Abstract
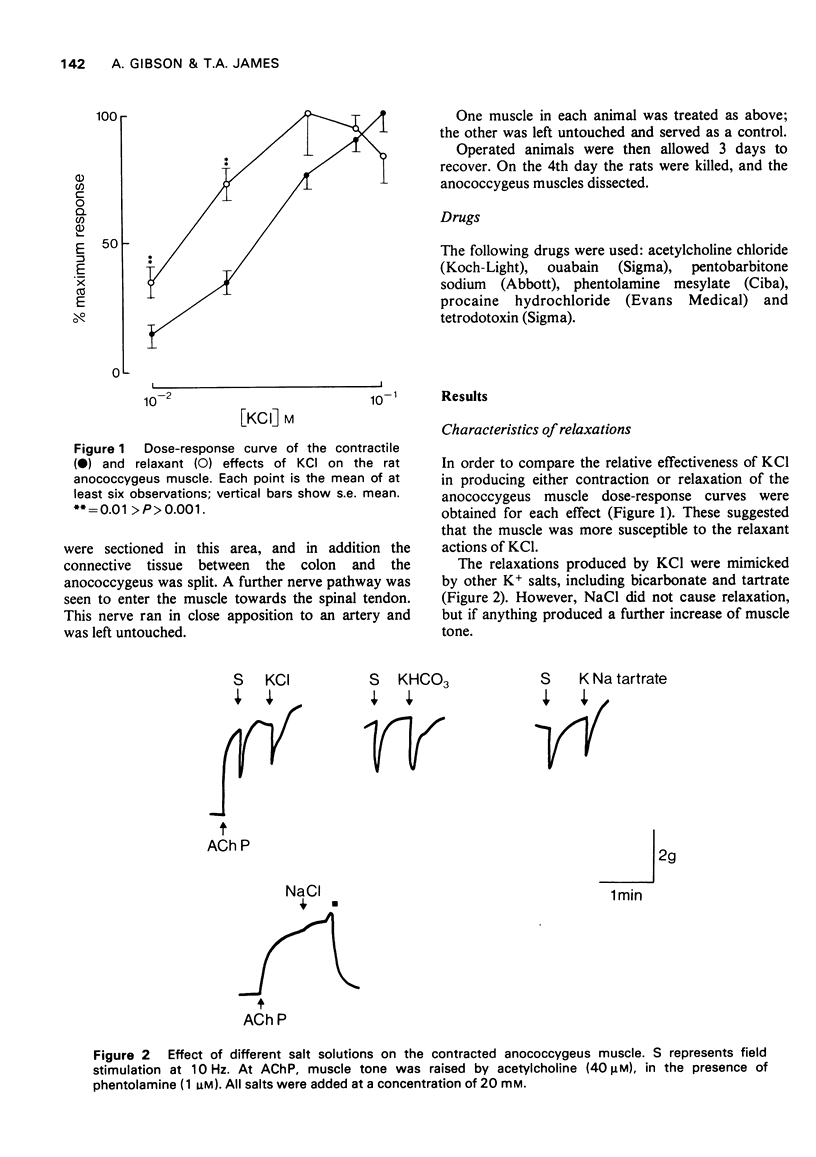
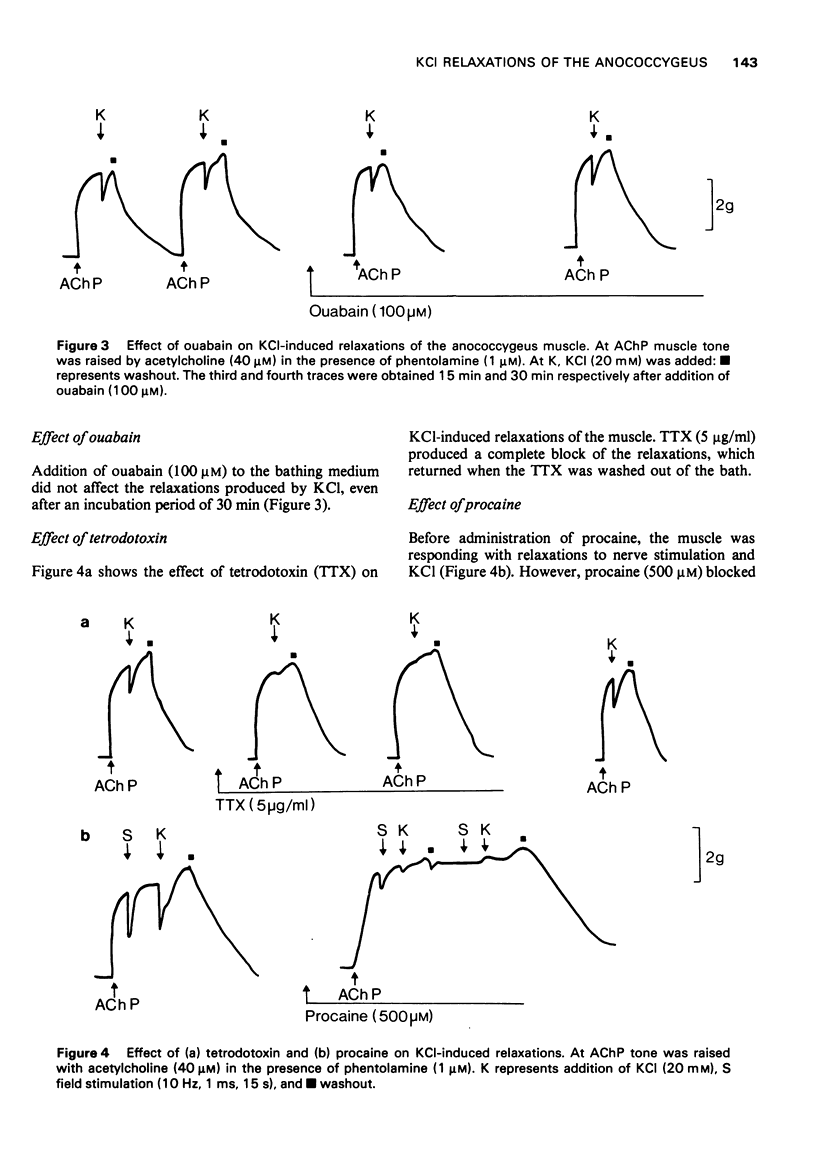
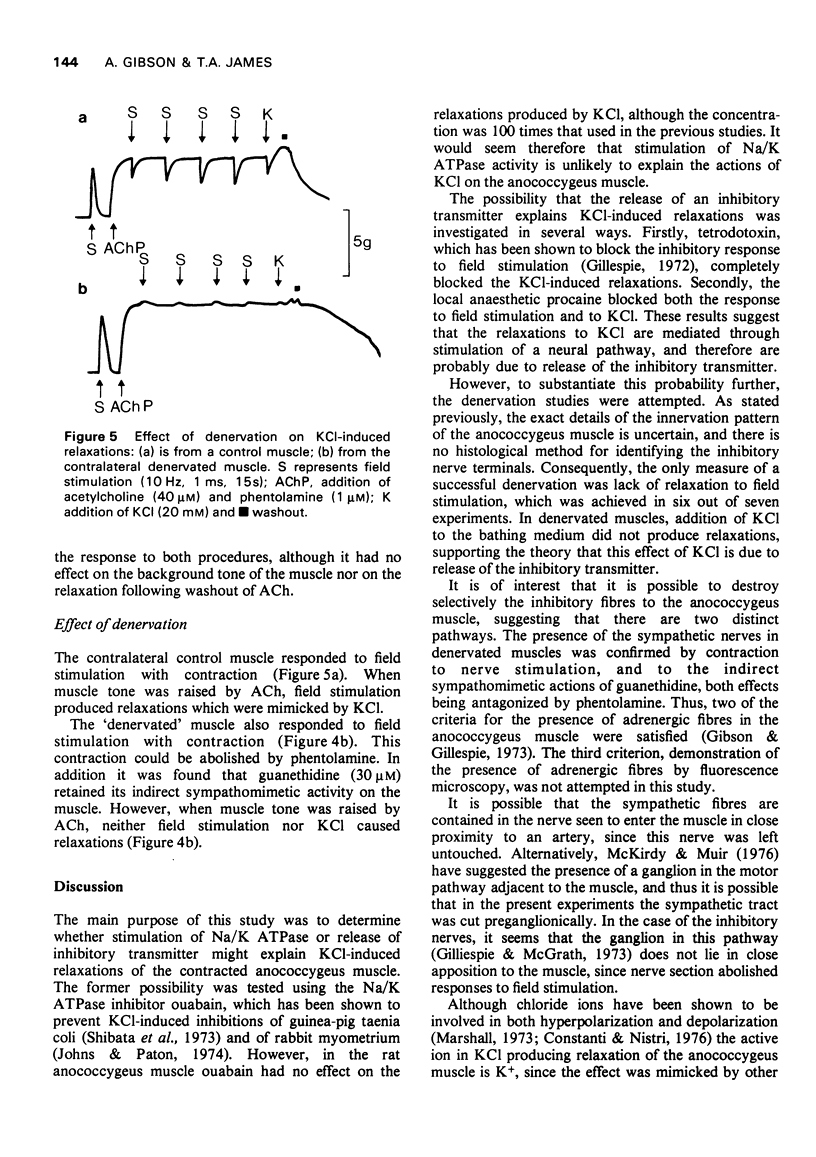
1. The nature of KCl-induced relaxations of the rat anococcygeus muscle was investigated. 2. The relaxations were mimicked by other K+ salts, but not by NaCl. 3. The muscle was more susceptible to the relaxant effects of KCl than the contractile effects. 4. Addition of ouabain (100 micron) had no effect on the relaxations. 5. The relaxations were abolished by tetrodotoxin (5 microgram/ml), procaine (500 micron), and by section of the inhibitory nerves. 6. The results suggest that KCl-induced relaxations are due to stimulation of the inhibitory nerves by K+.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constanti A., Nistri A. A comparative study of the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid and piperazine on the lobster muscle fibre and the frog spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):347–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Gillespie J. S. The effect of immunosympathectomy and of 6-hydroxydopamine on the responses of the rat anococcygeus to nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., James T. A. K+-induced relaxations of the rat anococcygeus muscle [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;58(2):305P–305P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Pollock D. The effects of drugs on the sensitivity of the rat anococcygeus muscle to agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;49(3):506–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb17261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The spinal origin of the motor and inhibitory innervation of the rat anococcygeus muscles. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):659–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S. The rat anococcygeus muscle and its response to nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;45(3):404–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns A., Paton D. M. Inhibitory effect of sodium pumping on spontaneous contractility of rabbit myometrium. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):786–790. doi: 10.1139/y74-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M. Effects of catecholamines on the smooth muscle of the female reproductive tract. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:19–32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKirdy H. C., Muir T. C. The response of the rat anococcygeus muscle to stimulation of the individual extrinsic nerves and its modification by drugs [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;57(3):434P–434P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


