Abstract
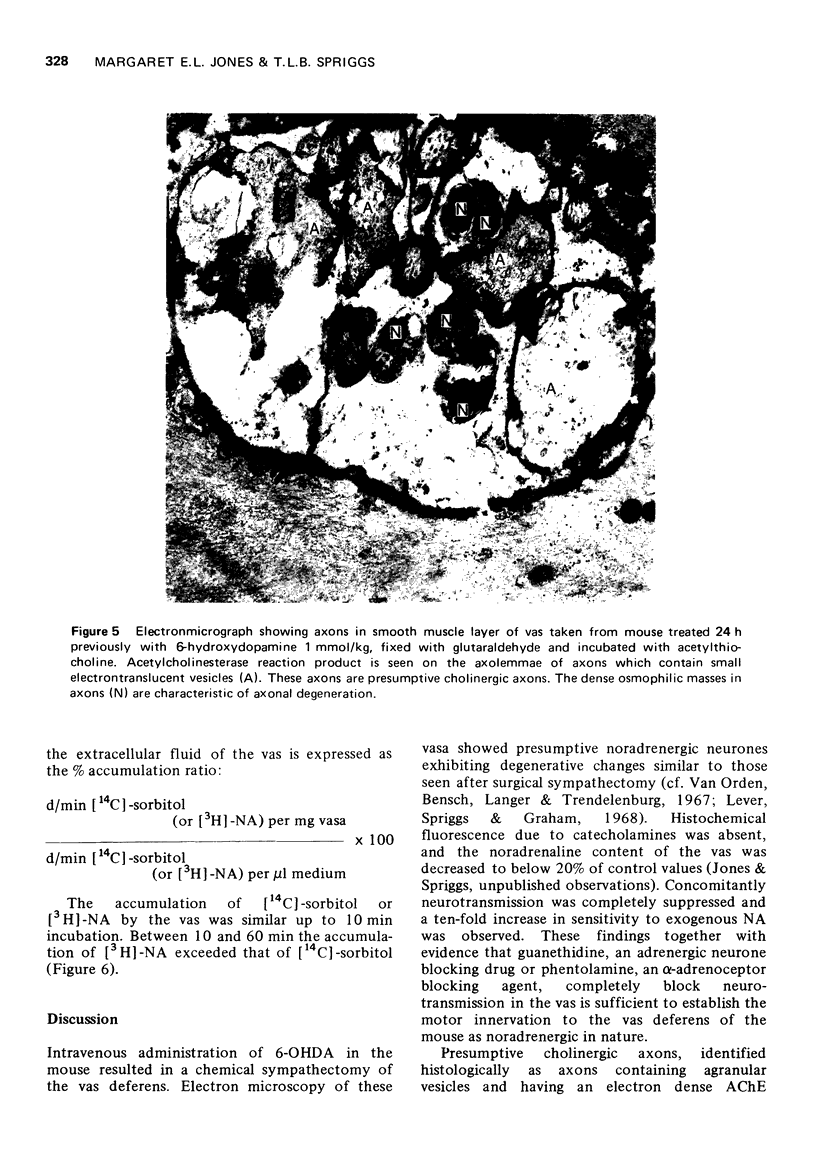
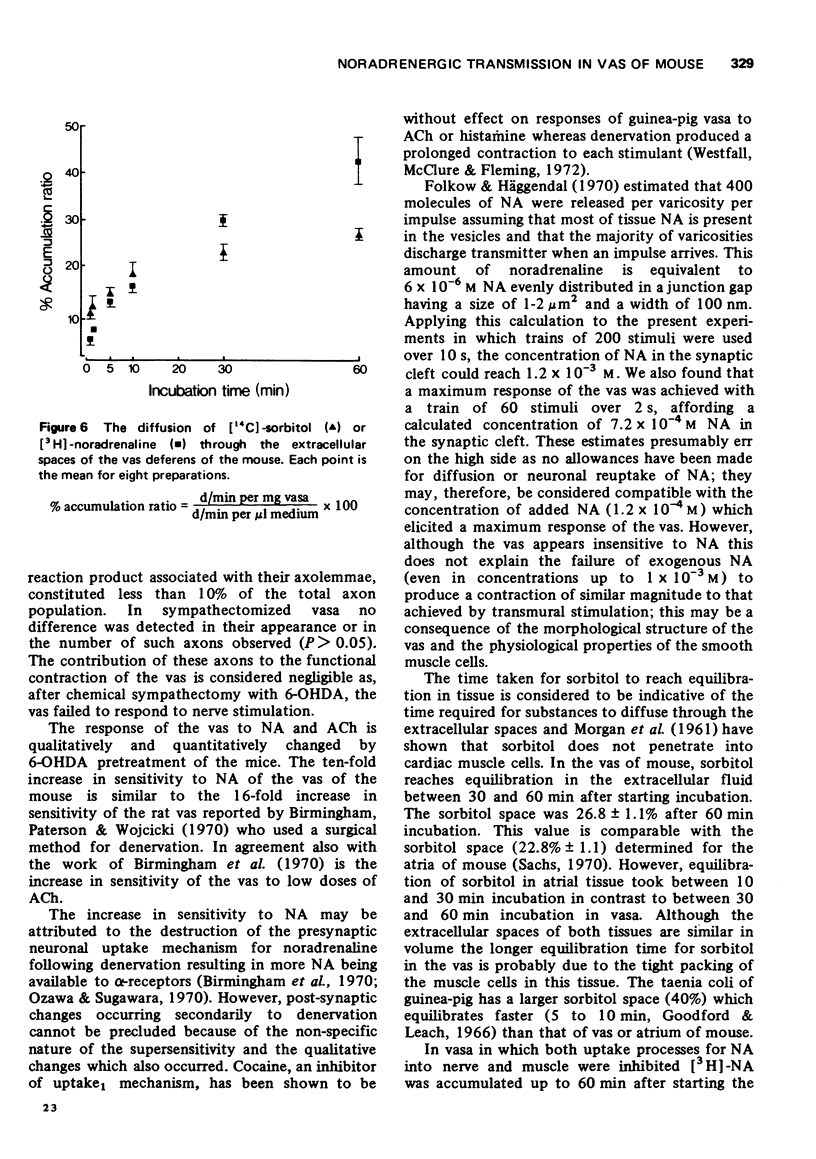
1. A comprehensive investigation of the innervation of the vas deferens of the mouse was made using pharmacological, histochemical and electronmicroscopical techniques. 2. Guanethidine inhibited the response of the vas to transmural stimulation and potentiated the response to noradrenaline (NA). Phentolamine abolished responses to NA and to transmural stimulation. 3. After chemical sympathectomy degenerative changes were seen in presumptive noradrenergic axons; histochemical fluorescence due to catecholamines was absent. The vas failed to respond to transmural stimulation, and a 10-fold increase in sensitivity of the vas to exogenous NA was observed. 4. NA is shown to diffuse slowly through this tissue whose muscle cells are densely packed. This is disscussed in relation to the apparent "insensitivity" of the vas to exogenous NA. 5. A cholinergic component was identified histochemically which did not contribute significantly to the motor response of the vas as chemical sympathectomy abolished completely the motor response elicited by transmural stimulation. 6. It is concluded that NA is the motor trnasmitter for the smooth muscle of the vas deferens of the mouse.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRMINGHAM A. T., WILSON A. B. PREGANGLIONIC AND POSTGANGLIONIC STIMULATION OF THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED VAS DEFERENS PREPARATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:569–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham A. T., Paterson G., Wójcicki J. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Aug;39(4):748–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham A. T. Sympathetic denervation of the smooth muscle of the vas deferens. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):645–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Burnstock G. A comparative study of spike potentials in response to nerve stimulation in the vas deferens of the mouse, rat and guinea-pig. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Oct 15;31(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Hamilton D. N., Hosie J. A. The extraneuronal uptake and localization of noradrenaline in the cat spleen and the effect on this of some drugs, of cold and of denervation. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):563–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J., Leach E. H. The extracellular space of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):1–10. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUKOVIC S. Responses of the isolated sympathetic nerveductus deferens preparation of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Apr;16:188–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb00312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The distribution of cholinesterase in cholinergic neurons demonstrated with the electron microscope. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):381–390. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., HENDERSON M. J., REGEN D. M., PARK C. R. Regulation of glucose uptake in muscle. I. The effects of insulin and anoxia on glucose transport and phosphorylation in the isolated, perfused heart of normal rats. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa H., Sugawara K. Sensitivity of the isolated vas deferens of the guinea-pig to norepinephrine and acetylcholine after denervation, decentralization and treatments by various agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul 1;11(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroff C. P., Patt H. H., Nair P. P. A rapid method for dissolving tissue for liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1965 Oct;16(10):599–601. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(65)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C. The fine structure of autonomic nerve endings in smooth muscle of the rat vas deferens. J Anat. 1962 Oct;96:427–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs T. L., Lever J. D., Rees P. M., Graham J. D. Controlled formaldehyde-catecholamine condensation in cryostat sections to show adrenergic nerves by fluorescence. Stain Technol. 1966 Nov;41(6):323–327. doi: 10.3109/10520296609116333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Orden L. S., 3rd, Bensch K. G., Langer S. Z., Trendelenburg U. Histochemical and fine structural aspects of the onset of denervation supersensitivity in the nictitating membrane of the spinal cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Aug;157(2):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall D. P., McClure D. C., Fleming W. W. The effects of denervation, decentralization and cocaine on the response of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens to various drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 May;181(2):328–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Burnstock G. Post-natal development of the innervation of the mouse vas deferens. A fine structural study. J Anat. 1969 Jan;104(Pt 1):17–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]