Abstract
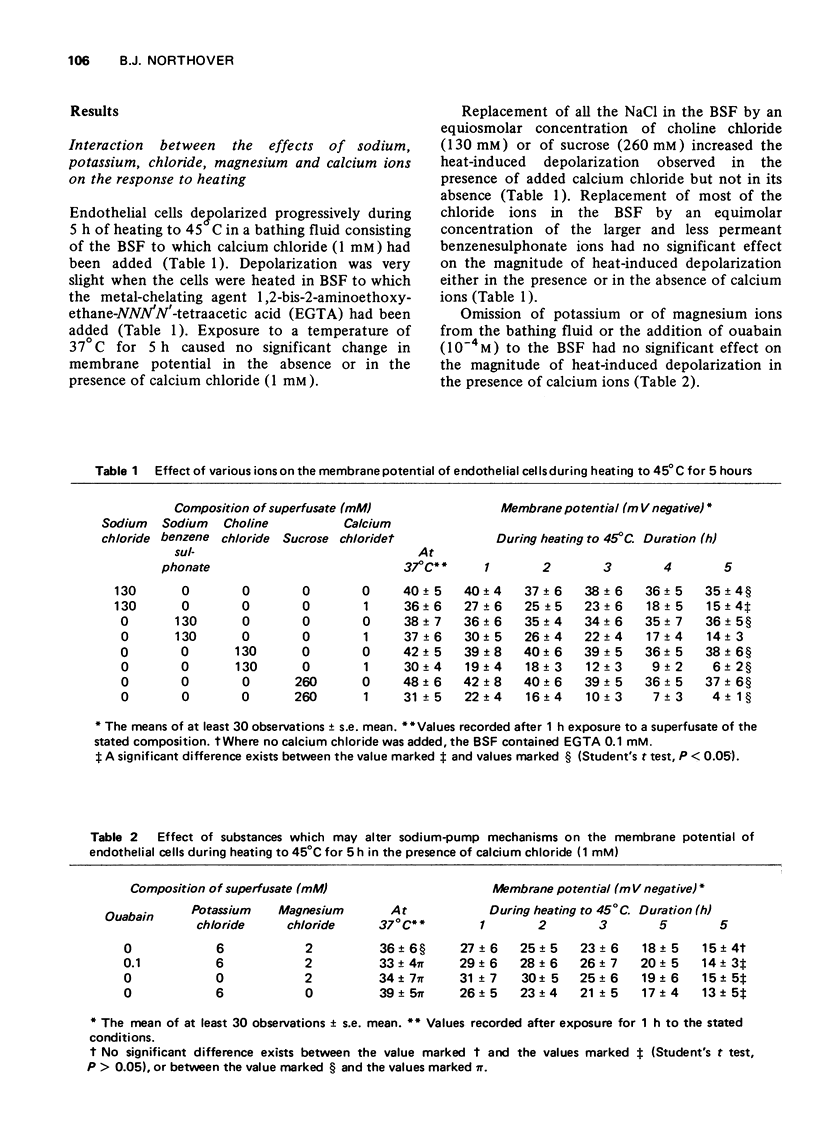
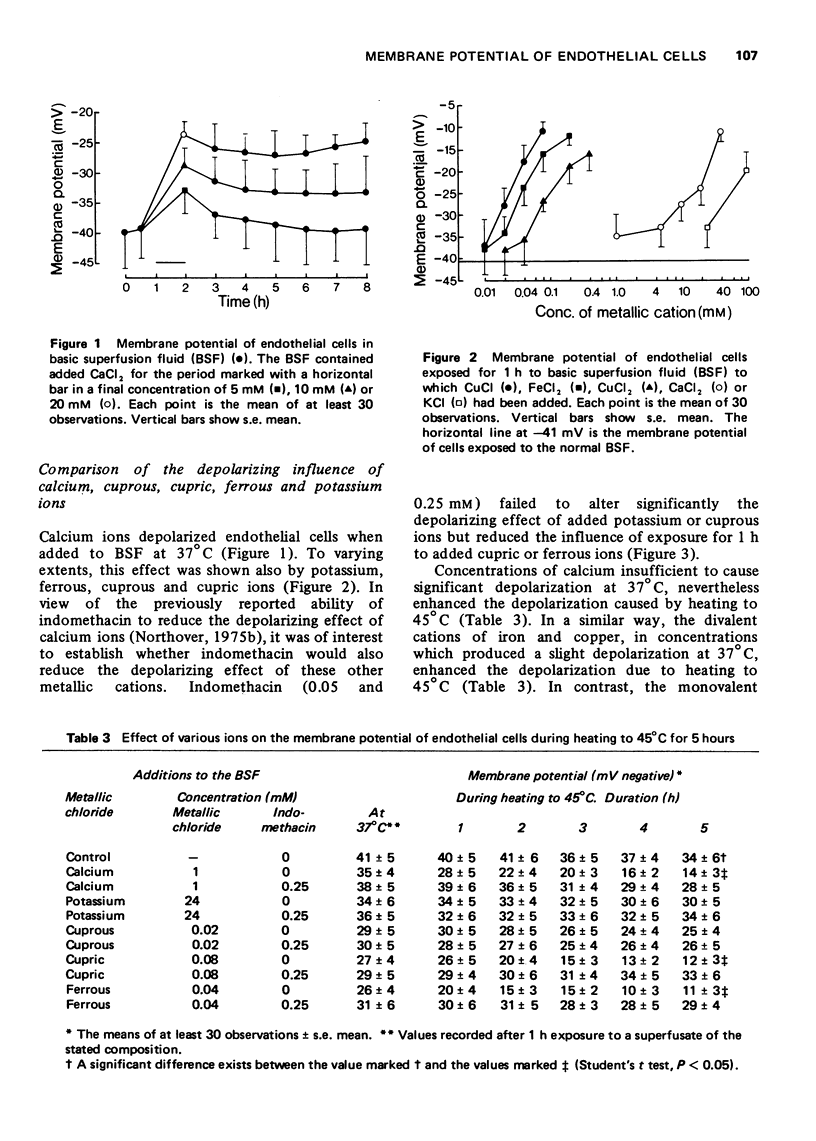
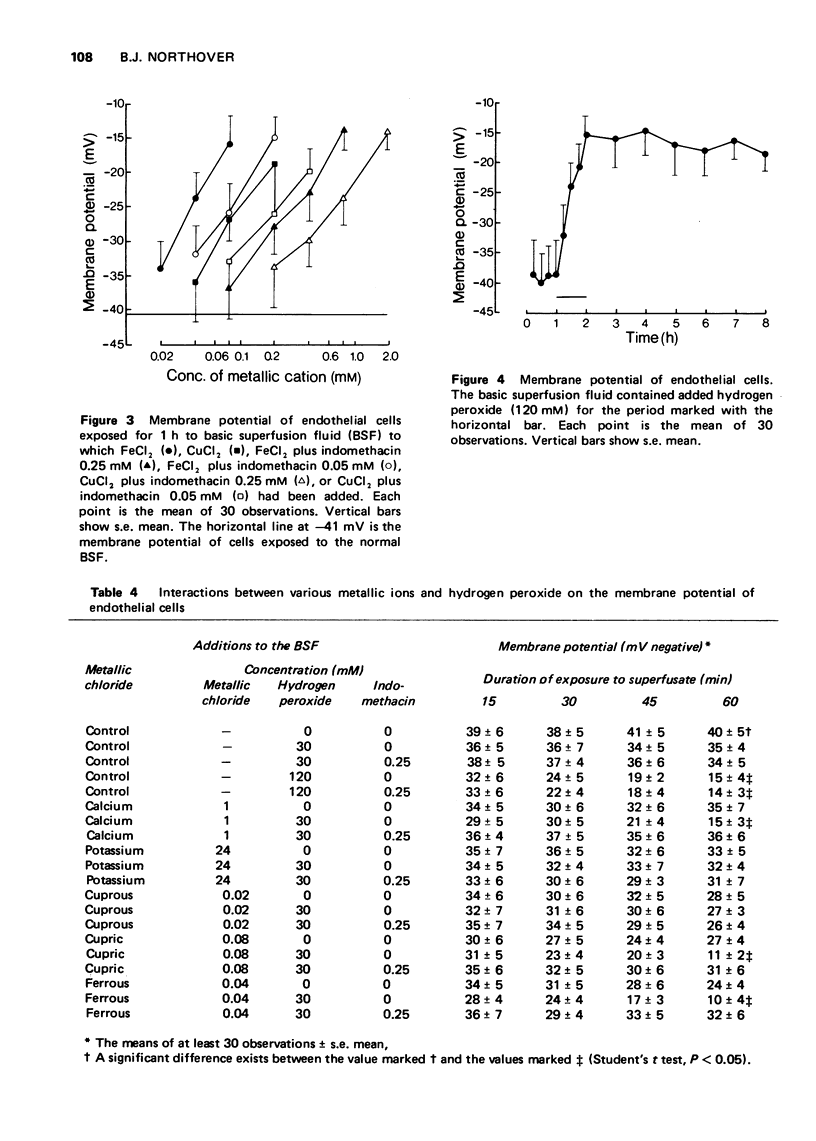
1 Endothelial cells depolarized progressively when heated for 5 h at 45 degrees C in the presence of calcium (1 mM), cupric (0.08 mM) or ferrous (0.04mM) ions. In the absence of these ions, heating caused only slight depolarization. Higher concentrations of these ions caused depolarization even at normal body temperature (37 degrees C). 2 Cuprous and potassium ions, although producing depolarization at 37 degrees C, failed to augment the depolarization due to heating to 45 degrees C. 3 Hydrogen peroxide caused depolarization which was potentiated by the presence of calcium, cupric or ferrous ions, but not by the presence of cuprous or potassium ions. 4 Indomethacin (0.25 mM) reduced the depolarization caused by calcium, cupric or ferrous ions at 37 degrees C and also reduced the potentiation of heat-induced and hydrogen peroxide-induced depolarization which these divalent metallic cations produced. However, indomethacin failed to modify the depolarization caused by cuprous or potassium ions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr D. F., Seidel C., Sobieski J. Possible role of sodium-calcium pumps in tension development of vascular smooth