Abstract
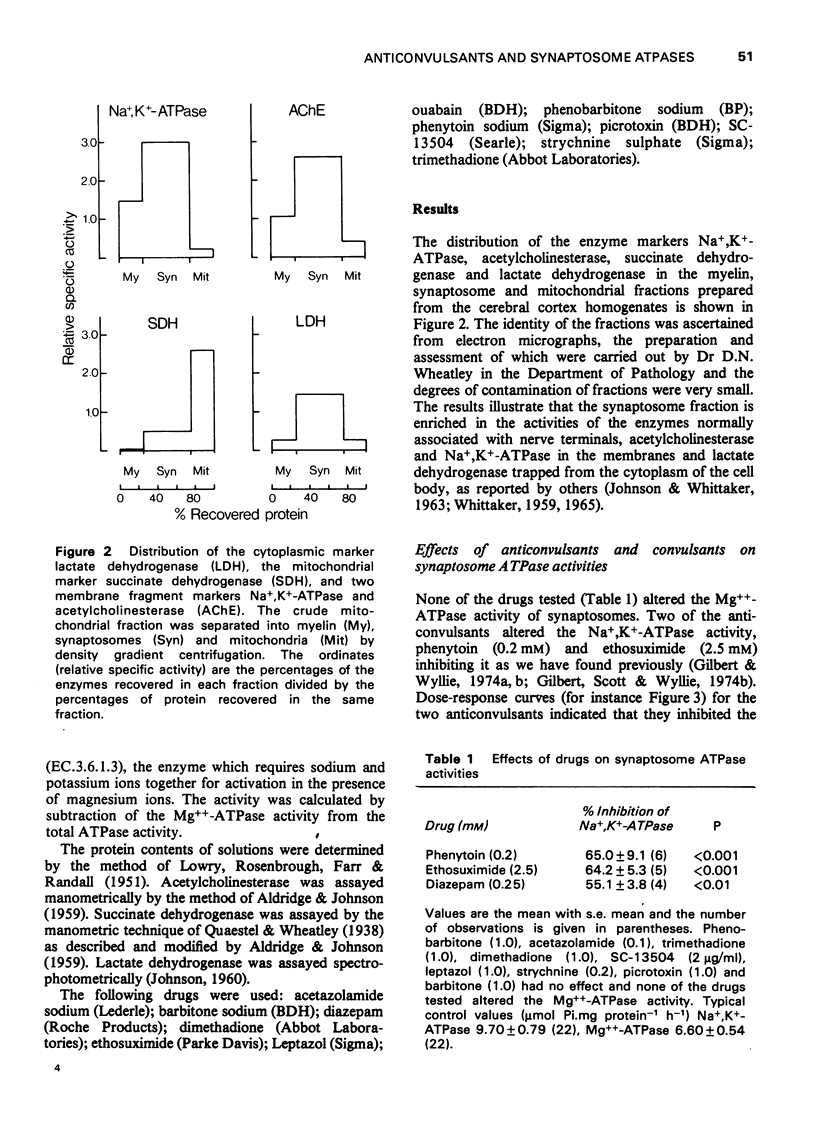
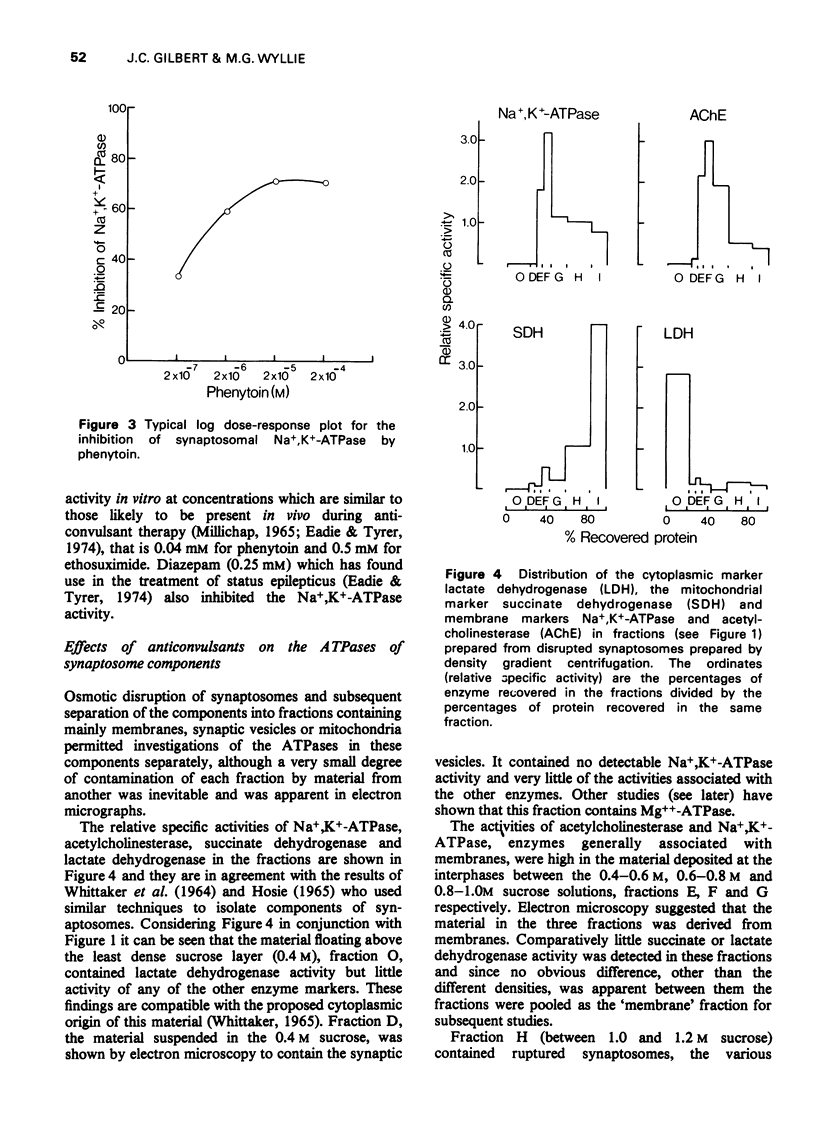
1. The effects of anticonvulsants, and other drugs on the Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) (ouabain-sensitive) and Mg++-ATPase activities of synaptosomes and their components have been determined. 2. The Mg++-ATPase activity of synaptosomes was not affected by the drugs but the Na+, K+-ATPase activity was inhibited by phenytoin (diphenylhydantoin), ethosuximide and diazepam. 3. Fractions containing mainly membranes, mitochondria or synaptic vesicles, were prepared from synaptosomes by osmotic shock and subsequent density gradient centrifugation. Inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity by phenytoin, ethosuximide and diazepam was apparent only in the membrane fraction. 4. The fraction containing synaptic vesicles exhibited pronounced Md++-ATPase but no Na+, K+-ATPase activity. In contrast to the enzymes of the membranes and mitochondria, the Mg++-ATPase of the vesicles was inhibited by diazepam and all of the anticonvulsants tested.
Full text
PDF

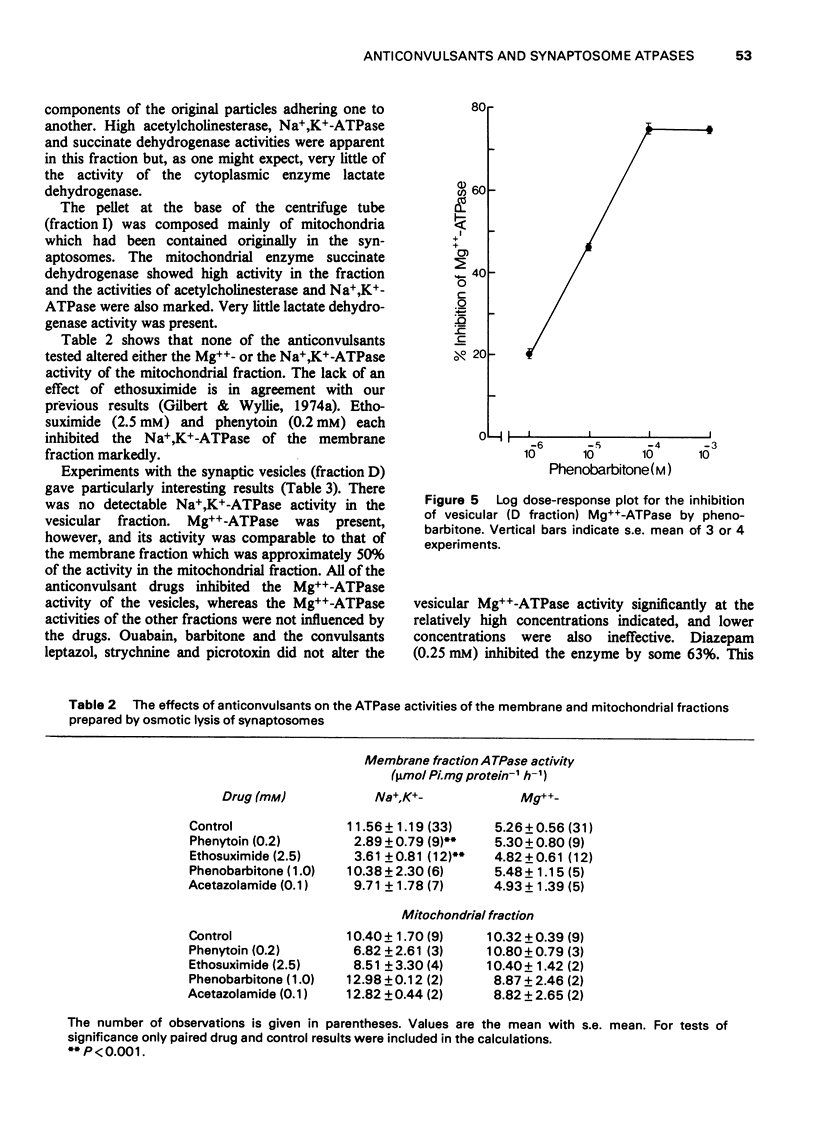




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., JOHNSON M. K. Cholinesterase, succinic dehydrogenase, nucleic acids, esterase and glutathione reductase in sub-cellular fractions from rat brain. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:270–276. doi: 10.1042/bj0730270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANKS P. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ADRENAL CHROMAFFIN GRANULES. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:490–496. doi: 10.1042/bj0950490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. W., Brody T. M. Inhibition of Na+K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity in rat brain by substituted phenothiazines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Jun;15(6):703–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESPLIN D. W. Effects of diphenylhydantoin on synaptic transmission in cat spinal cord and stellate ganglion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Jul;120(3):301–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escueta A. V., Appel S. H. The effects of electrically induced seizures on potassium transport within isolated nerve terminals. Neurology. 1970 Apr;20(4):392–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festoff B. W., Appel S. H. Effect of diphenylhydantoin on synaptosome sodium-potassium-ATPase. