Abstract
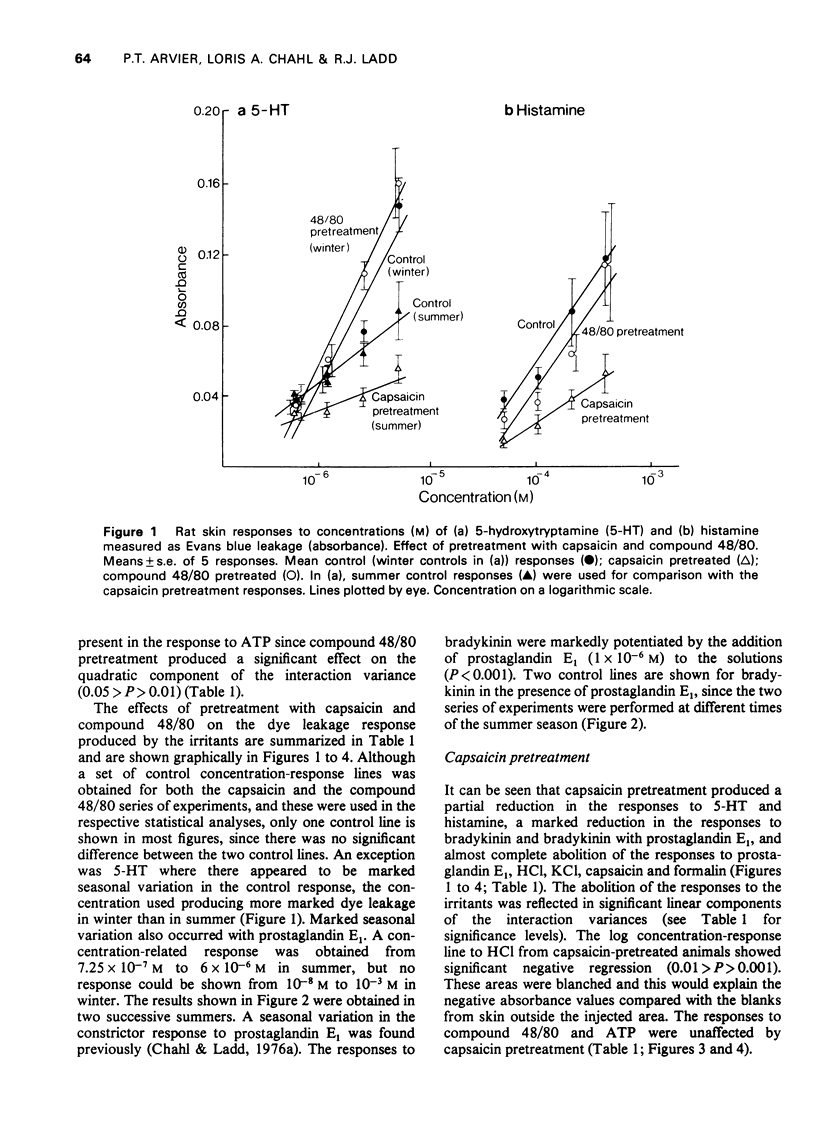
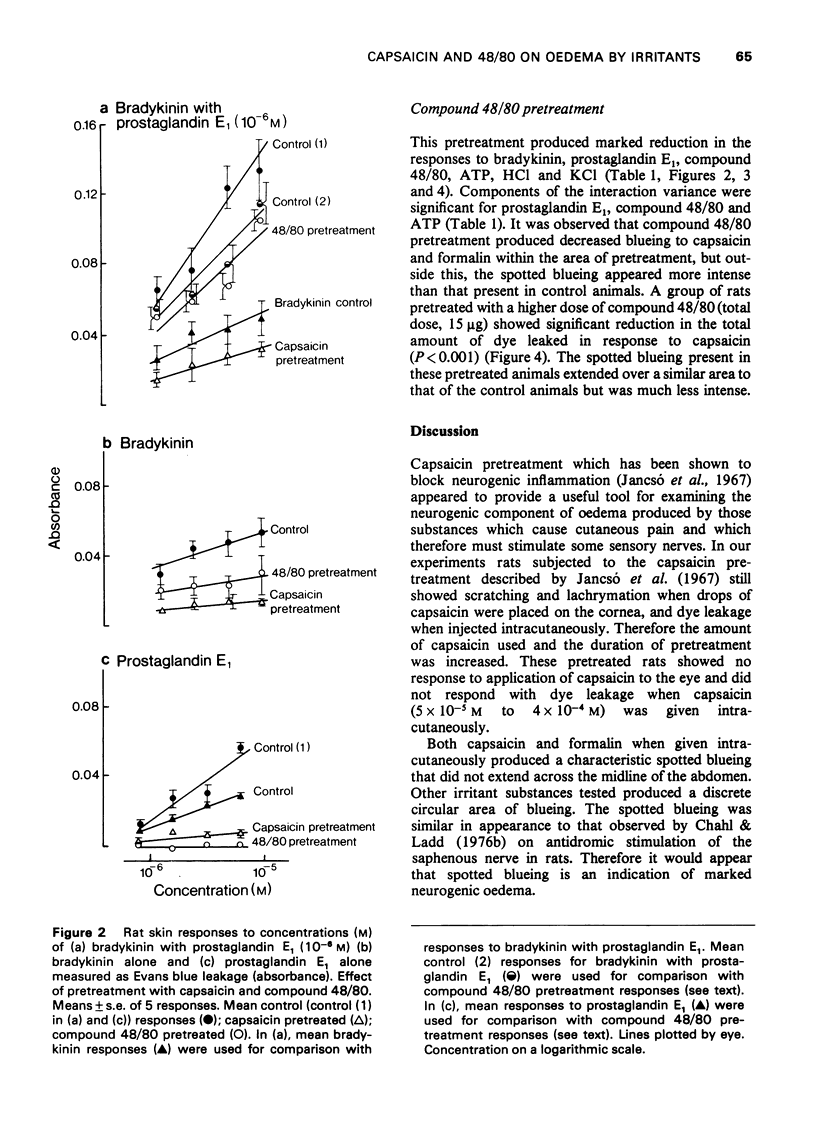
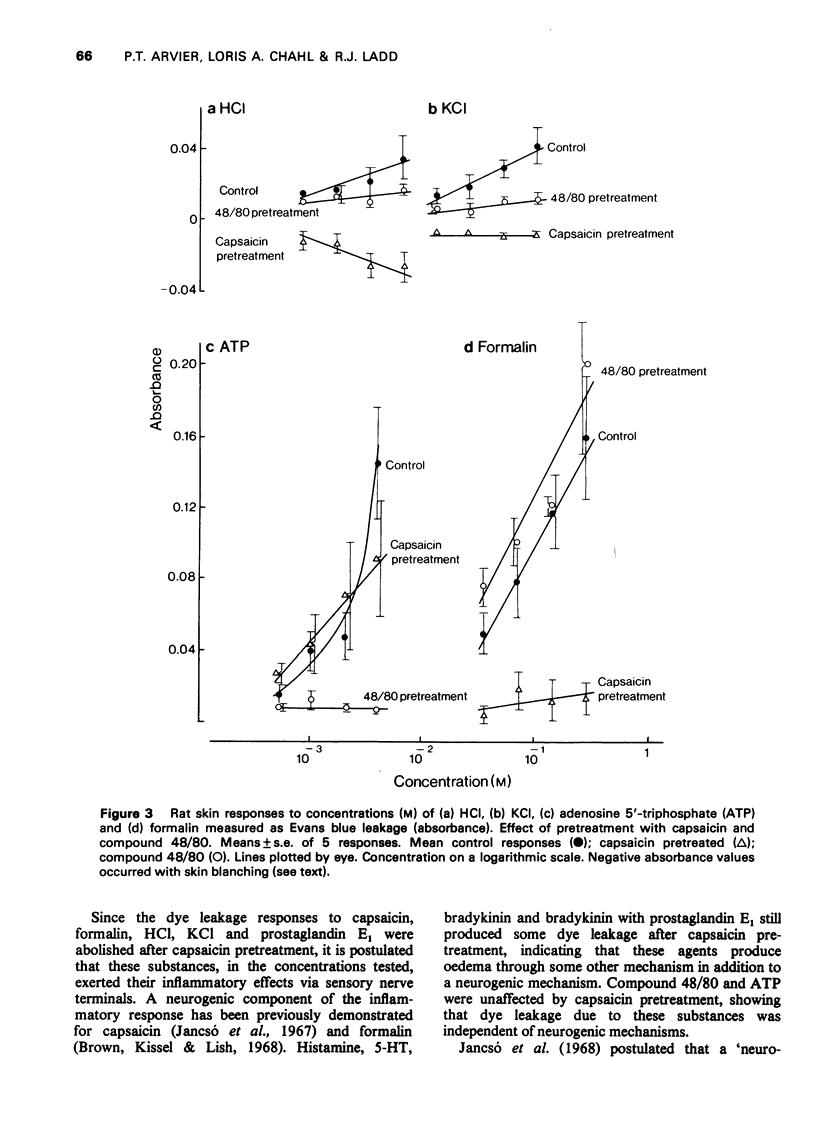
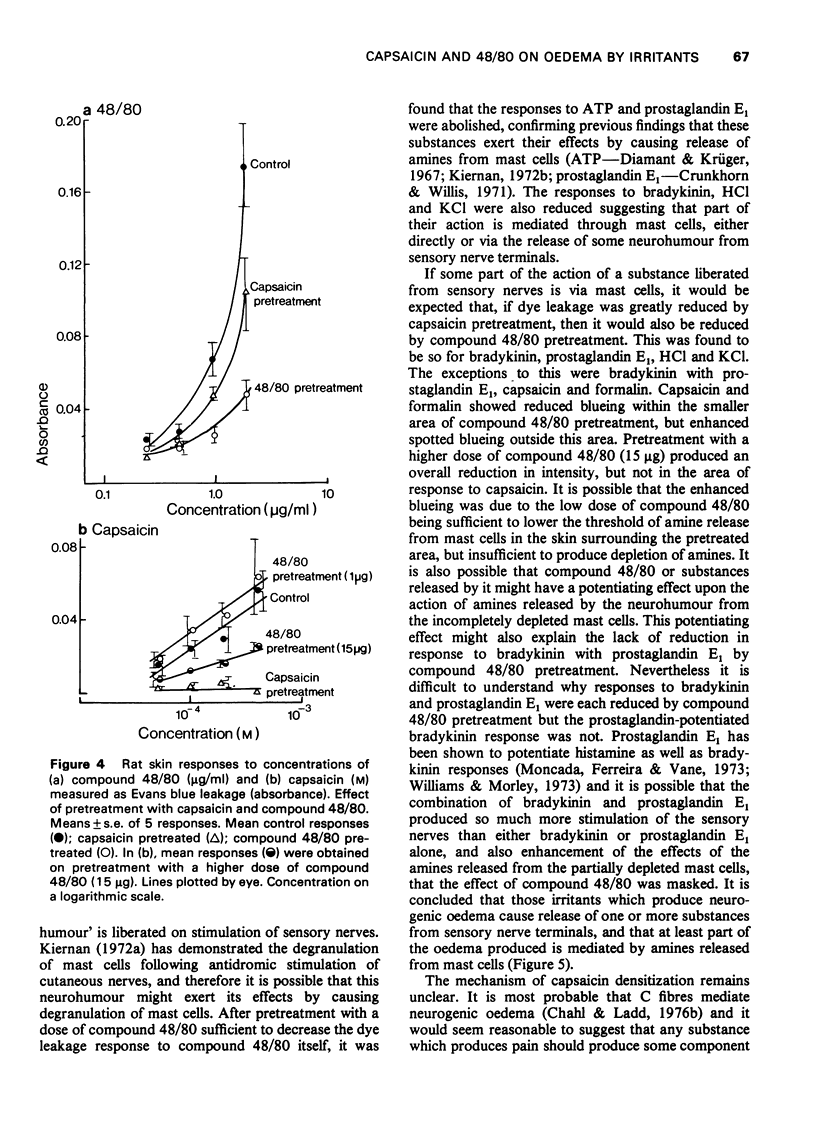
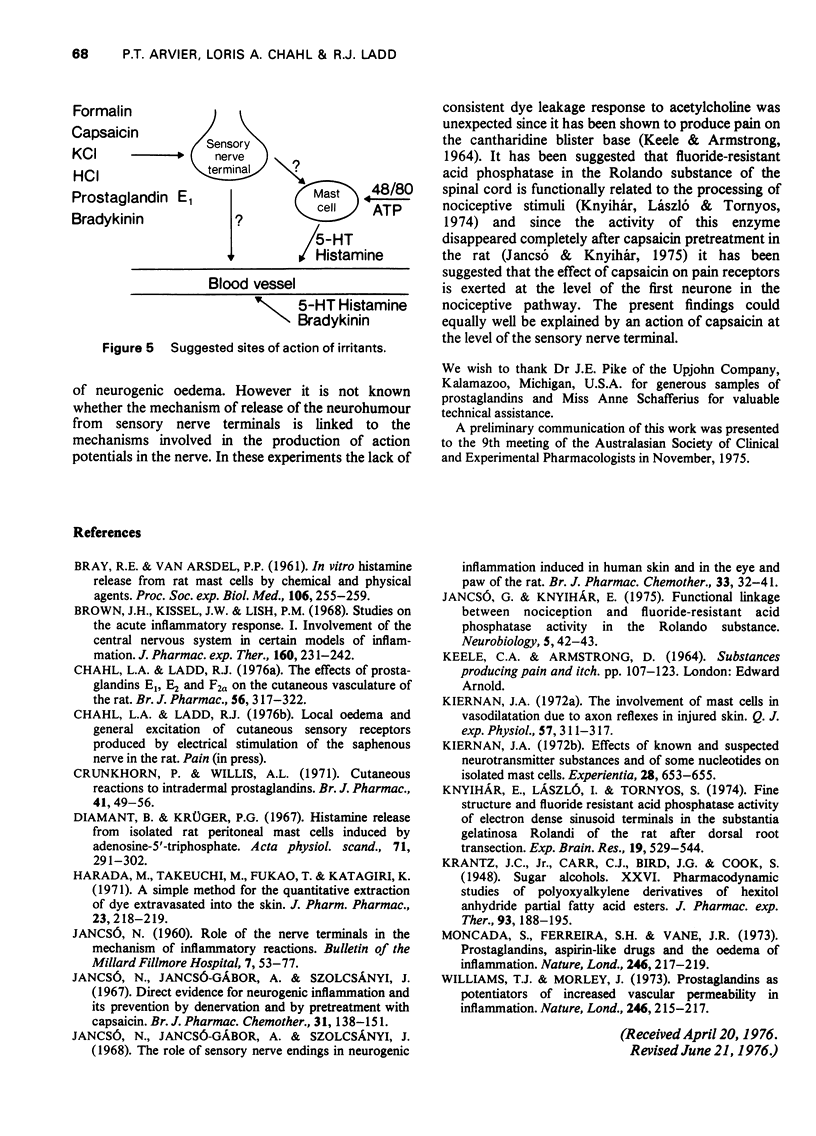
Concentration-related dye leakage produced by intracutaneous injections of irritants was measured in rats by an Evans blue technique. 2 In rats pretreated with a total dose of 50 mg capasaicin over 4 days, the response to capsaicin, formalin, HCl, KCl, prostaglandin E1, bradykinin and bradykinin with prostglandin E1 (10(-6) M) were greatly reduced, the responses to histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine were slightly reduced and those to adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and compound 48/80 were unaffected. 3 Pretreatment with intracutaneous injections of compound 48/80 (0.5 mug, 24 and 48 h previously) recuded the responses to ATP, compound 48/80, HCl, KCl, prostaglandin E1, and bradykinin but did not affect those to histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine or bradykinin with prostaglandin E1 (10(-6) M). 