Abstract
1 The concentration of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the rabbit brainstem was measured during fevers produced by either an injection of bacterial pyrogen (BP) or continuous infusion of leucocyte pyrogen (LP). 2 Both procedures had little effect on the concentration of noradrenaline in the preoptic/hypothalamic area but significantly (P smaller than 0.001) lowered the concentration of noradrenaline in the midbrain and pons/medulla. 3 BP significantly (P smaller than 0.01) lowered the concentration of 5-HT in the preoptic/hypothalamic area but had no effect in the midbrain or pons/medulla, whereas LP significantly (P smaller than 0.01) lowered the concentration of 5-HT in the midbrain and pons/medulla but had little effect in the hypothalamus. 4 The concentration of dopamine throughout the brainstem was little affected by either BP or LP fevers. However the concentration in the midbrain was significantly reduced by LP (P smaller than 0.001). 5 Alpha-Methyltyrosine (200 mg/kg) pretreatment diminished the pyrogenic response to both BP and LP whilst p-chlorophenylalanine (300 mg/kg) slightly enhanced the response to both forms of challenge. 6 Reserpine (1 mg/kg) diminished both types of fever whilst a combination of alpha-methyltyrosine and p-chlorophenylalanine slightly enhanced the fevers produced by either BP or LP. 7 The results obtained are discussed in relation to the mechanisms involved in the production of fever and to the possible function of noradrenaline and 5-HT as thermoregulatory transmitters.
Full text
PDF

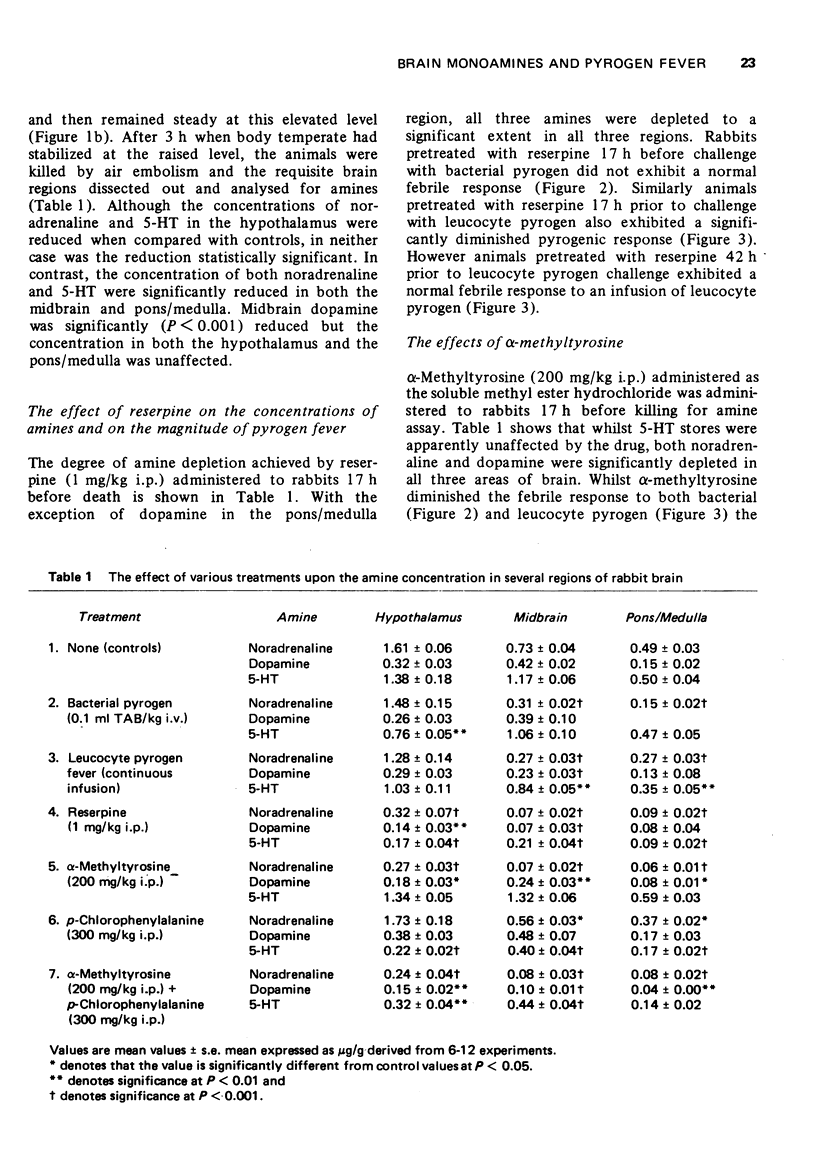


Selected References
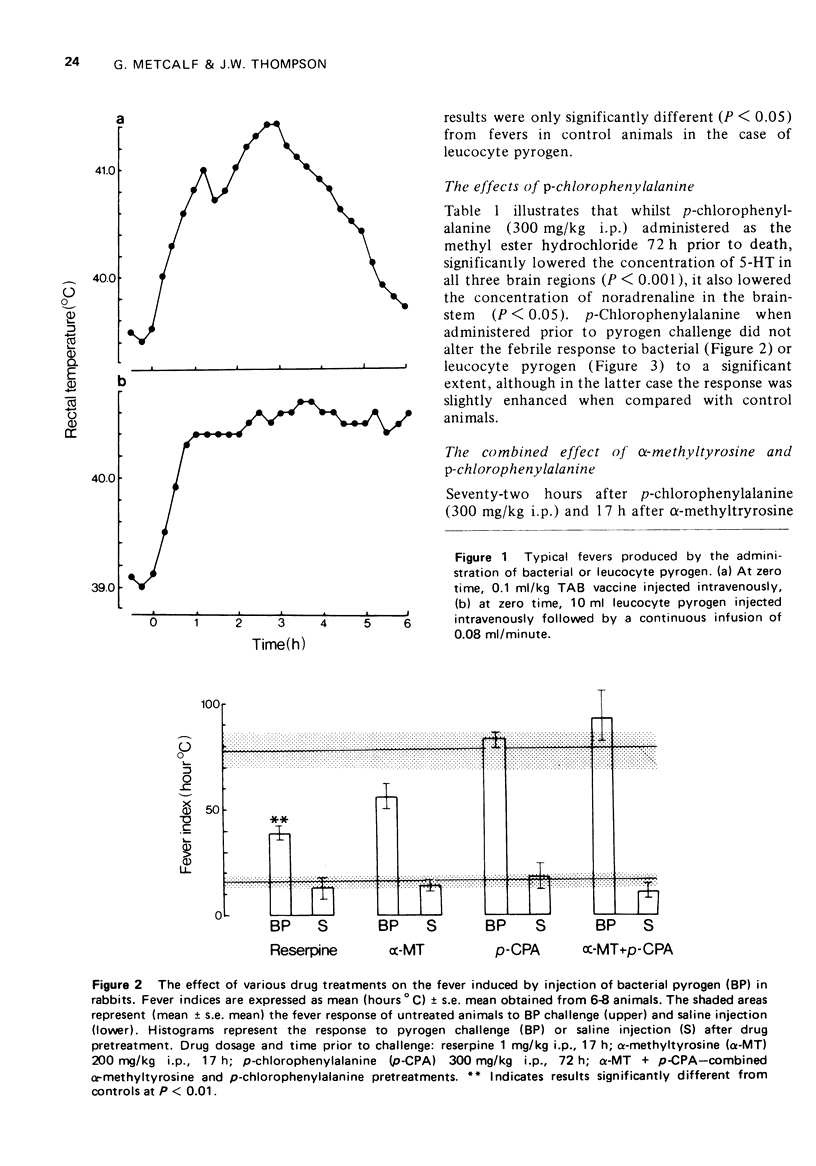
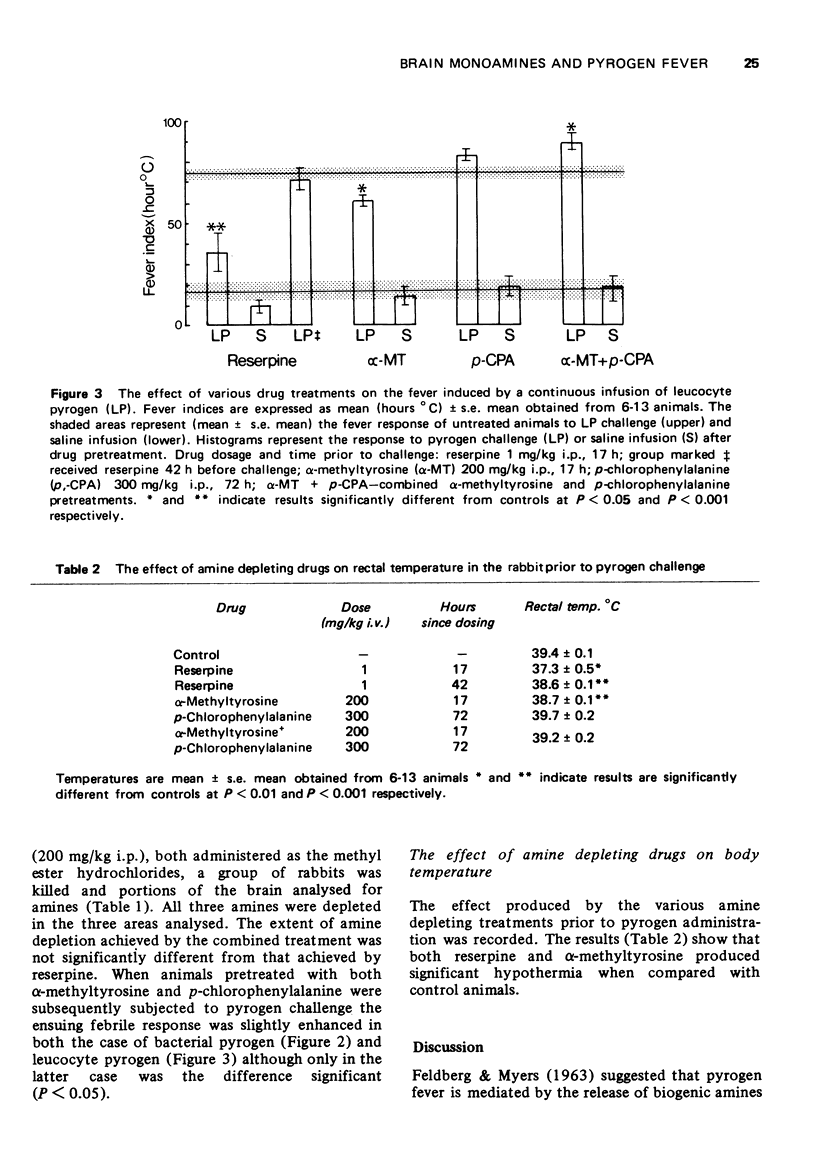
