Abstract
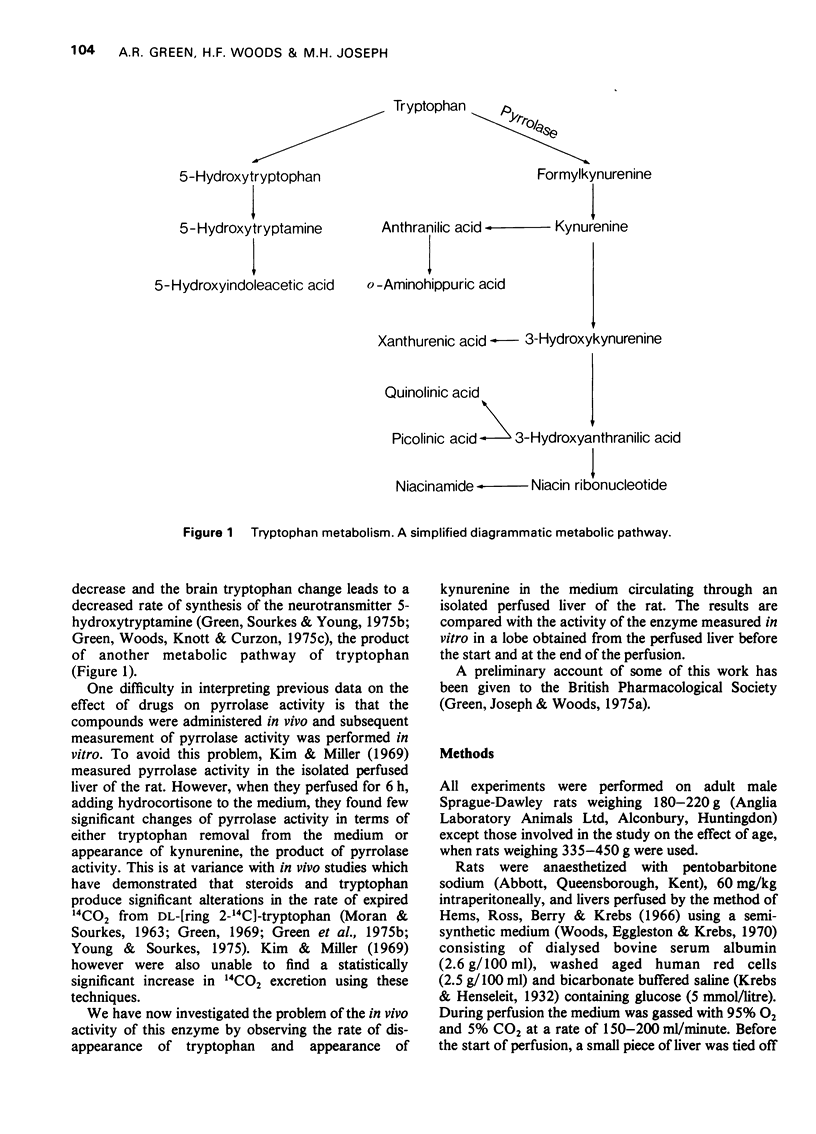
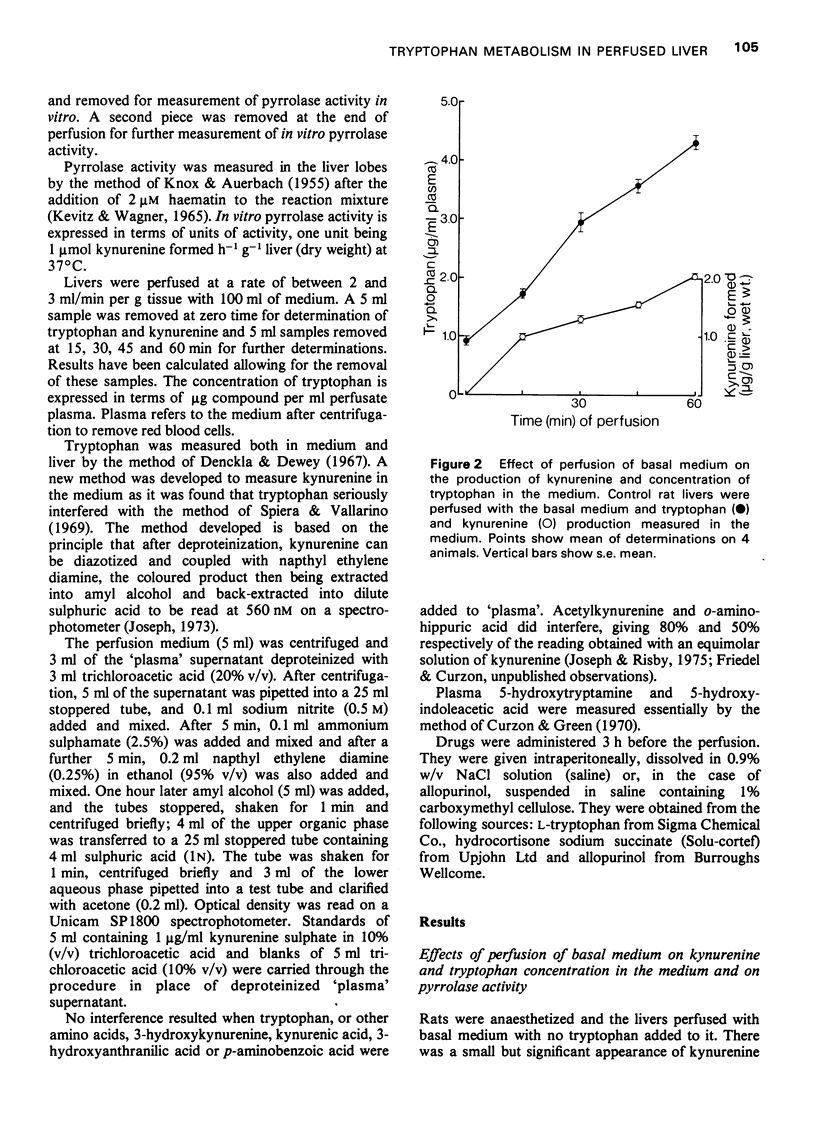
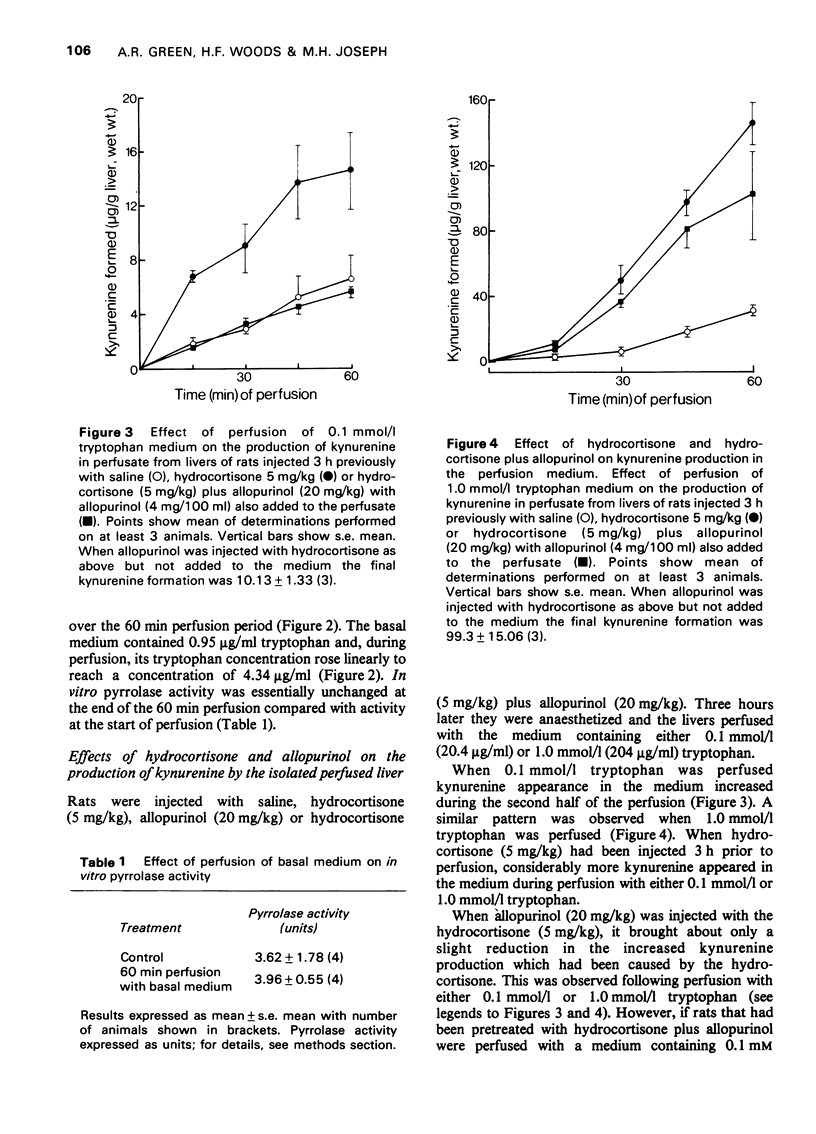
1 The effect of tryptophan concentration on the rate of kynurenine appearance and tryptophan disappearance in the medium perfused through the isolated liver of the rat has been investigated. The effect of pretreatment of the rat with hydrocortisone or allopurinol was also examined, together with the effects of these treatments on liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity measured in vitro at the beginning and end of perfusion. 2 Hydrocortisone (5 mg/kg) injection 3 h before perfusion resulted in a four-fold increase in kynurenine production by the liver during perfusion with a medium containing either 0.1 mmol/1 or 1.0 mmol/1 tryptophan. Injection of allopurinol (20 mg/kg) together with hydrocortisone and addition of