Abstract
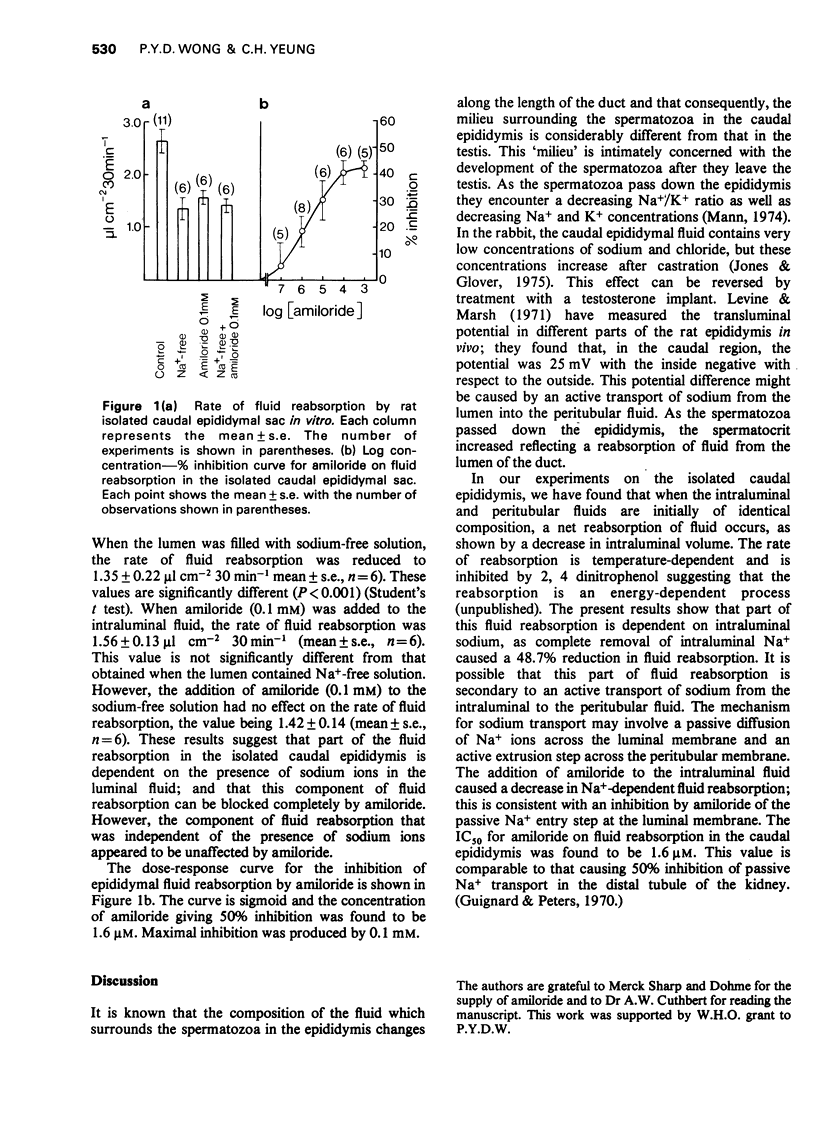
The rate of fluid reabsorption was studied in the rat isolated caudal epididymal sac in vitro. 2 Part of the fluid reabsorption was found to be dependent on intraluminal Na+. Amiloride (0.1 mM) completely inhibited this component of fluid reabsorption. 3 The log dose-inhibition curve to amiloride was sigmoid and the IC50 value was found to be 1.6 muM.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Guignard J. P., Peters G. Effects of triamterene and amiloride on urinary acidification and potassium excretion in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 May;10(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine N., Marsh D. J. Micropuncture studies of the electrochemical aspects of fluid and electrolyte transport in individual seminiferous tubules, the epididymis and the vas deferens in rats. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):557–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneyer L. H. Amiloride inhibition of ion transport in perfused excretory duct of rat submaxillary gland. Am J Physiol. 1970 Oct;219(4):1050–1055. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.4.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


