Abstract
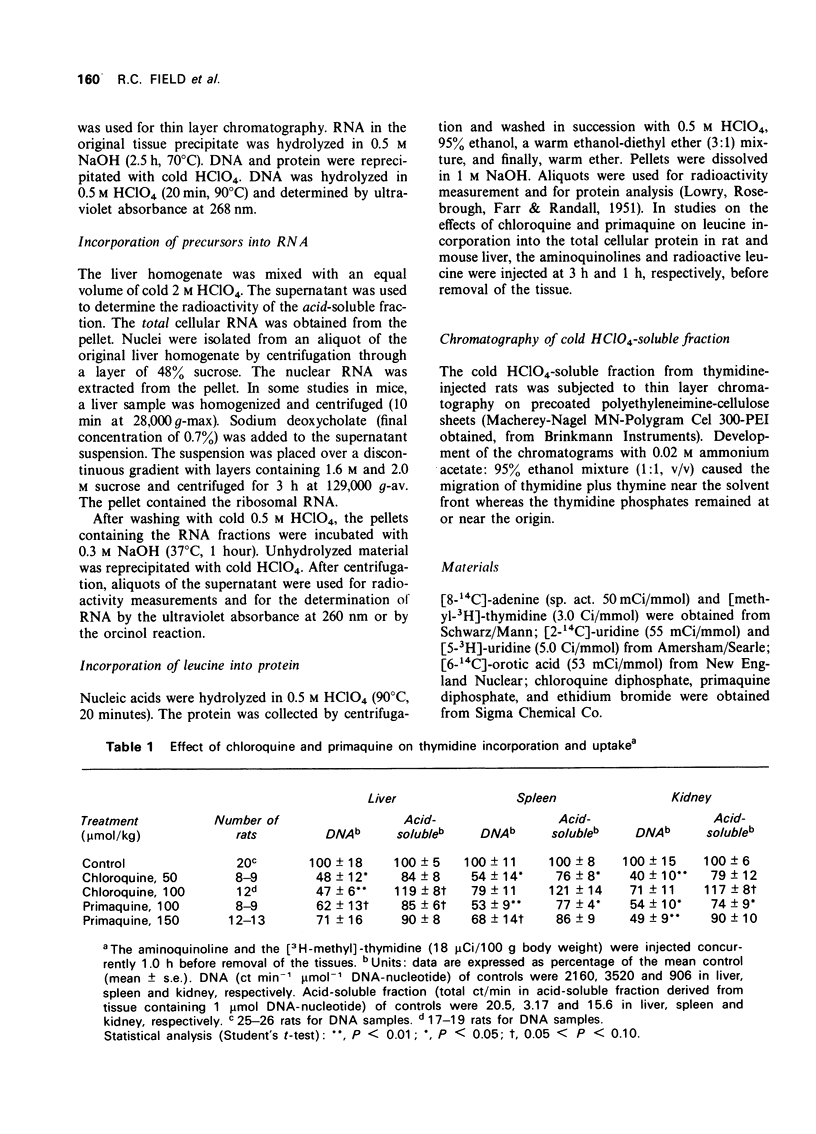
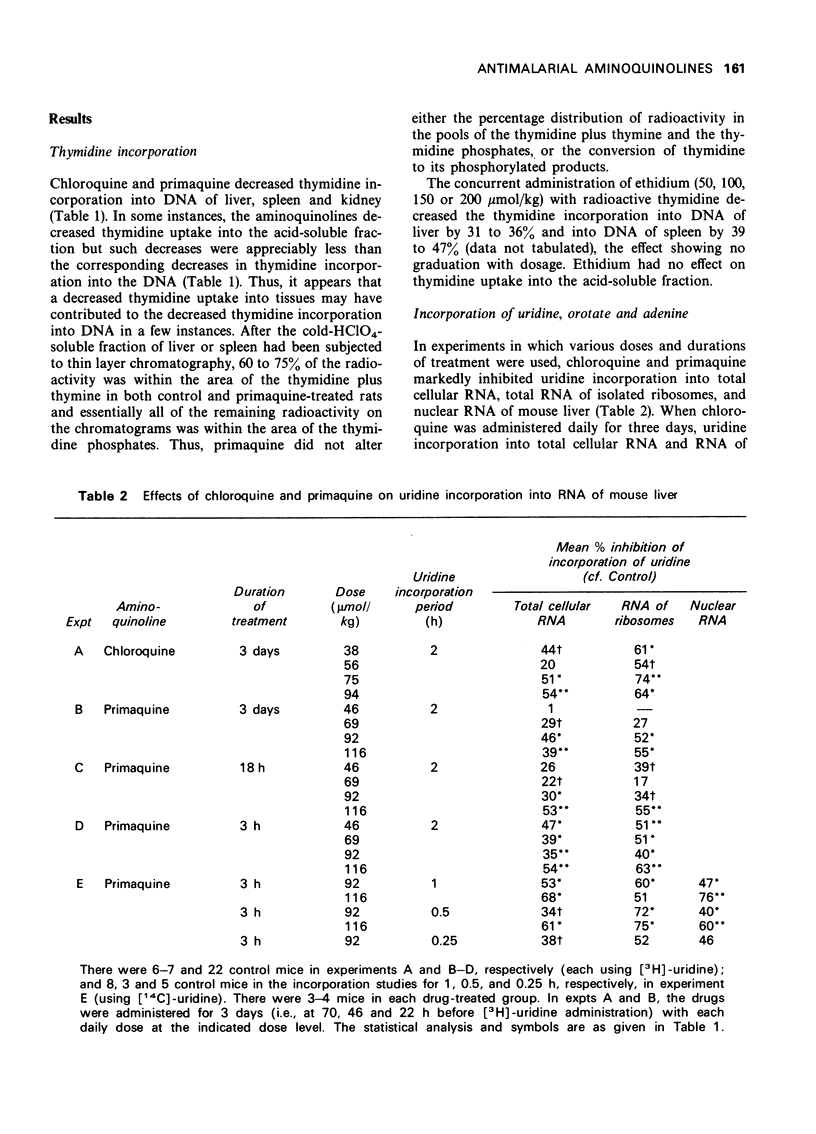
1 Chloroquine, primaquine and ethidium inhibitied thymidine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid of rat tissues when administered concurrently with the labelled precursor. 2 Chloroquine and primaquine inhibited the incorporation of uridine and adenine, but not orotate, into various ribonucleic acid fractions of liver of rats and mice. These drugs had no effect on leucine incorporation into hepatic protein in rats or mice. 3 Although chloroquine and primaquine are active against different stages in the life cycle of the malarial parasites, the two aminoquinolines exert similar effects in rodent tissues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudoin R. L., Aikawa M. Primaquine-induced changes in morphology of exoerythrocytic stages of malaria. Science. 1968 Jun 14;160(3833):1233–1234. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3833.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Jr, Huang R. C., Irvin J. L. Purification and characterization of a deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7275–7283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushnell D. E., Whittle E. D., Potter V. R. Differential utilization of pyrimidines for RNA synthesis in two classes of rat liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;179(2):497–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Yielding K. L. Inhibition of DNA and RNA polymerase reactions by chloroquine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):521–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. A., Chou S. C. The effects of antimalarial drugs on uptake and incorporation of macromolecular precursors by Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jan;180(1):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. A., Heu P., Chou S. C. The effects of antimalarial drugs on nucleic acid synthesis in vitro in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 May;9(3):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. L., Fukuyama K., Epstein J. H. Ultraviolet light, DNA repair and skin carcinogenesis in man. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1766–1771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABOUREL J. D. Effects of hydroxychloroquine on the growth of mammalian cells in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jul;141:122–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Ilan J. Aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases from cell-free extract of Plasmodium berghei. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):560–562. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuebbing D., Werner R. A model for compartmentation of de novo and salvage thymidine nucleotide pools in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3333–3336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landez J. H., Roskoski R., Jr, Coppoc G. L. Ethidium bromide and chloroquine inhibition of rat liver cell-free aminoacylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):276–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefler C. F., Lilja H. S., Holbrook D. J., Jr Inhibition of aminoacylation and polypeptide synthesis by chloroquine and primaquine in rat liver in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Mar 15;22(6):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magus R. D., Harrison J. D., King S. W. Aminoquinoline antimalarials--paradoxical regulation of hepatic tryptophan oxygenase and tyrosine aminotransferase by