allopurinol (4 mg/100 ml) to the medium abolished the hydrocortisone-induced rise of kynurenine in the 0.1 mmol/tryptophan medium but not the 1.0 mmol/1 tryptophan medium. 3 Injection of cycloheximide (30 mg/kg) with hydrocortisone (5 mg/kg) 3 h before perfusion inhibited the hydrocortisone-induced rise of kynurenine production and the increase in pyrrolase activity measured in vitro both before and at the end of perfusion with 1.0 mmol/1 tryptophan. This last result suggests that protein synthesis is involved not only in hydrocortisone induction of pyrrolase but also in substrate induction. 4 Kynurenine production in the 1.0 mmol/1 tryptophan medium was less in both saline- and hydrocortisone-treated older rats (335-450 g) compared to younger rats (180-220 g). In agreement with a previous study, pyrrolase activity in vitro was also lower in both saline- and hydrocortisone- treated older rats at the beginning of the perfusion although activity had risen equally in both young and older rats at the end of perfusion. 5 There was little correlation between the rate of tryptophan disappearance from the medium and the activity of tryptophan pyrrolase either as measured in vitro or as indicated by the rate of kynurenine production. 6 In general, the production of kynurenine in the medium at the end of the 60 min perfusion was indicative of in vitro pyrrolase activity at the start of the perfusion. 7 It is concluded that while in vitro pyrrolase assay does not give a quantitative index of kynurenne production, it does provide a qualitative index. Furthermore, if kynurenine production in the isolated perfused liver of the rat is indicative of in vivo pyrrolase activity, then hydrocortisone must induce pyrrolase activity in vivo.