4 Responses to capsaicin and formalin produced spotted blueing extending over a large area and were suppressed by compound 48/80 in the smaller pretreated area only. Capsaicin responses were reduced with larger doses of compound 48/80 (total dose 15 mug). 5 It is concluded that the production of neurogenic oedema involves both sensory nerves and mast cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. H., Kissel J. W., Lish P. M. Studies on the acute inflammatory response. I. Involvement of the central nervous system in certain models of inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Mar;160(1):231–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A., Ladd R. J. The effects of prostaglandins E1, E2 and F2alpha on the cutaneous vasculature of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunkhorn P., Willis A. L. Cutaneous reactions to intradermal prostaglandins. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;41(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb09934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant B., Krüger P. G. Histamine release from isolated rat peritoneal mast cells induced by adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Dec;71(4):291–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Takeuchi M., Fukao T., Katagiri K. A simple method for the quantitative extraction of dye extravasated into the skin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;23(3):218–219. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó G., Knyihár E. Functional linkage between nociception and fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase activity in the Rolando substance. Neurobiology. 1975 Mar;5(1):42–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó N., Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):138–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó N., Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. The role of sensory nerve endings in neurogenic inflammation induced in human skin and in the eye and paw of the rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 May;33(1):32–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. Effects of known and suspected neurotransmitter substances and of some nucleotides on isolated mast cells. Experientia. 1972 Jun 15;28(6):653–655. doi: 10.1007/BF01944958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. The involvement of mast cells in vasodilatation due to axon reflexes in injured skin. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Jul;57(3):311–317. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knyihár E., László I., Tornyos S. Fine structure and fluoride resistant acid phosphatase activity of electron dense sinusoid terminals in the substantia gelatinosa Rolandi of the rat after dorsal root transection. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Mar 29;19(5):529–544. doi: 10.1007/BF00236116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and the oedema of inflammation. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):217–219. doi: 10.1038/246217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Morley J. Prostaglandins as potentiators of increased vascular permeability in inflammation. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):215–217. doi: 10.1038/246215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