primaquine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;20(2):486–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. R., Simpson M. V. DNA biosynthesis in mitochondria. Differential inhibition of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA polymerases by the mutagenic dyes ethidium bromide and acriflavin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 27;34(2):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90637-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. R., Andrew L. V., Whichard L. P., Holbrook D. J., Jr The binding of antimalarial aminoquinolines to nucleic acids and polynucleotides. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 May;6(3):240–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Márquez V. E., Cranston J. W., Ruddon R. W., Burckhalter J. H. Binding to deoxyribonucleic acid and inhibition of ribonucleic acid polymerase by analogs of chloroquine. J Med Chem. 1974 Aug;17(8):856–862. doi: 10.1021/jm00254a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Olenick J. G., Hahn F. E. Reactions of quinine, chloroquine, and quinacrine with DNA and their effects on the DNA and RNA polymerase reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1511–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Nucleotide pools of Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. II. Independent nucleotide pools for nucleic acid synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):241–248. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Barr C. F. Chloroquine and dihydroquinine. In vitro studies by their antimalarial effect upon Plasmodium knowlesi. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Dec;164(2):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr, Jaskunas S. R. Chloroquine and primaquine inhibition of rat liver cell-free polynucleotide-dependent polypeptide synthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Feb 1;21(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHELLENBERG K. A., COATNEY G. R. The influence of antimalarial drugs on nucleic acid synthesis in Plasmodium gallinaceum and Plasmodium berghei. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 May;6:143–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedwick W. D., Wang T. S., Korn D. Purification and properties of nuclear and cytoplasmic deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5026–5033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelton F. S., Pardini R. S., Heidker J. C., Folkers K. Inhibition of coenzyme Q systems by chloroquine and other antimalarials. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Sep 11;90(19):5334–5336. doi: 10.1021/ja01021a084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke K., Szustkiewicz C., Lantz C. H., Saxe L. H. Studies concerning the mechanism of action of antimalarial drugs. Inhibition of the incorporation of adenosine-8-3H into nucleic acids of Plasmodium berghei. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1417–1425. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington M. E., White L. A., Holbrook D. J., Jr Binding of antimalarial aminoquinolines to chromatin, reconstituted deoxyribonucleohistone and ribosomes from mammalian tissues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Feb 15;22(4):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichard L. P., Washington M. E., Holbrook D. J., Jr The inhibition in vitro of bacterial DNA polymerases and RNA polymerase by antimalarial 8-aminoquinolines and by chloroquine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):52–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


