Abstract
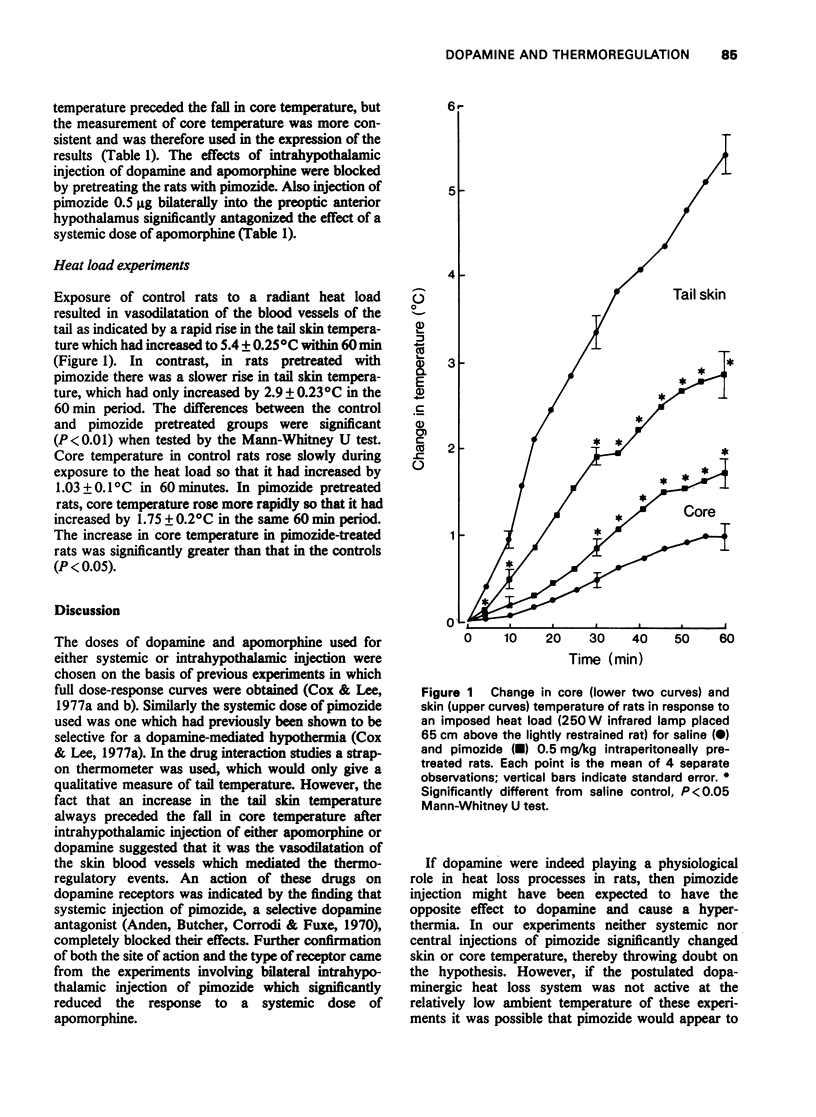
1 Core and tail skin temperature was measured in rats which had guide cannulae implanted into their brains to allow drug injections directly into the preoptic anterior hypothalamus. 2 Apomorphine and dopamine (10 microgram in 1 microliter) injected into the area of the preoptic anterior hypothalamus caused a fall in core temperature which was preceded by a rise in tail skin temperature. 3 The decrease in core temperature following central injection of either apomorphine or dopamine was significantly reduced by pretreating rats for 2 h with pikozide 0.5 mg/kg i.p.). 4 Bilateral intrahypothalamic injection of pimozide (0.5 microgram in 1 microliter) significantly reduced the hypothermic effect of systemic apomorphine (1.25 mg/kg i.p.). 5 Control rats placed 65 cm below a 250 W infrared lamp responded with vasodilation of tail skin blood vessels as indicated by an increase in tail skin temperature. Pimozide pretreatment (0.5 mg/kg i.p.) significantly reduced this response. 6 These results suggest that the preoptic anterior hypothalamus contains dopamine receptors which mediate hypothermia in rodents and raise the possibility that endogenous dopamine has a physiological role in thermoregulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Butcher S. G., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Ungerstedt U. Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970;11(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain R. T., Handley S. L. Temperature changes produced by the injection of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine into the cerebral ventricles of the conscious mouse. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):805–813. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruinvels J. Effect of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine on body temperature in the rat after intracisternal administration. Neuropharmacology. 1970 May;9(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B., Lee T. F. Location of receptors mediating hypothermia after injection of dopamine agonists in rats [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):467P–468P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MYERS R. D. A NEW CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE REGULATION BY AMINES IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS. Nature. 1963 Dec 28;200:1325–1325. doi: 10.1038/2001325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jell R. M. Responses of rostral hypothalamic neurones to peripheral temperature and to amines. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):295–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. S., Burks T. F. Dopamine receptors in the central thermoregulatory mechanism of the cat. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Feb;13(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruk Z. L. The effect of drugs acting on dopamine receptors on the body temperature of the rat. Life Sci I. 1972 Sep 15;11(18):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley E., Nistico G. Effects of catecholamines and adenosine derivatives given into the brain of fowls. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):619–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Gale C. C. Hypothermia-mediating dopamine receptors in the preoptic anterior hypothalamus of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;285(3):297–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00498998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rewerski W. J., Gumulka W. The effect of alpha-MT on hyperthermia induced by chlorpromazine. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Jul;8(4):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rewerski W. J., Jori A. Microinjection of chlorpromazine in different parts of rat brain. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 Jul;7(4):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


