Abstract
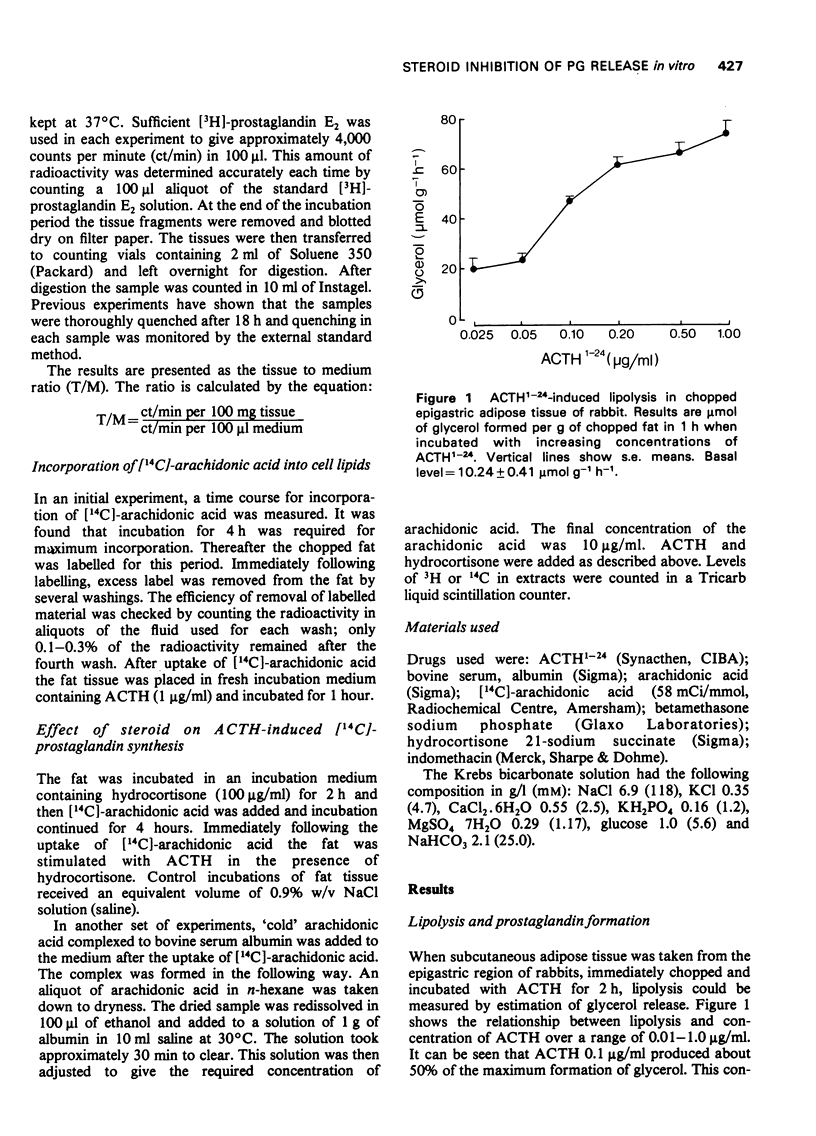
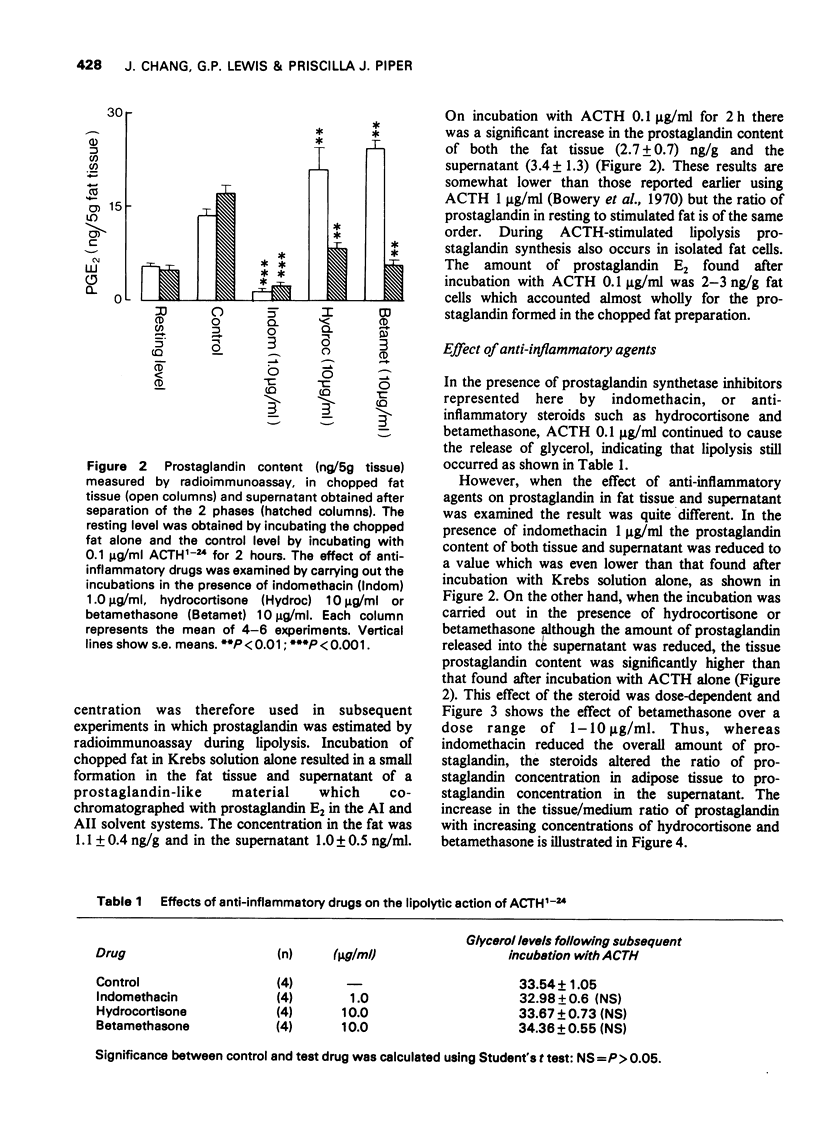
1 When rabbit chopped adipose tissue was incubated with a lipolytic agent (adrenocorticotrophic hormone, ACTH1-24, 0.1 microng/ml) in Krebs solution, prostaglandin E2 was formed in the tissue and about the same amount was found in the medium. 2 In the presence of indomethacin (1 microng/ml) the appearance of prostaglandin E2 was almost abolished both in the tissue and in the medium. 3 When the incubation was carried out in the presence of hydrocortisone or betamethasone (1-10 microng)ml) the concentration of prostaglandin E2 leaking or carried into the medium was significantly reduced, whereas that remaining in the tissue was significantly increased. This action of the steroids was not reversed by increasing substrate (arachidonic acid) concentration in the medium. 4 The steroids did not affect lipolysis, nor did they influence prostaglandin metabolism since such activity was not detectable in the adipose tissue. 5 Anti-inflammatory steroids therefore did not reduce prostaglandin formation but increased the tissue/medium ratio, which supports the view that they inhibit the release of prostaglandins after these have been synthesized.
Full text
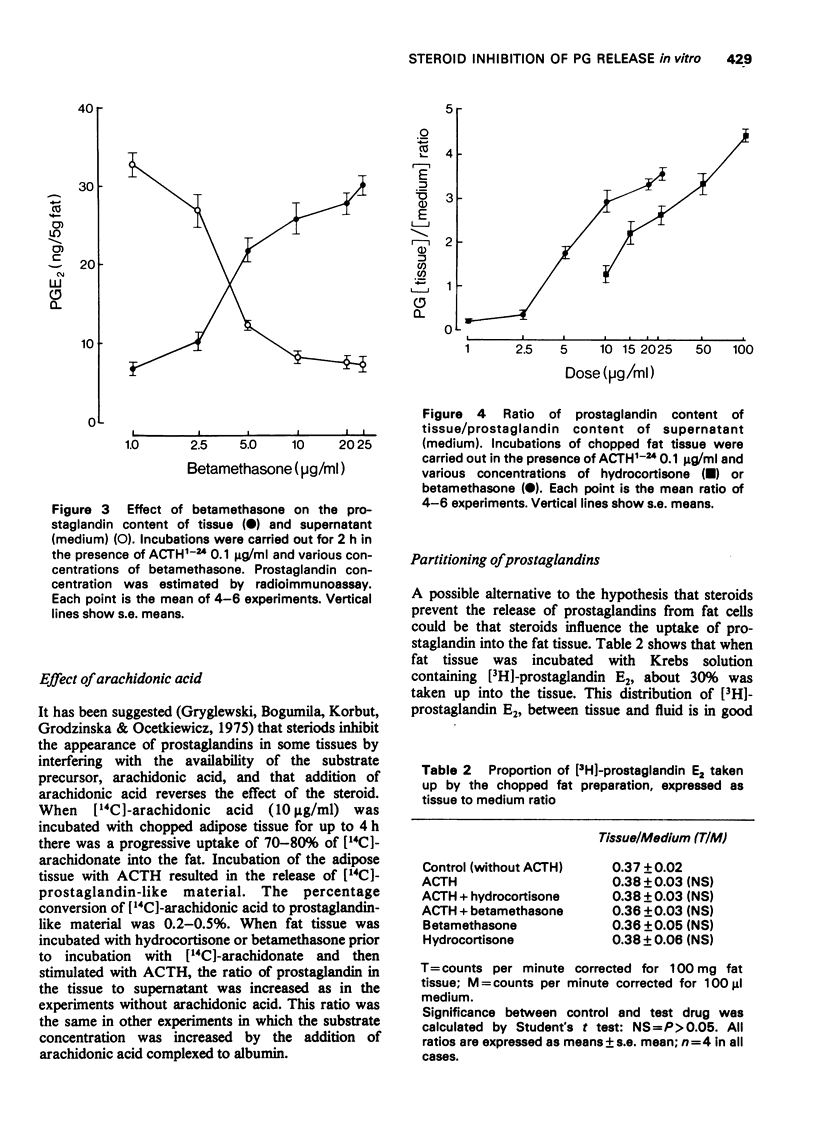
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bito L. Z. Accumulation and apparent active transport of prostaglandins by some rabbit tissues in vitro. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):371–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery B., Lewis G. P. Inhibition of functional vasodilatation and prostaglandin formation in rabbit adipose tissue by indomethacin and aspirin. