Abstract
1. Evidence is presented to elucidate the nature of the adrenergic mechanisms involved in responses of the guinea-pig to anaphylatoxin (AT).
2. Investigation by means of adrenalectomy, adrenergic neurone blockade, α- and β- adrenoceptor blockade and exclusion of autonomic reflexes, revealed that the adrenergic mechanisms provoked included catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla, sympathetic reflex activity, stimulation of adrenergic neurones and α- and β-adrenoceptor activity.
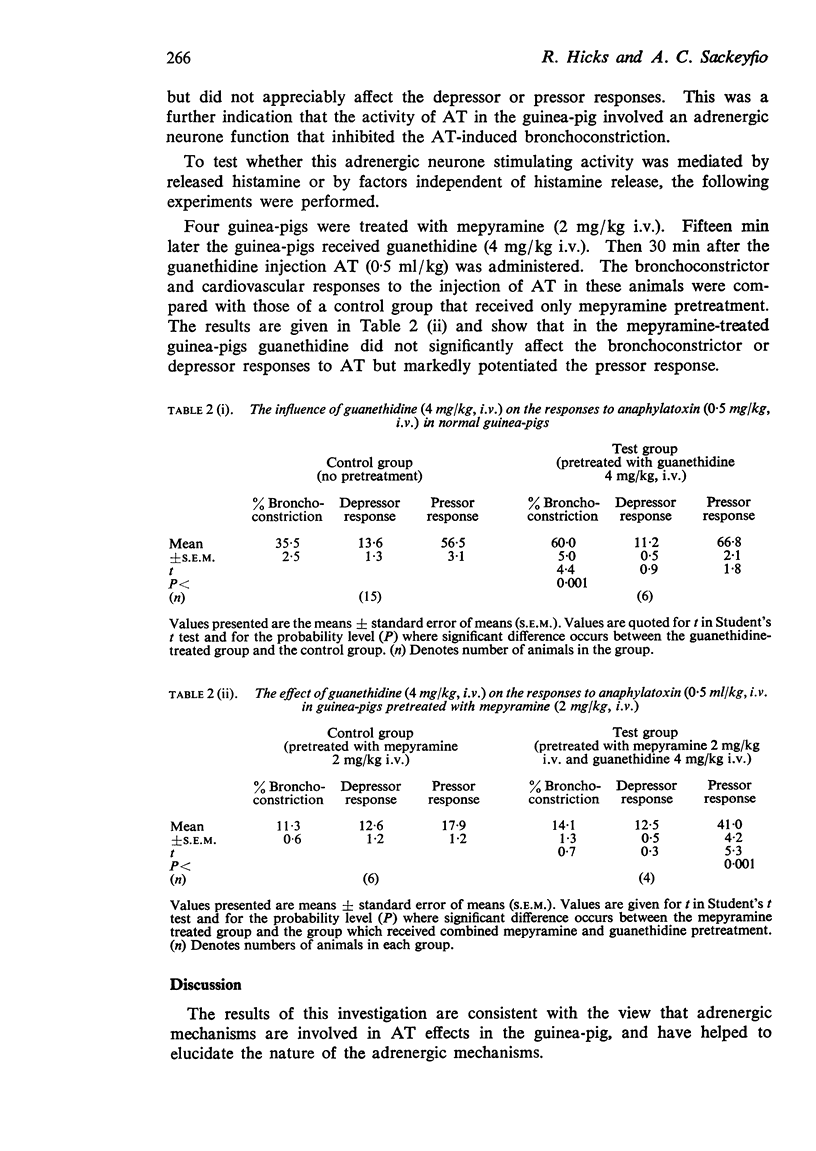
3. The cardiovascular effects of AT, mediated by histamine release, were largely attributable to adrenal medullary and adrenergic neuronal mechanisms. These mechanisms also exerted a restraint on the predominantly histamine mediated bronchoconstrictor effect of AT.
4. The cardiovascular effects of AT activity, not attributable to histamine release, were also probably associated with catecholamine release. However, the bronchoconstrictor component of this AT activity was not significantly affected by guanethidine, and it would, therefore, appear that neuronal bronchodilator mechanisms did not exert a restraint upon this aspect of AT activity.
5. These findings are generally compatible with previous work showing that adrenergic mechanisms operate during AT-induced responses. In contrast to previous reports, however, the adrenergic activity was predominantly associated with the effects of released histamine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernauer W., Hahn F., Beck E., Kury H. The role of histamine and catecholamines in anaphylatoxin shock as compared to the anaphylactic shock. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1970;266(3):208–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00997283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodammer G., Vogt W. Actions of anaphylatoxin on circulation and respiration of the guinea pig. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1967;32(5):417–428. doi: 10.1159/000229953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodammer G., Vogt W. Contraction of the guinea-pig ileum induced by anaphylatoxin independent of histamine release. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):648–657. doi: 10.1159/000230389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. E. Contributions to the physiology of the lungs: Part I. The bronchial muscles, their innervation, and the action of drugs upon them. J Physiol. 1903 Mar 16;29(2):97–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1903.sp000947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTING G., AXELROD J., WHITBY L. G. Effect of drugs on the uptake and metabolism of H3-norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:146–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS R., LEACH G. D. QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF GUINEA-PIG ANAPHYLAXIS IN VIVO. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:441–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch M. W., Proctor C., Rand M. J. Evidence for an adrenergic homeostatic bronchodilator reflex mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;2(3):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKERSON M. Blockade of the actions of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 2):443–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Collier H. O. Release of catecholamines in the guinea-pig by substances involved in anaphylaxis. Nature. 1967 Feb 25;213(5078):838–840. doi: 10.1038/213838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSCHILD A. M., ROCHA E SILVA M. Activation of a histamine-releasing agent (anaphylatoxin) in normal rat plasma. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Oct;35(5):507–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackeyfio A. C. Definition of the histaminic component of the bronchoconstrictor and cardiovascular effects of anaphylatoxin in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):424P–425P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