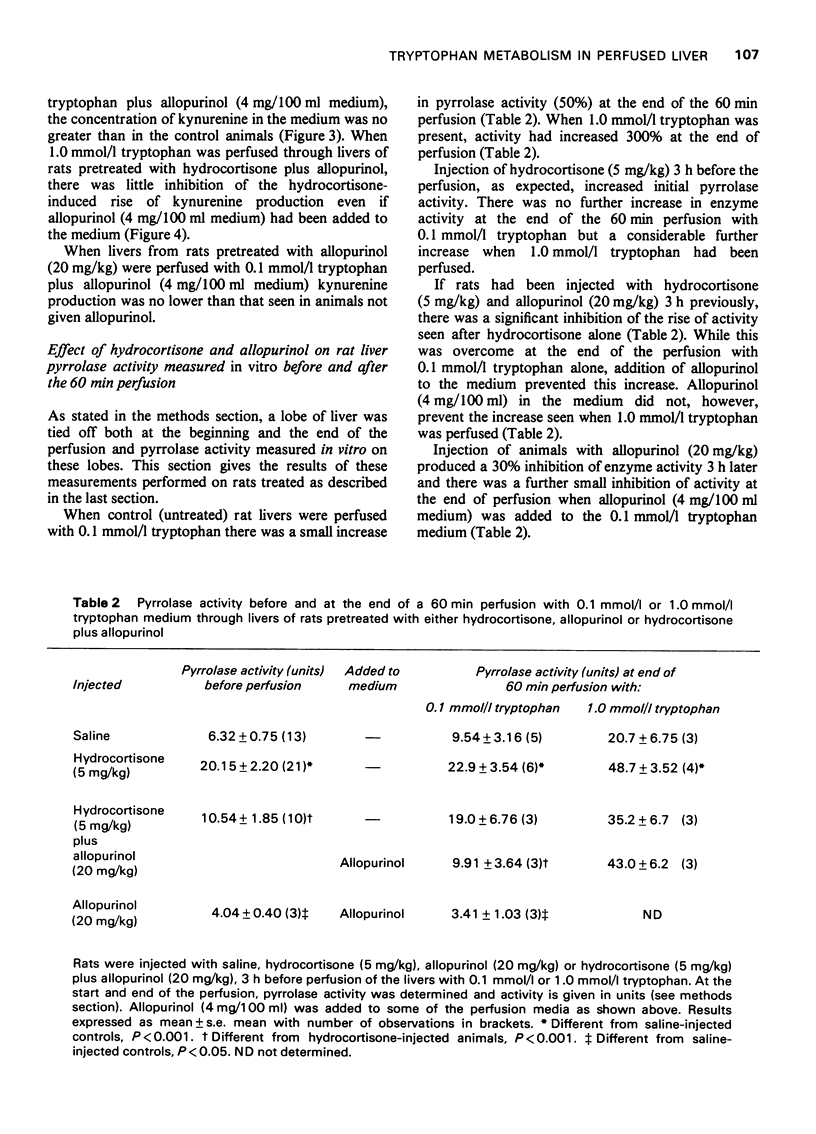
Full text
PDF
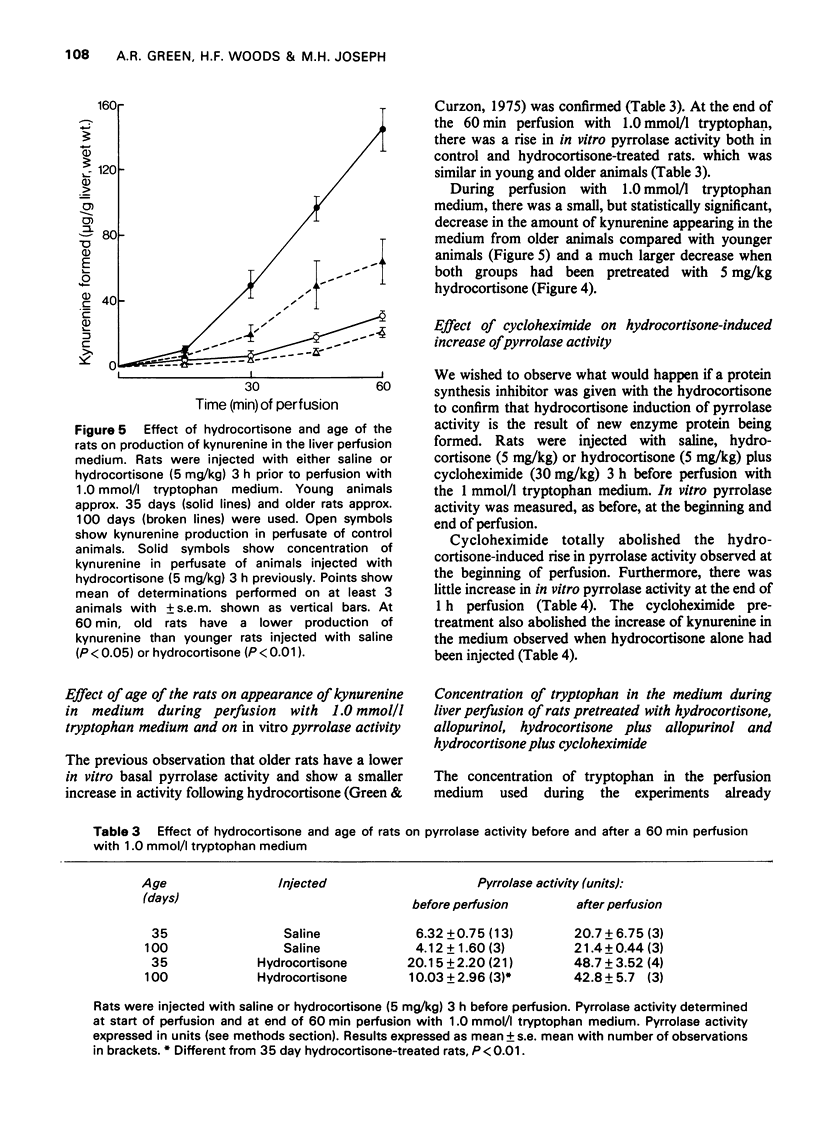
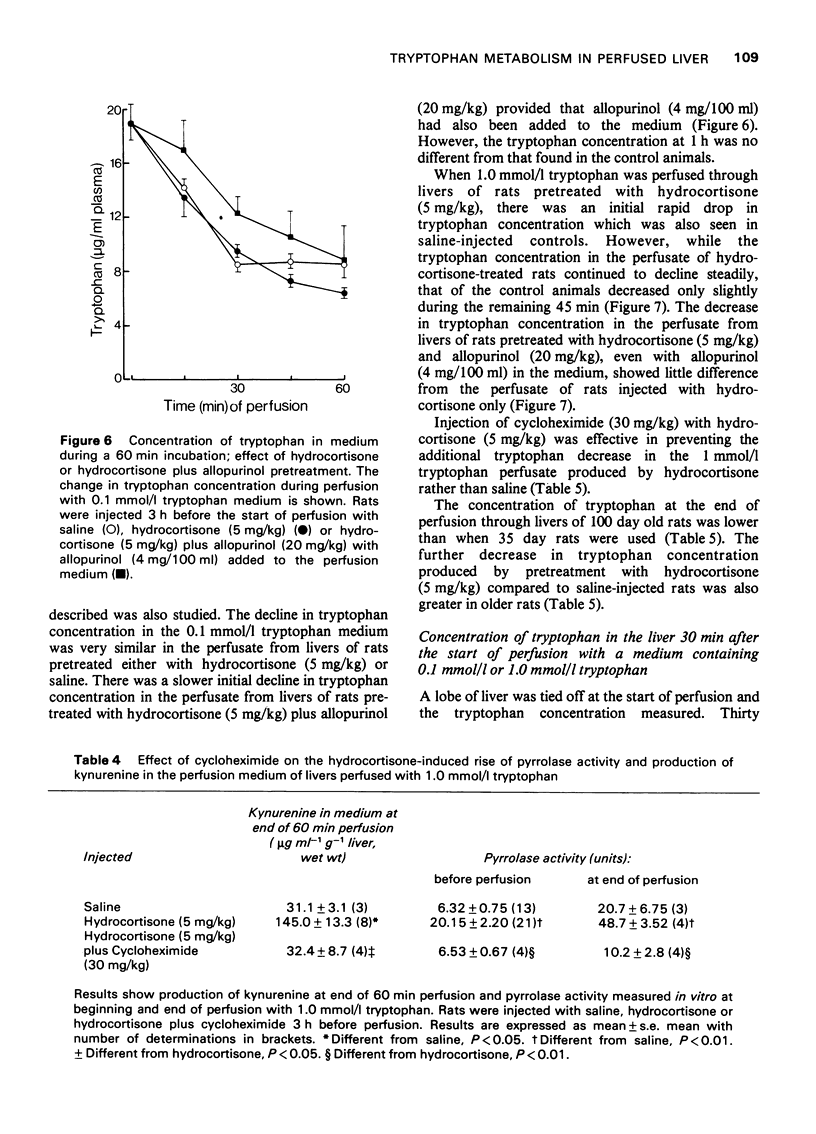
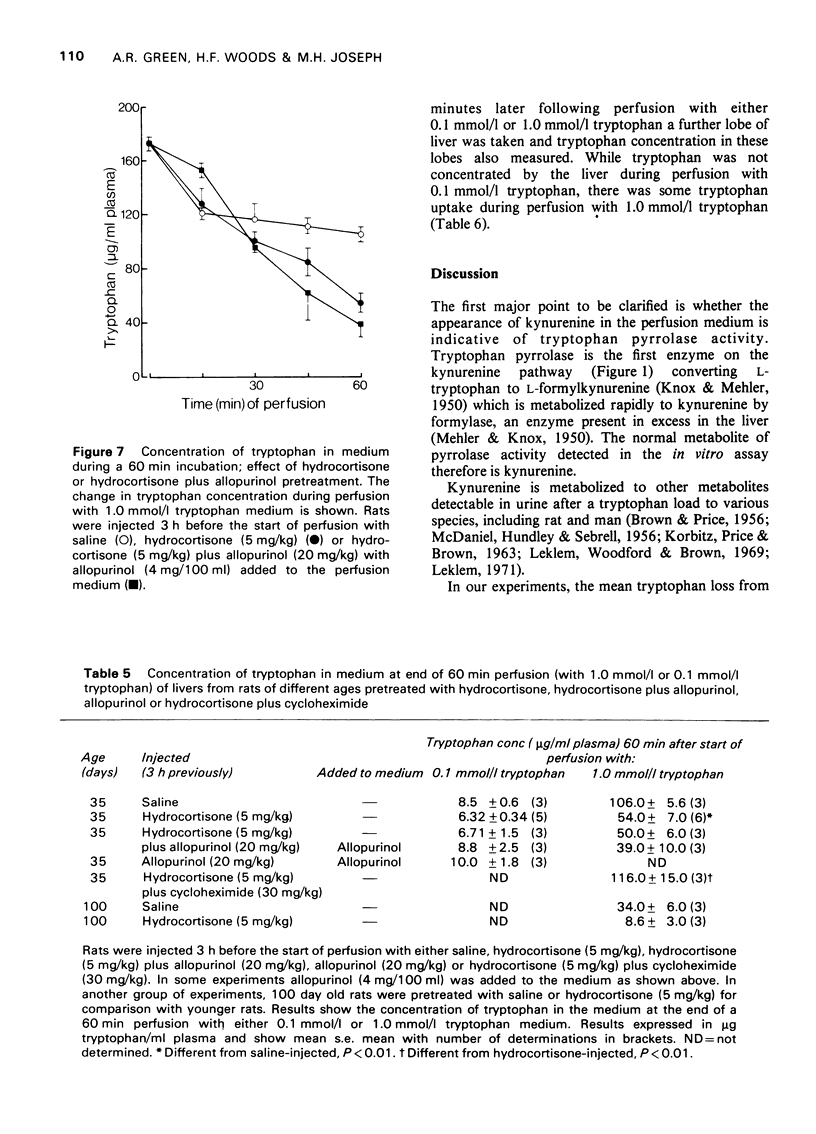




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN R. R., PRICE J. M. Quantitative studies on metabolites of tryptophan in the urine of the dog, cat, rat, and man. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):985–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Letter: Tryptophan plus a pyrrolase inhibitor for depression? Lancet. 1974 Nov 16;2(7890):1209–1210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90849-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The mechanism of inhibition of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by 4-hydroxypyrazolo(3,4-d)pyrimidine (Allopurinol). Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj1330585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becking G. C., Johnson W. J. Pyrazolo- and triazolopyrimidines as inhibitors of tryptophan pyrrolase. Life Sci. 1969 Aug 15;8(16):843–851. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becking G. C., Johnson W. J. The inhibition of tryptophan pyrrolase by allopurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Can J Biochem. 1967 Nov;45(11):1667–1672. doi: 10.1139/o67-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F. Activation of liver tryptophan oxygenase by adenosine 3',5'-phosphate and by other purine derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):893–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll W. W., Turner M. D., Haining J. L. Changes in tryptophan pyrrolase induction with age. J Gerontol. 1965 Oct;20(4):507–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Green A. R. Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):653–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando J. C., Joseph M. H., Curzon G. Letter: Tryptophan plus a pyrrolase inhibitor for depression? Lancet. 1975 Jan 18;1(7899):171–171. