Abstract
The ionophore X-537A depolarized frog skeletal muscle fibres about 10 mV in 10 min and a further 30 mV or so over the next 50 minutes. With A23187, depolarization was relatively feeble and delayed in onset but was hastened when calcium was removed from the bathing medium. The results support conjecture that some functional responses to these ionophores are attributable, in part, to depolarization.
Full text
PDF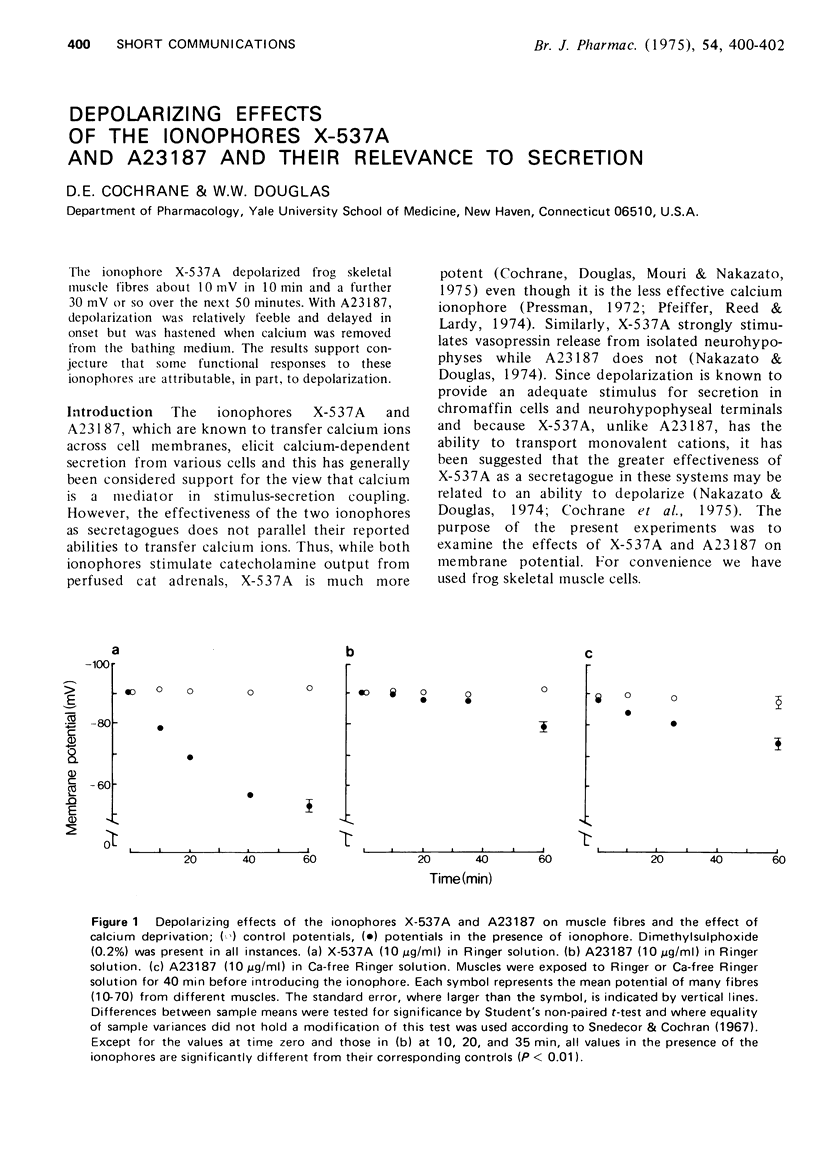


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caswell A. H., Pressman B. C. Kinetics of transport of divalent cations across sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles induced by ionophores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Célis H., Estrada S., Montal M. Model translocators for divalent and monovalent ion transport in phospholipid membranes. I. The ion permeability induced in lipid bilayers by the antibiotic X-537A. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(2):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01870111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devore D. I., Nastuk W. L. Effects of 'calcium ionophore' X537A on frog skeletal muscle. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):644–646. doi: 10.1038/253644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., KAO C. Y., ALTAMIRANO M. Bioelectric effects of ions microinjected into the giant axon of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):245–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Experiments on the injection of substances into squid giant axons by means of a microsyringe. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):592–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H., Van der Kloot W. Calcium ionophore X-537A increases spontaneous and phasic quantal release of acetylcholine at frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1974 Aug 23;250(5468):658–660. doi: 10.1038/250658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato Y., Douglas W. W. Vasopressin release from the isolated neurohypophysis induced by a calcium ionophore, X-537A. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):479–481. doi: 10.1038/249479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. Ultraviolet and fluorescent spectral properties of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 and its metal ion complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4007–4014. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Baldassare J., Inesi G. The effect of calcium ionophores on fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):735–749. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Costa J. L., Moss J., Kopin I. J. Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurones by the calcium ionophores X 537A and A 23187. Life Sci. 1974 May 1;14(9):1705–1719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Wilkinson J. R., Hamill R. L., Horng J. S. Effects of antibiotic ionophore, A23187, on oxidative phosphorylation and calcium transport of liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):578–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


