Abstract
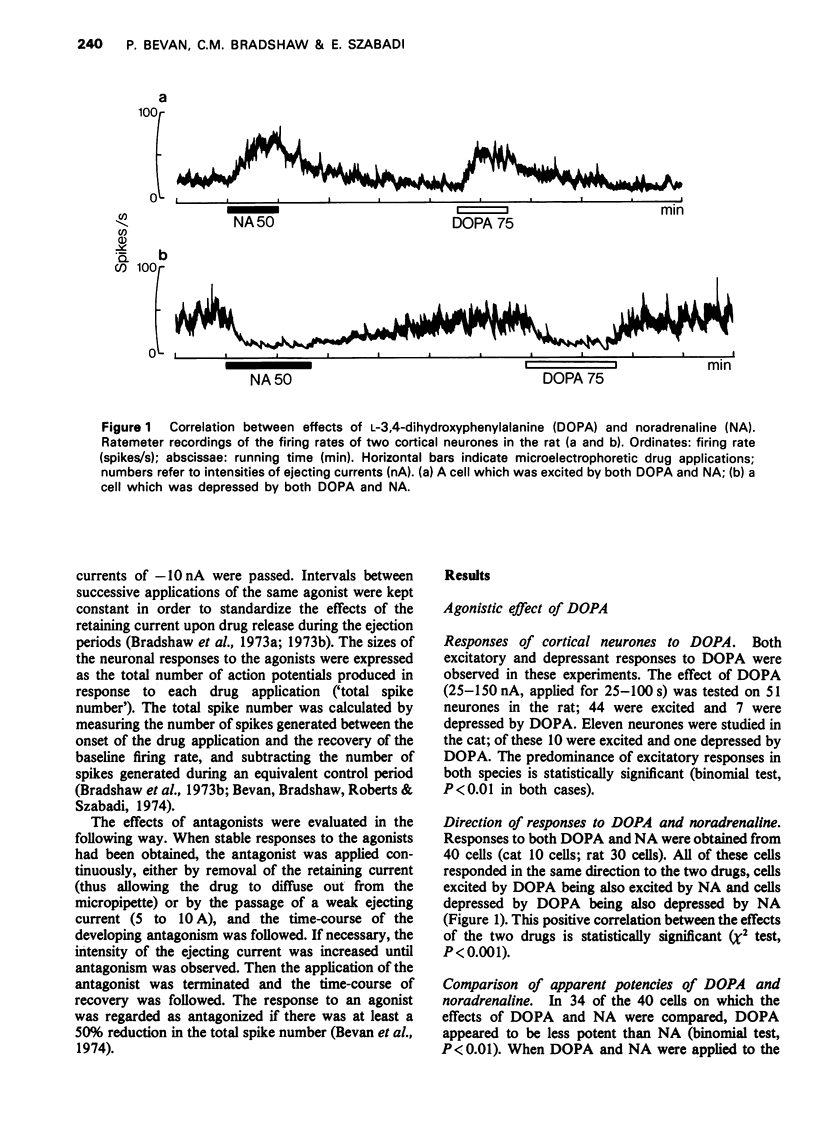
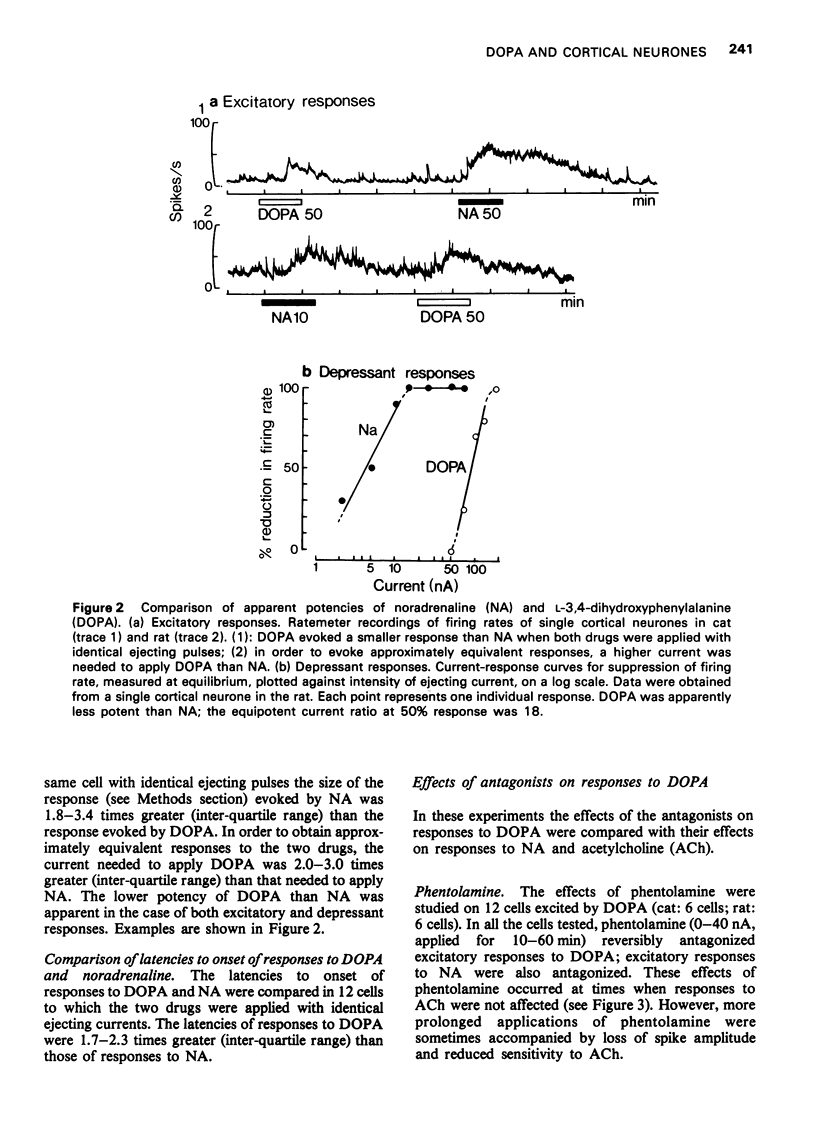
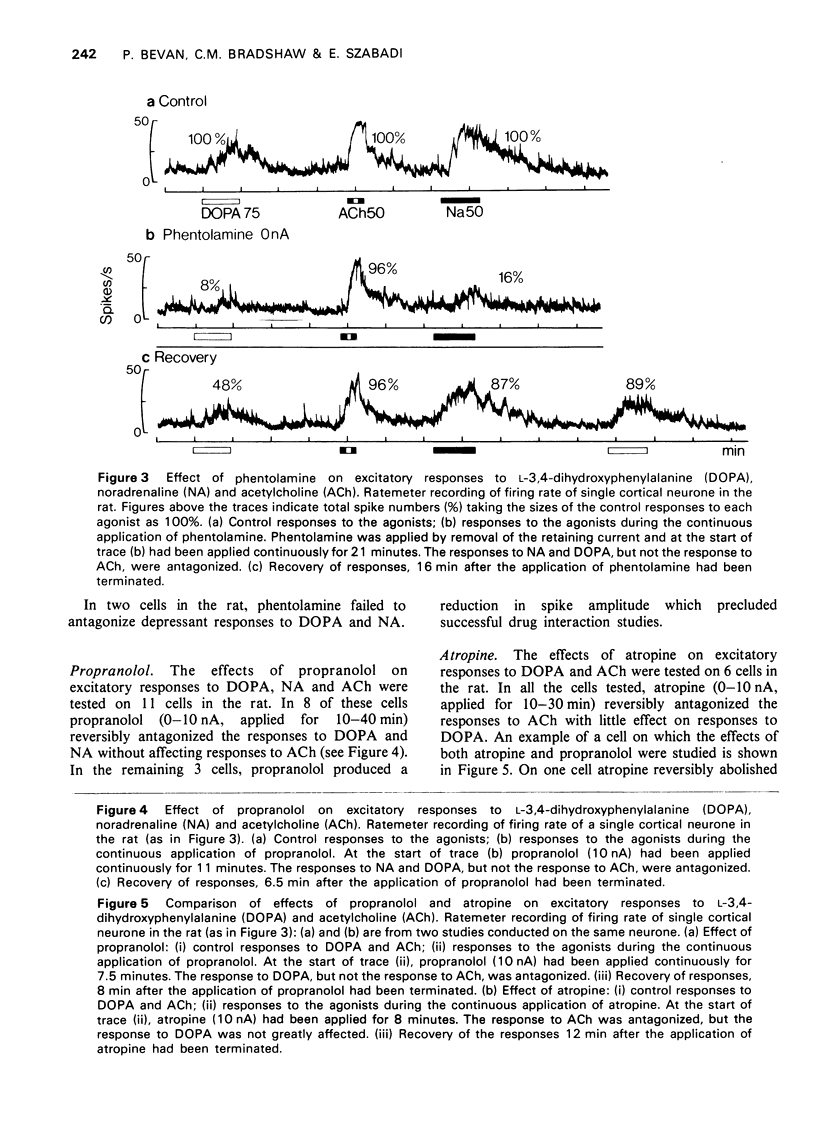
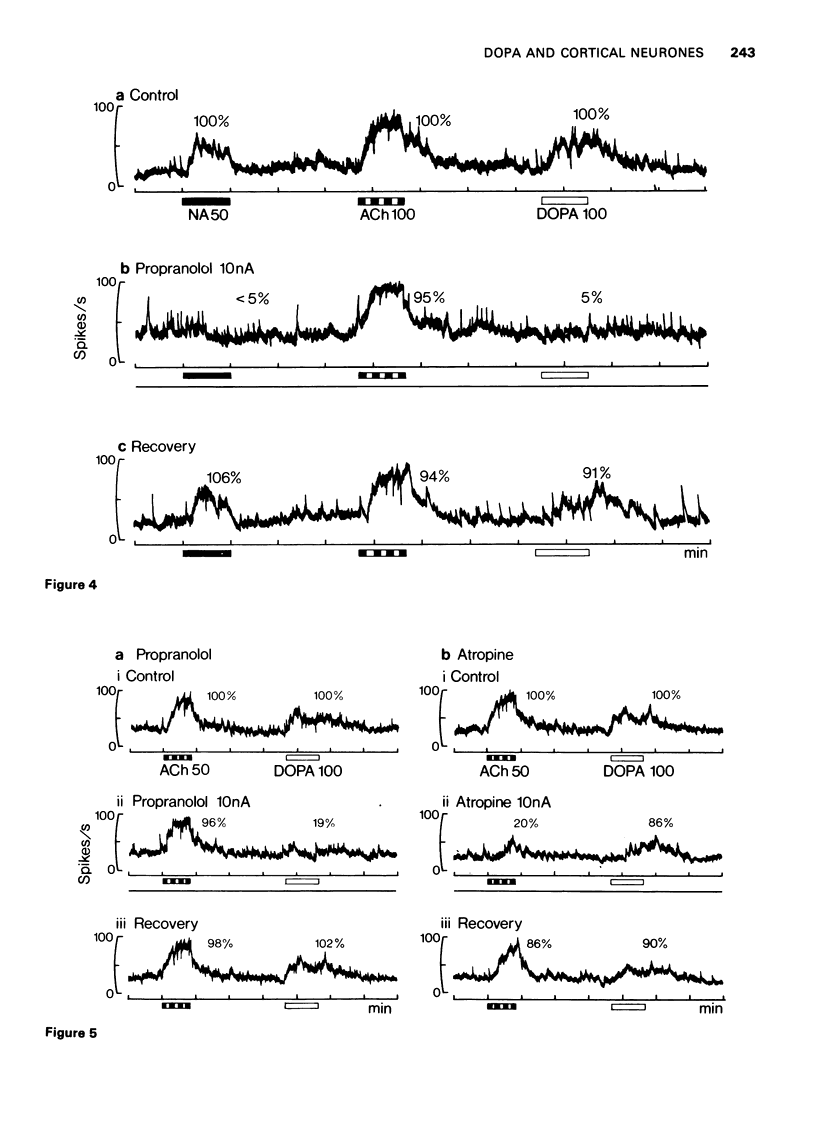
The technique of microelectrophoresis was used in order to compare the actions of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and noradrenaline on single neurones in the cerebral cortices of cats and rats. DOPA could both excite and depress cortical neurones. Cells excited by DOPA were also excited by noradrenaline and cells depressed by DOPA were also depressed by noradrenaline. In the case of both excitatory and depressant responses, DOPA appeared to be less potent than noradrenaline. Responses to DOPA and noradrenaline could be antagonized by phentolamine and propranolol. Responses to acetylcholine were not affected. Responses to acetylcholine, but not responses to DOPA, were antagonized by atropine. The results indicate that locally applied DOPA may mimic the actions of noradrenaline on cortical neurones. Possible mechanisms for these effects of DOPA are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Carlsson A., Häggendal J. Adrenergic mechanisms. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1969;9:119–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Engel J., Rubenson A. Central decarboxylation and uptake of L-DOPA. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;273(1):11–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00508077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Engel J., Rubenson A. Mode of action of L-DOPA on central noradrenaline mechanisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;273(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00508076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan P., Bradshaw C. M., Roberts M. H., Szabadi E. The effect of microelectrophoretically applied mescaline on cortical neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Nov;13(10-11):1033–1045. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan P., Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E. Effects of iprindole on responses of single cortical and caudate neurones to monoamines and acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):17–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan P., Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E. Proceedings: Comparison of the effects of DOPA and noradrenaline on single cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):301P–302P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Roberts M. H., Szabadi E. Kinetics of the release of noradrenaline from micropipettes: interaction between ejecting and retaining currents. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):667–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E., Roberts M. H. The reflection of ejecting and retaining currents in the time-course of neuronal responses to microelectrophoretically applied drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;25(7):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher L., Engel J., Fuxe K. L-dopa induced changes in central monoamine neurons after peripheral decarboxylase inhibition. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;22(4):313–316. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Ljungdahl A., Ogren S. O. Studies on the action of some psychoactive drugs on central noradrenaline neurons after inhibition of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 18;24(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. IV. DISTRIBUTION OF MONOAMINE NERVE TERMINALS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965:SUPPL 247–247:37+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluxe K., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Jonsson G., Lidbrink P., Ljungdahl A. The origin of the dopamine nerve terminals in limbic and frontal cortex. Evidence for meso-cortico dopamine neurons. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 27;82(2):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornykiewicz O. The mechanisms of action of L-dopa in Parkinson's disease. Life Sci. 1974 Oct 1;15(7):1249–1259. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Fuxe K., Johansson O. Dopamine nerve terminals in the rat limbic cortex: aspects of the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Sobieszek A., Straughan D. W. Noradrenaline sensitive cells in cat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Dec;8(6):549–566. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Actions of certain amines on cerebral cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:471–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabadi E., Bradshaw C. M. The role of physical and biological factors in determining the time course of neuronal responses. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jun;13(6):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Hirsch J. C., Tassin J. P., Blanc G., Glowinski J. Presence of dopaminergic terminals and absence of dopaminergic cell bodies in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 11;79(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90567-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