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91478-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. D., Camiener G. W., Bhuyan B. K. Nogalamycin effects in rat liver: inhibition of tryptophan pyrrolase induction and nucleic acid biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1966 Dec;26(12):2419–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Curzon G. Decrease of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain provoked by hydrocortisone and its prevention by allopurinol. Nature. 1968 Dec 14;220(5172):1095–1097. doi: 10.1038/2201095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Curzon G. Effects of hydrocortisone and immobilization on tryptophan metabolism in brain and liver of rats of different ages. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 15;24(6):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Joseph M. H., Woods H. F. Proceedings: Tryptophan metabolism by the isolated perfused rat liver. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):253P–254P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Sourkes T. L., Young S. N. Liver and brain tryptophan metabolism following hydrocortisone administration to rats and gerbils. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Woods H. F., Knott P. G., Curzon G. Letter: Factors influencing effect of hydrocortisone on rat brain tryptophan metabolism. Nature. 1975 May 8;255(5504):170–170. doi: 10.1038/255170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNDLEY J. M., MCDANIEL E. G., SEBRELL W. H. Tryptophan-niacin metabolism in alloxan diabetic rats. J Nutr. 1956 Jul 10;59(3):407–423. doi: 10.1093/jn/59.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haining J. L., Correll W. W. Tryptophan accumulation and tryptophan pyrrolase induction in rat liver as a function of age. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):266–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90411-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. W., Miller L. L. Influence of actinomycin D and puromycin on net synthesis of plasma albumin and fibrinogen by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):4817–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph M. H., Risby D. The determination of kynurenine in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Sep 1;63(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian J., Chytil F. Participation