Abstract
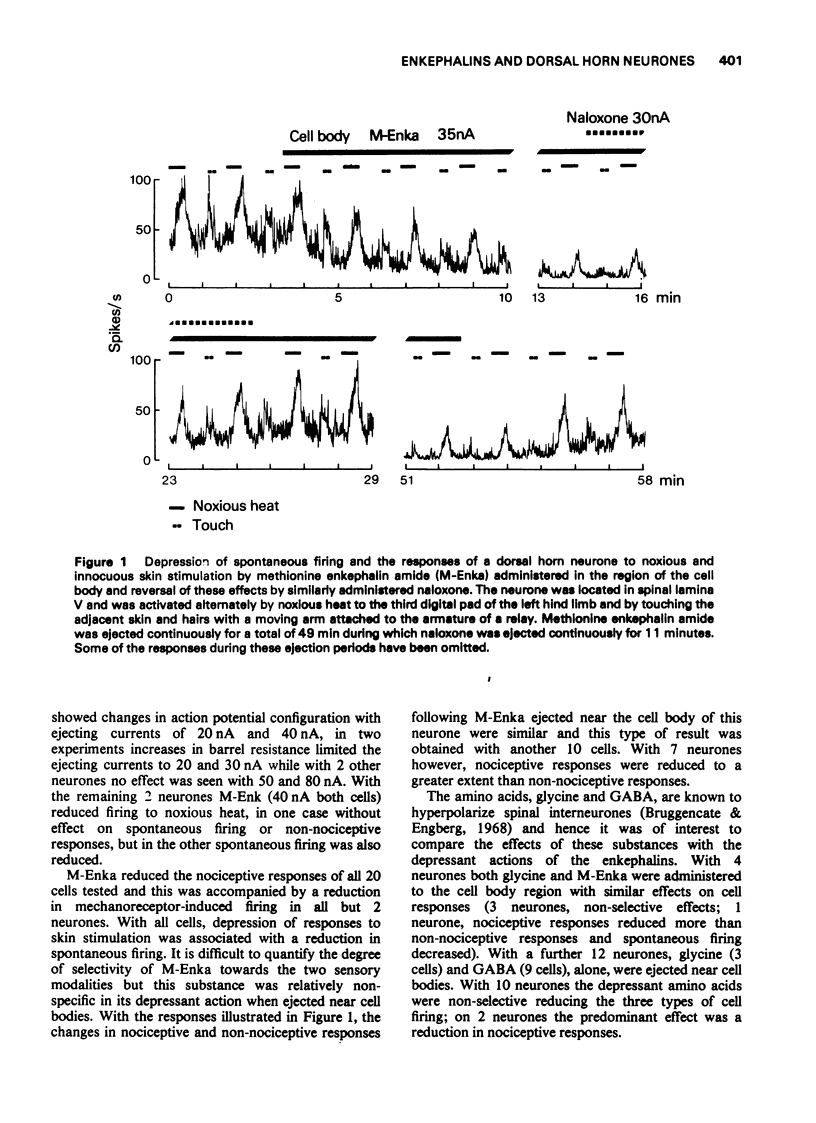
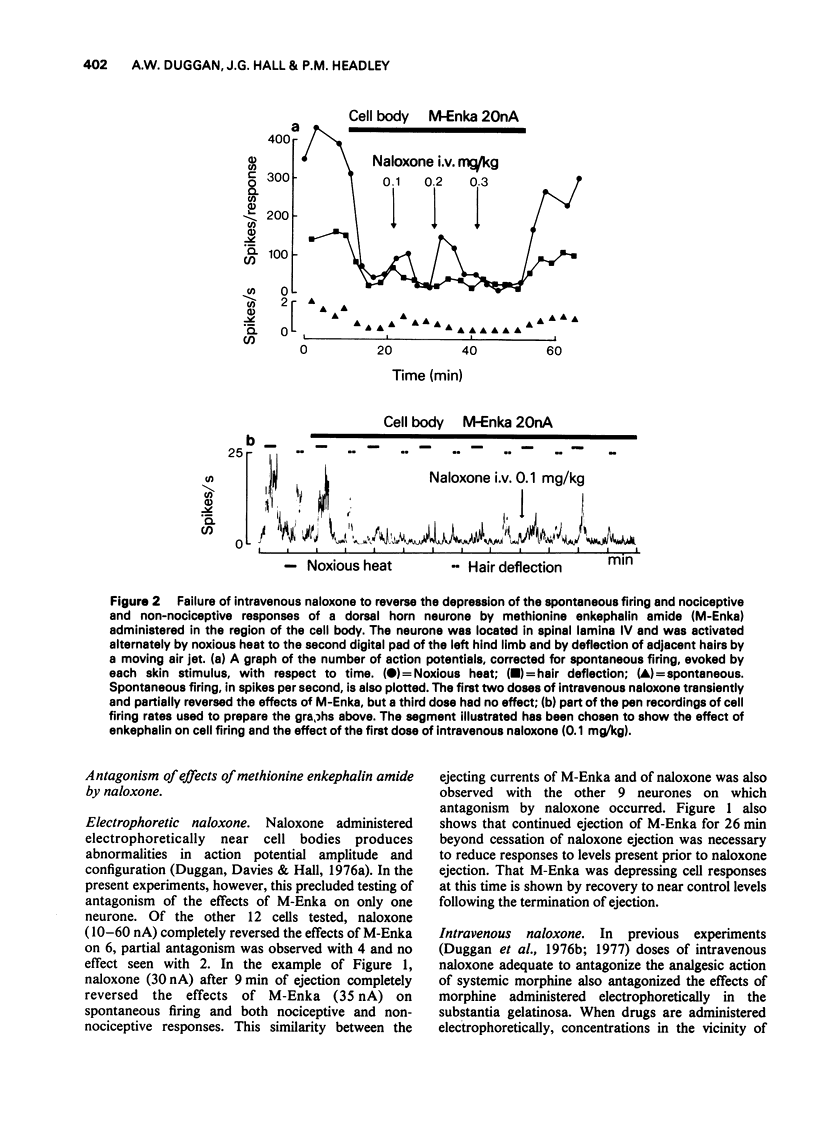
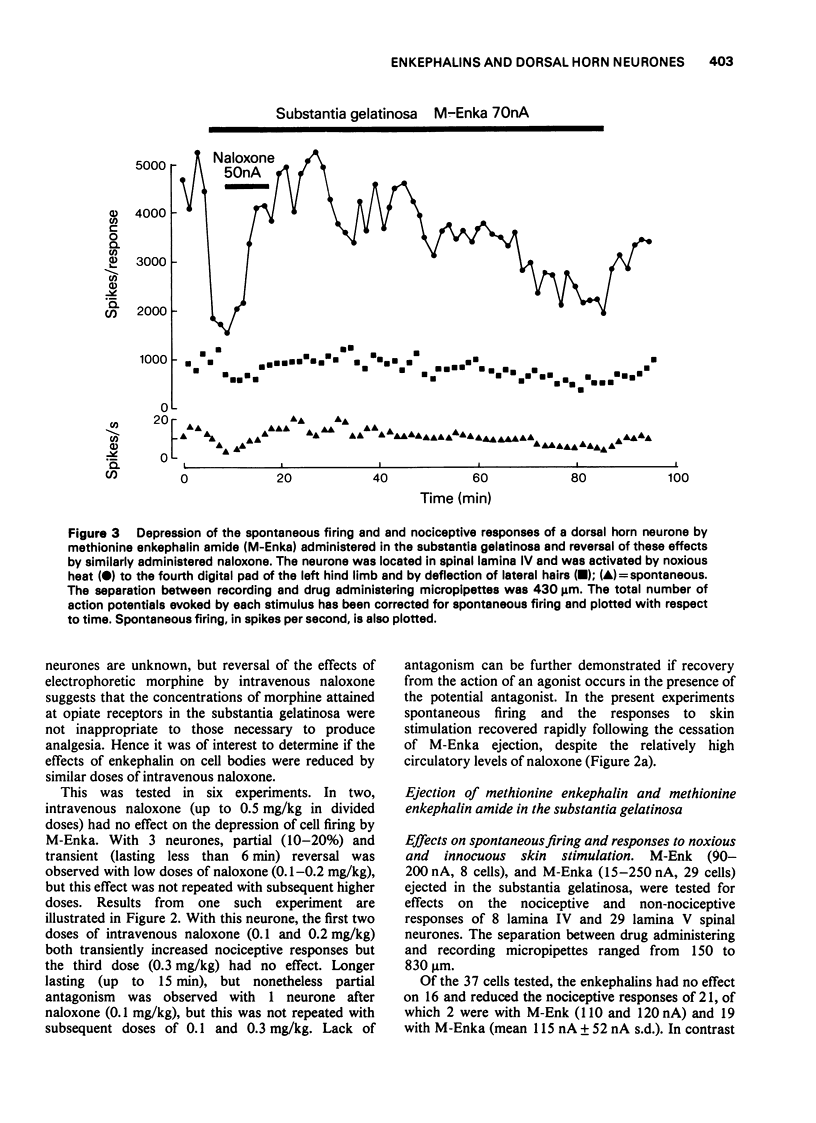
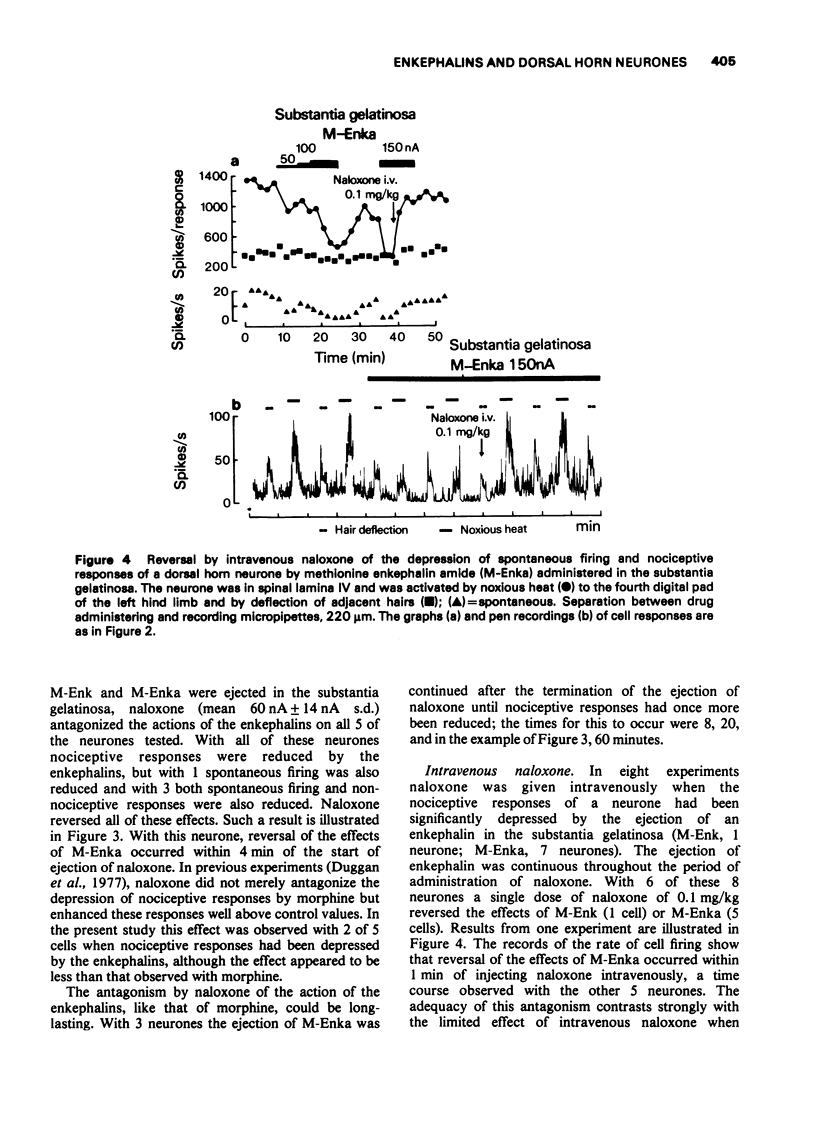
1. In spinal cats anaesthetized with alpha-chloralose, a study was made of the effects of methionine enkephalin and methionine enkephalin amide on the responses of neurones of spinal laminae IV and V to noxious and innocuous skin stimuli. The enkephalins were ejected from micropipettes either in the region of cell bodies or in the substantia gelatinosa. 2. Administered near cell bodies the enkephalins reduced spontaneous firing and cell responses to both types of skin stimuli. These effects were antagonized by naloxone when administered near cell bodies but not when given intravenously in doses (0.3-0.6 mg/kg) more than adequate to antagonize analgesic doses of morphine. 3. Administered in the substantia gelatinosa the enkephalins were more selective in their action. The predominant effect was a reduction in nociceptive responses with little effect on non-nociceptive responses although spontaneous firing was commonly reduced. Naloxone administered either in the substantia gelatinosa or intravenously (0.1-0.3 mg/kg) reversed these effects of the enkephalins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi J. D., Grant N., Garsky V., Sarantakis D., Wise C. D., Stein L. Analgesia induced in vivo by central administration of enkephalin in rat. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):625–626. doi: 10.1038/260625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Bradbury A. F., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C., Smyth D. G., Snell C. R. Interactions of peptides derived from the C-fragment of beta-lipotropin with brain opiate receptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):460P–461P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Gayton R. J., Lambert L. A. Effects of microiontophoretically applied methionine-enkephalin on single neurones in rat brain. