Abstract
1 The effects of the ionophores, X-537A and A23187 on the noradrenaline output from peripheral adrenergic neurones of isolated vas deferens of the guinea-pig were investigated in the presence of various divalent cations.
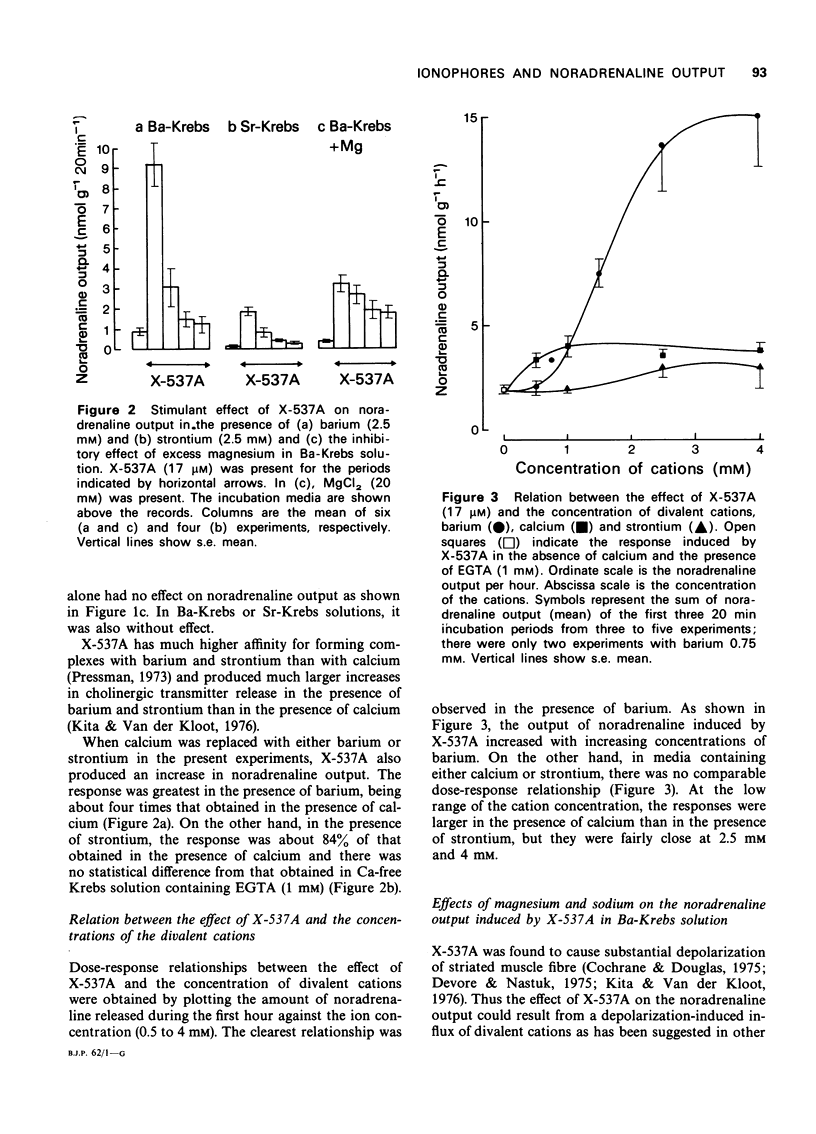
2 X-537A (17 μM) caused an increase in the noradrenaline output in the presence of barium, calcium and strontium. The effectiveness of the cations was Ba > Ca ≥ Sr.
3 In the absence of calcium and in the presence of ethyleneglycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′,-tetraacetic acid (EGTA, 1 mM), the response was reduced by about 50% of that obtained in the presence of calcium.
4 Calcium was the most effective cation in stimulating noradrenaline output when reintroduced after pretreatment with A23187 (191 μM). The response increased in an almost linear fashion with the concentration of calcium 1 mM to 10 mM.
5 Excess magnesium (20 mM) reduced the response induced by X-537A in the presence of barium. However, it was without effect on the response produced by reintroduction of calcium after pretreatment with A23187.
6 The response induced by X-537A in the presence of barium increased with an increase in the concentration of external sodium from 25 mM to 143 mM.
7 It is suggested that X-537A may cause an increase in the noradrenaline output by depolarization as well as by transferring cations as an ionophore. On the other hand, A23187 may produce an increase in the noradrenaline output, transferring calcium across the membrane as a specific calcium ionophore.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. An electrophysiological analysis of the effect of Ca ions on neuromuscular transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane D. E., Douglas W. W., Mouri T., Nakazato Y. Calcium and stimulus-secretion coupling in the adrenal medulla: contrasting stimulating effects of the ionophores X-537A and A23187 on catecholamine output. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohrane D. E., Douglas W. W. Depolarizing effects of the ionophores X-537A and A23187 and their relevance to secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;54(3):400–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Célis H., Estrada S., Montal M. Model translocators for divalent and monovalent ion transport in phospholipid membranes. I. The ion permeability induced in lipid bilayers by the antibiotic X-537A. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(2):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01870111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devore D. I., Nastuk W. L. Effects of 'calcium ionophore' X537A on frog skeletal muscle. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):644–646. doi: 10.1038/253644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eimerl S., Savion N., Heichal O., Selinger Z. Induction of enzyme secretion in rat pancreatic slices using the ionophore A-23187 and calcium. An experimental bypass of the hormone receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3991–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. G., Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C. A calcium ionophore stimulating the secretion of catecholamines from the cat adrenal. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):253–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W. The release of dopamine from synaptosomes from rat striatum by the ionophores X 537A and A 23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 14;375(1):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Miledi R. The effect of calcium-ionophores on acetylcholine release from Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Feb 11;196(1122):51–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Catecholamine equilibration gradients of isolated chromaffin vesicles induced by the ionophore X-537 A. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H., Van Der Kloot W. Effects of the ionophore X-537A on acetylcholine release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):177–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Eisenberg M. Antibiotics and membrane biology. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):335–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato Y., Douglas W. W. Vasopressin release from the isolated neurohypophysis induced by a calcium ionophore, X-537A. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):479–481. doi: 10.1038/249479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Currell G. A. The mechanism of calcium ionophore-induced secretion from the rat neurohypophysis. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):646–647. doi: 10.1038/253646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. Ultraviolet and fluorescent spectral properties of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 and its metal ion complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4007–4014. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. T., Hansen E. L., Thorn N. A. Calcium and stimulus-secretion coupling in the neurohypophysis. III. Ca2+ ionophore (A-23187)-induced release of vasopressin from isolated rat neurophypophyses. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Nov;77(3):443–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadt M., Haeusler G. Permeability of lipid bilayer membranes to biogenic amines and cations: changes induced by ionophores and correlations with biological activities. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(3-4):277–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01870117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Costa J. L., Moss J., Kopin I. J. Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurones by the calcium ionophores X 537A and A 23187. Life Sci. 1974 May 1;14(9):1705–1719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Wooten G. F., Axelrod J., Kopin I. J. On the mechanism of release of norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves induced by depolarizing agents and sympathomimetic drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;11(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Lee M. Pancreatic acinar cells: use of Ca++ ionophore to separate enzyme release from the earlier steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):542–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