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2752–2758. doi: 10.1172/JCI105956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B. The in vivo and in vitro effect of diphenylhydantoin and phenobarbitone on K+ activated phosphohydrolase and (Na+, K+)-activated ATPase in particulate membrane fractions from rat brain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;22(2):81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Gray P., Heaton G. M. Anticonvulsant drugs and brain glucose. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;20(1):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Scott A. K., Wyllie M. G. Proceedings: Effects of ethosuximide on adenosine triphosphatase activities of some subcellular fractions prepared from rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;50(3):452P–453P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Wyllie M. G., Davison D. V. Nerve terminal ATPase as possible trigger for neurotransmitter release. Nature. 1975 May 15;255(5505):237–238. doi: 10.1038/255237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Wyllie M. G. Effects of prostaglandins on the ATPase activities of synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Feb 15;24(4):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Wyllie M. G. Proceedings: The effects of phenytoin on adenosine triphosphatase activities of synaptosomes and their components. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;52(3):445P–445P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. C., Wyllie M. G. Proceedings: The effects of the anticonvulsant ethosuximide on adenosine triphosphatase activities of synaptosomes prepared from rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):139P–140P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosie R. J. The localization of adenosine triphosphatases in morphologically characterized subcellular fractions of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):404–412. doi: 10.1042/bj0960404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON M. K. The intracellular distribution of glycolytic and other enzymes in rat-brain homogenates and mitochondrial preparations. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:610–618. doi: 10.1042/bj0770610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON M. K., WHITTAKER V. P. LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE AS A CYTOPLASMIC MARKER IN BRAIN. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:404–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0880404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R. Biochemical effects of the anticonvulsants trimethadione, ethosuximide and chlordiazepoxide in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1937–1946. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S., Zar M. A. The mechanism of acetylcholine release from parasympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):819–848. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H. Steady-state kinetics of catecholamine transport by chromaffin-granule "ghosts". Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):319–325. doi: 10.1042/bj1440319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel J. H., Wheatley A. H. Anaerobic oxidations. On ferricyanide as a reagent for the manometric investigation of dehydrogenase systems. Biochem J. 1938 May;32(5):936–943. doi: 10.1042/bj0320936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson M. D., Pincus J. H. The effect of diphenylhydantoin on sodium, potassium, magnesium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in microsomal fractions of rat and guinea pig brain and on whole homogenates of human brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Apr;17(4):573–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner G., Hasselbach W. Die Bedeutung der Sulfhydryl-Gruppen für den Catecholamin-Transport der Vesikel des Nebennierenmarkes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968 May 7;260(1):58–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner G. The membrane of catecholamine storage vesicles of adrenal medulla. Catecholamines fluxes and ATPase activity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;270(4):392–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Stimulation, by inhibition of (Na + -K + -Mg 2+ )-activated ATP-ase, of acetylcholine release in cortical slices from rat brain. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):95–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation and characterization of acetylcholine-containing particles from brain. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:694–706. doi: 10.1042/bj0720694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The application of subcellular fractionation techniques to the study of brain function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:39–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