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):305–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Lewis G. P., Matthews J. The relationship between functional vasodilatation in adipose tissue and prostaglandin. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Lewis G. P., Piper P. J. Proceedings: The effects of anti-inflammatory steroids on levels of prostaglandin in adipose tissue in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):342P–343P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton C., Hope W. C. Cyclic AMP regulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis in fat cells. Prostaglandins. 1974 May 10;6(3):227–242. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W., Tomlinson R. Proceedings: Effect of cromoglycate and eicosatetraynoic acid on the release of prostaglandins and SRS-a from immunologically challenged guinea pig lungs. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):107P–108P. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09695.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakins K. E., Whitelocke R. A., Bennett A., Martenet A. C. Prostaglandin-like activity in ocular inflammation. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 19;3(5824):452–453. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5824.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggstein M., Kreutz F. H. Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. I. Prinzip, Durchführung und Besprechung der Methode. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Mar 1;44(5):262–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01747716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R., Gryglewski R., Herbaczyńska-Cedro K., Vane J. R. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on prostaglandin biosynthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio238104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Panczenko B., Korbut R., Grodzinska L., Ocetkiewicz A. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin release from perfused mesenteric blood vessels of rabbit and from perfused lungs of sensitized guinea pig. Prostaglandins. 1975 Aug;10(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennam J. F., Johnson D. A., Newton J. R., Collins W. P. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandin F-2-alpha in peripheral venous plasma from men and women. Prostaglandins. 1974 Mar 25;5(6):531–542. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz F., Robinson D. R., McGuire M. B., Levine L. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin production by rheumatiod synovia. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):737–739. doi: 10.1038/258737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Piper P. J. Inhibition of release of prostaglandins as an explanation of some of the actions of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Nature. 1975 Mar 27;254(5498):308–311. doi: 10.1038/254308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS S., VAUGHAN M. Alpha-Glycerophosphate synthesis and breakdown in homogenates of adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:44–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Vane J. R. Release of additional factors in anaphylaxis and its antagonism by anti-inflammatory drugs. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):29–35. doi: 10.1038/223029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., McDonough J., Levine L. Hydrocortisone inhibits prostaglandin production by mouse fibrosarcoma cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):739–741. doi: 10.1038/258739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


