of guanethidine by human blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):90–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Zucker M. B. Changes in platelet volume produced by temperature, metabolic inhibitors, and aggregating agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):296–301. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper I. A., Firkin B. G. Amino acid transport into human platelets and subsequent incorporation into protein. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Feb 28;23(1):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUROFF G., KING W., UNDENFRIEND S. The uptake of tyrosine by rat brain in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1773–1777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G., Parfitt A. G. Tryptophan transport across the synaptosomal membrane. J Neurochem. 1970 Sep;17(9):1339–1353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb06869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., STACEY R. S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine in normal human platelets. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):711–720. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., TOH C. C. Absorption of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) and histamine by dog platelets. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):300–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. Role of transmitter uptake mechanisms in synaptic neurotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;41(4):571–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. Unique high affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspartic acids in central nervous tissue of the rat. Nature. 1971 Dec 3;234(5327):297–299. doi: 10.1038/234297b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Pickles H. G. Uptake of 14C glycine by spinal cord. Nature. 1969 May 17;222(5194):679–680. doi: 10.1038/222679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paasonen M. K. Platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine as a model in pharmacology. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1968;46(3):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletscher A. Metabolism, transfer and storage of 5-hydroxytryptamine in blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon H. M., Spirt N. M., Abrams W. B. The accumulation and metabolism of dopamine by the human platelet. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Nov-Dec;11(6):838–845. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970116838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Laster L., Shulman N. R. Protein synthesis by human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2094–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve P. D., Solomon H. M. Uptake of amino acids by the human platelet. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):58–61. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