of xanthine oxidase in the activation of liver tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1161–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX W. E., AUERBACH V. H. The hormonal control of tryptophan peroxidase in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX W. E., MEHLER A. H. The conversion of tryptophan to kynurenine in liver. I. The coupled tryptophan peroxidase-oxidase system forming formylkynurenine. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):419–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX W. E. Two mechanisms which increase in vivo the liver tryptophan peroxidase activity: specific enzyme adaptation and stimulation of the pituitary adrenal system. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Oct;32(5):462–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORBITZ B. C., PRICE J. M., BROWN R. R. Quantitative studies on tryptophan metabolism in the pyridoxine-deficient rat. J Nutr. 1963 May;80:55–59. doi: 10.1093/jn/80.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. H., Miller L. L. The functional significance of changes in activity of the enzymes, tryptophan pyrrolase and tyrosine transaminase, after induction in intact rats and in the isolated, perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1410–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leklem J. E. Quantitative aspects of tryptophan metabolism in humans and other species: a review. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Jun;24(6):659–672. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.6.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leklem J. E., Woodford J., Brown R. R. Comparative tryptophan metabolism in cats and rats: differences in adaptation of tryptophan oxygenase and in vivo metabolism of tryptophan, kynurenine and hydroxykynurenine. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)92171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHLER A. H., KNOX W. E. The conversion of tryptophan to kynurenine in liver. II. The enzymatic hydrolysis of formylkynurenine. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORAN J. F., SOURKES T. L. INDUCTION OF TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE BY ALPHA-METHYLTRYPTOPHAN AND ITS METABOLIC SIGNIFICANCE IN VIVO. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3006–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng C. Y., Hagino Y., Swan P. B., Henderson L. M. Metabolism of tryptophan in isolated perfused rat liver. J Nutr. 1969 Dec;99(4):465–473. doi: 10.1093/jn/99.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimassek H., Gerok W. Control of the levels of free amino acids in plasma by the liver. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 31;343(4):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sweeney E. W., Berlin C. M. An analysis of the kinetics of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase induction: the significance of both enzyme synthesis and degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Mar 26;15(3):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiera H., Vallarino R. Serum kynurenine in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):856–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI106043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vályi-Nagy T., Daróczy A. Effects of primycin on the synthesis of tryptophan pyrrolase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jun;16(6):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods H. F., Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. The cause of hepatic accumulation of fructose 1-phosphate on fructose loading. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):501–510. doi: 10.1042/bj1190501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods H. F., Krebs H. A. Lactate production in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):129–139. doi: 10.1042/bj1250129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Sourkes T. L. Antidepressant action of tryptophan. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):897–898. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Sourkes T. L. Tryptophan catabolism by tryptophan pyrrolase in rat liver. The effect of tryptophan loads and changes in tryptophan pyrrolase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5009–5014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