muscle. Microvasc Res. 1969 Oct;1(4):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(69)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Effects of electrogenic sodium pumping on the membrane potential of longitudinal smooth muscle from terminal ileum of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):693–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. The action of ouabain on the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):131–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly I. de B., Clark A. J. The action of ions upon the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1921 Mar 15;54(5-6):367–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1921.sp001938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTGAU H. C., NIEDERGERKE R. The antagonism between Ca and Na ions on the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):486–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. I. An activable permeability factor and its inhibitor in guinea-pig serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):71–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariano M., de Lourdes B. M., de Moraes S., Palermo Neto J. Cobalt ion action on the vascular permeability and mast cells of the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;21(10):709–710. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sutter M. C. Ouabain-induced changes in the contractile and electrical activity, potassium content, and response to drugs, of smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 May;45(3):509–520. doi: 10.1139/y67-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northover A. M. Action of histamine on endothelial cells of guinea-pig isolated hepatic portal vein and its modification by indomethacin or removal of calcium. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Feb;56(1):52–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northover B. J. Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on the membrane potential of vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;53(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitrin M. D., Bohr D. F. Ca and Na interaction in vascular smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1124–1128. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. H., Wilhelm D. L. The inflammatry reaction in chemical injury. II. Vascular permeability changes and necrosis induced by intracutaneous injection of various chemicals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Dec;48(6):592–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