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):425–426. doi: 10.1038/261425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buscher H. H., Hill R. C., Römer D., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Pless J. Evidence for analgesic activity of enkephalin in the mouse. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):423–425. doi: 10.1038/261423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvillo O., Henry J. L., Neuman R. S. Effects of morphine and naloxone on dorsal horn neurones in the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(6):1207–1211. doi: 10.1139/y74-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. K., Fong B. T., Pert A., Pert C. B. Opiate receptor affinities and behavioral effects of enkephalin: structure-activity relationship of ten synthetic peptide analogues. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 15;18(12):1473–1481. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Effects of enkephalin and morphine on Renshaw cells in feline spinal cord. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):603–604. doi: 10.1038/262603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostrovsky J. O., Pomeranz B. Interaction of iontophoretically applied morphine with responses of interneurons in cat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 1976 Aug;52(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Davies J., Hall J. G. Effects of opiate agonists and antagonists on central neurons of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Morphine, enkephalin and the substantia gelatinosa. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):456–458. doi: 10.1038/264456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Suppression of transmission of nociceptive impulses by morphine: selective effects of morphine administered in the region of the substantia gelatinosa. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):65–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Norris F. H. Enkephalin-induced depression of single neurons in brain areas with opiate receptors--antagonism by naloxone. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):440–442. doi: 10.1126/science.10625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent J. P., Wolstencroft J. H. Effects of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin compared with those of morphine on brainstem neurones in cat. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):426–427. doi: 10.1038/261426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. Opioid peptides endorphins in pituitary and brain. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.959823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbaud G., Oliveras J. L., Giesler G., Besson J. M. Effects induced by stimulation of the centralis inferior nucleus of the raphe on dorsal horn interneurons in cat's spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 May 6;126(2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90732-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerker H. O., Iggo A., Zimmermann M. Segmental and supraspinal actions on dorsal horn neurons responding to noxious and non-noxious skin stimuli. Pain. 1975 Jun;1(2):147–165. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(75)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Pepper C. M., Mitchell J. F. Depression of nociceptive and other neurones in the brain by iontophoretically applied met-enkephalin. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):604–606. doi: 10.1038/262604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Guillemin R. Morphinomimetic activity of synthetic fragments of beta-lipotropin and analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3308–3310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Hyperpolarization of myenteric neurones by enkephalin [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):504P–505P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Autoradiograhic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1849–1853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz B., Wall P. D., Weber W. V. Cord cells responding to fine myelinated afferents from viscera, muscle and skin. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. D., Browe A. C. Spinal cord coding of graded nonnoxious and noxious temperature increases. Exp Neurol. 1975 Aug;48(2):201–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. The regional distribution of a morphine-like factors enkephalin in monkey brain. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Bruggencate G., Engberg I. Analysis of glycine actions on spinal interneurones by intracellular recording. Brain Res. 1968 Nov;11(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Bayerl H. The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90826-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Fry J. P., Herz A., Moroder L., Wünsch E. Enkephalin-induced inhibition of cortical neurones and the lack of this effect in morphine tolerant/dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