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. I. The presence of transferable pyrogen in the blood stream following the injection of typhoid vaccine. J Exp Med. 1955 May 1;101(5):519–528. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATKINS E., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. II. Identification of an endogenous pyrogen in the blood stream following the injection of typhoid vaccine. J Exp Med. 1955 Nov 1;102(5):499–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.5.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT I. L., Jr, BEESON P. B. Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. II. Characterization of fever-producing substances from polymorphonuclear leukocytes and from the fluid of sterile exudates. J Exp Med. 1953 Nov;98(5):493–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Cranston W. I., Honour A. J. Effects of intraventricular and intrahypothalamic injection of noradrenaline and 5-HT on body temperature in conscious rabbits. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(4):852–864. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Cranston W. I., Honour A. J. Observations on the site & mode of action of pyrogens in the rabbit brain. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):325–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Luff R. H., Rawlins M. D., Rosendorff C. The effects of salicylate on temperature regulation in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1970 May;208(1):251–259. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R., Helman R., Oates J. A. Inhibition of endotoxin fever by reserpine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):746–749. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Myers R. D., Veale W. L. Perfusion from cerebral ventricle to cisterna magna in the unanaesthetized cat. Effect of calcium on body temperature. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):403–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giarman N. J., Tanaka C., Mooney J., Atkins E. Serotonin, norepinephrine, and fever. Adv Pharmacol. 1968;6(Pt A):307–317. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURUMA I., TAKAGI H., YAMADA H. [CHANGES OF BRAIN SEROTONIN AND CATECHOLAMINE LEVELS OF THE FEBRILE RABBIT. 1. THE DEGREE OF FEVER INDUCED BY PYREXAL AND CHANGES OF THE LEVELS IN THE BRAIN STEM OF THESE AMINES]. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1964 Nov 20;60:563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax P. Measurement of 'core' temperature in the rat. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):854–855. doi: 10.1038/210854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf G. A rapid method for the simultaneous determination of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5HT in small samples of brain tissue. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. A. An assay method for leukocyte pyrogen. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):745–761. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendorff C., Mooney J. J. Central nervous system sites of action of a purified leucocyte pyrogen. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):597–603. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Kuruma I. Effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the content of serotonin and norepinephrine in rabbit brain. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1966 Dec;16(4):478–479. doi: 10.1254/jjp.16.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


