Abstract
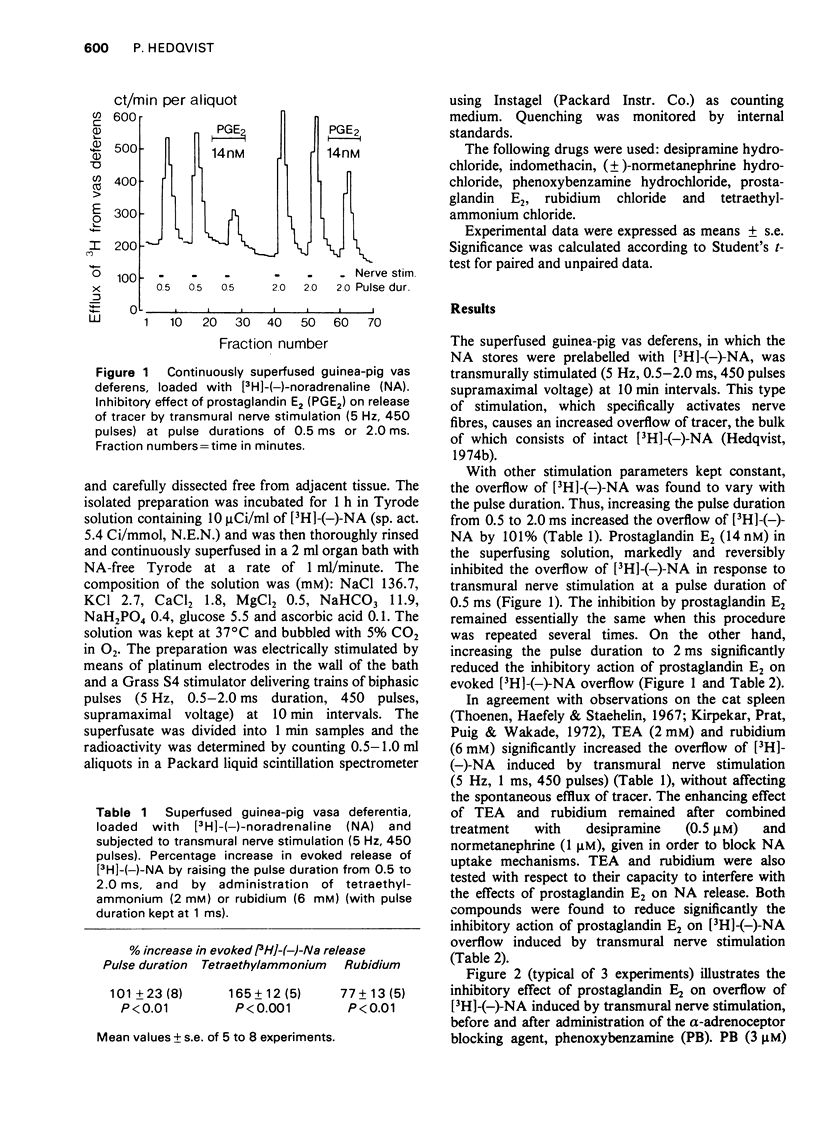
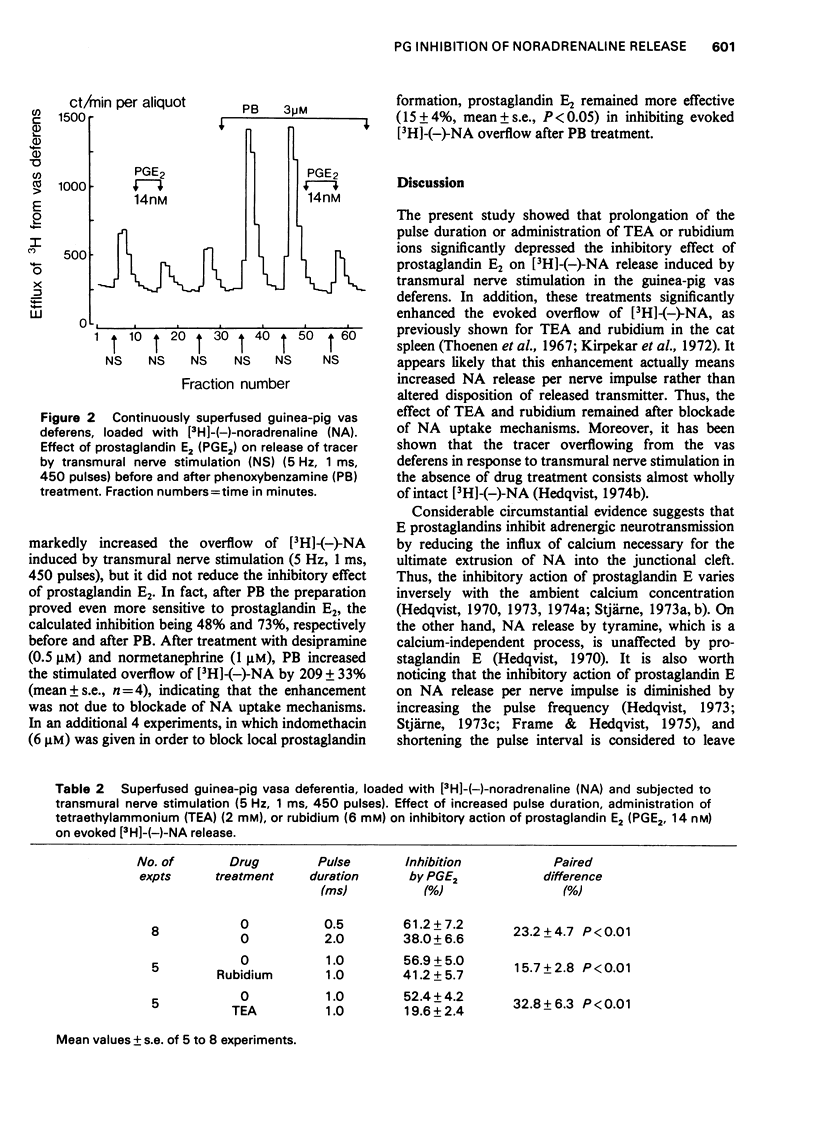
1 Guinea-pig vasa deferentia were continuously superfused after labelling the transmitter stores with [3H](-)-noradrenaline. Release of [3H]-(-)-noradrenaline was induced by transmural nerve stimulation. 2 Prostglandin E2 (14 nM) drastically reduced the release of [3H]-(-)-noradrenaline, while tetraethylammonium (2 mM), rubidium (6 mM), phenoxybenzamine (3 muM) each in the presence or absence of Uptake 1 or 2 blockade, and prolonged pulse duration (from 0.5 to 2.0 ms) all significantly increased the release of [3H]-(-)-noradrenaline per nerve impulse. 3 The inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E2 on evoked release of [3H]-(-)-noradrenaline was significantly reduced by tetraethylammonium, rubidium and prolonged pulse duration, whilst it was actually enhanced by phenoxybenzamine. This indicates that increased release of noradrenaline per nerve impulse does not per se counteract the inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E2. 4 It is concluded that tetraethylammonium, rubidium and prolonged pulse duration counteracted the inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E2 on T3H]-(-)-noradrenaline release by promoting calcium influx during the nerve action potential. The results are consistent with, and add more weight to the view that prostaglandins inhibit the release of noradrenaline by restriction of calcium availability.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm B., Efendic S., Löw H. Effect of lipolytic and antilipolytic agents on the uptake of 47 calcium into rat adipose tissue in vitro. Horm Metab Res. 1970 May;2(3):142–146. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Crovetti F. Interactions between prostaglandin E 1 and calcium at the level of the mitochondrial membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enero M. A., Langer S. Z., Rothlin R. P., Stefano F. J. Role of the -adrenoceptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;44(4):672–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Malamfors T. 3 H-noradrenaline release and mechanical response in the field stimulated mouse vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;371:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. H., Hedqvist P. Evidence for prostaglandin mediated prejunctional control of renal sympathetic transmitter release and vascular tone. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;54(2):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb06928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Interaction between prostaglandins and calcium ions on noradrenaline release from the stimulated guinea pig vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):153–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Prostaglandin action on noradrenaline release and mechanical responses in the stimulated guinea pig vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):86–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Prostaglandin action on transmitter release of adrenergic neuroeffector junctions. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1976;1:357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Studies on the effect of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on the sympathetic neuromuscular transmission in some animal tissues. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1970;345:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I. Mechanism of transmitter release. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:33–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K. Action of tetraethylammonium chloride on neuromuscular transmission in frogs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):213–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Puig M., Wakade A. R. Modification of the evoked release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by various ions and agents. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirtland S. J., Baum H. Prostaglandin E 1 may act as a "calcium ionophore". Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):47–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio236047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Biological significance of the prostaglandins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:139–187. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L. The role of calcium in neurohumoral and neurohormonal extrusion processes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1968 Dec;20(12):889–910. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1968.tb09672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Influence of extracellular noradrenaline on the stimulation-evoked secretion of noradrenaline from sympathetic nerves: evidence for an -receptor-mediated feed-back inhibition of noradrenaline release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;275(1):11–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00505064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Frequency dependence of dual negative feedback control of secretion of sympathetic neurotransmitter in guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;49(2):358–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E2 on noradrenaline secretion from sympathetic nerves as a function of external calcium. Prostaglandins. 1973 Jan;3(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Kinetics of secretion of sympathetic neurotransmitter as a function of external calcium: mechanism of inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Mar;87(3):428–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Haefely W., Staehelin H. Potentiation by tetraethylammonium of the response of the cat spleen to postganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Sep;157(3):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A. Studies on mechanisms controlling the secretion of neurotransmitters in the rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;365:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



