Abstract
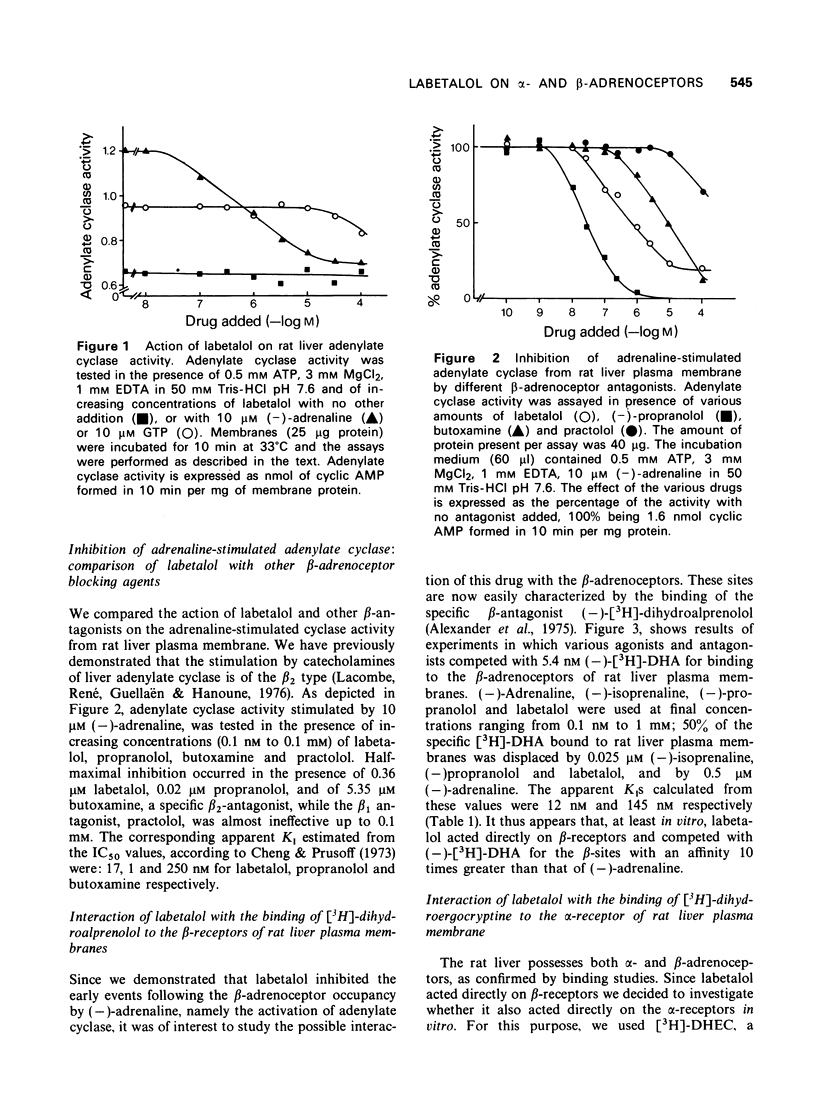
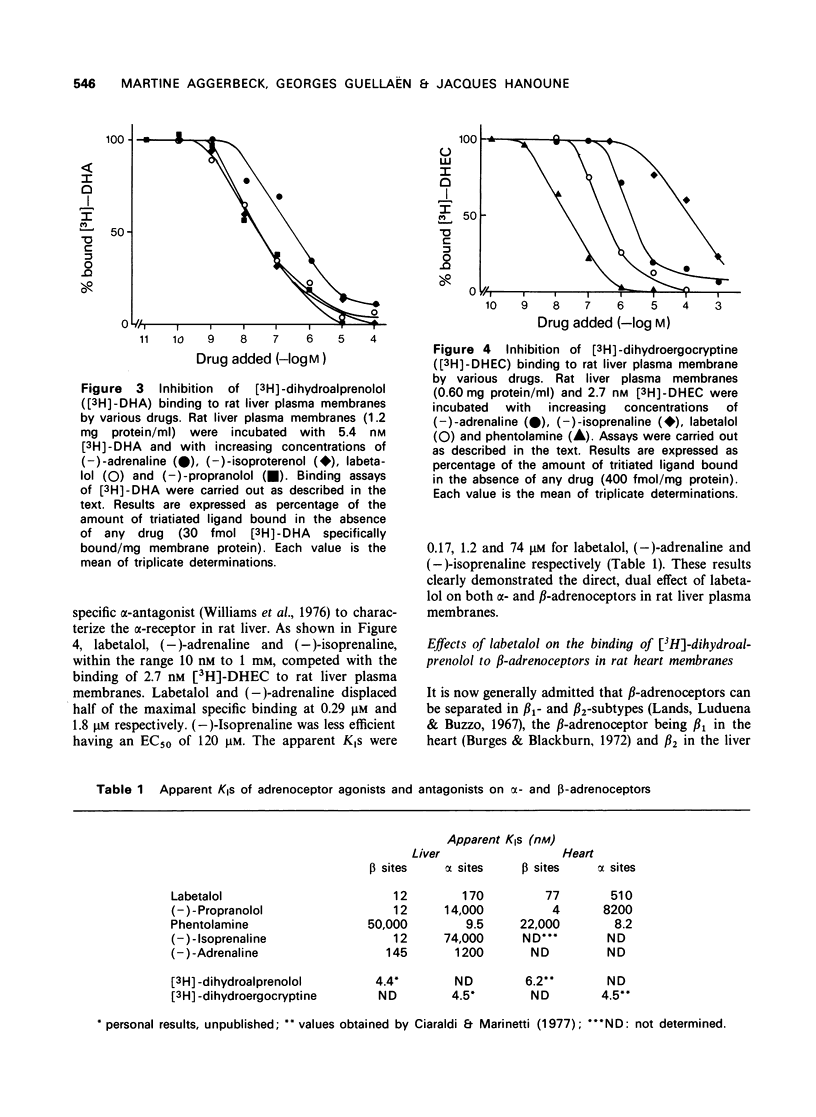
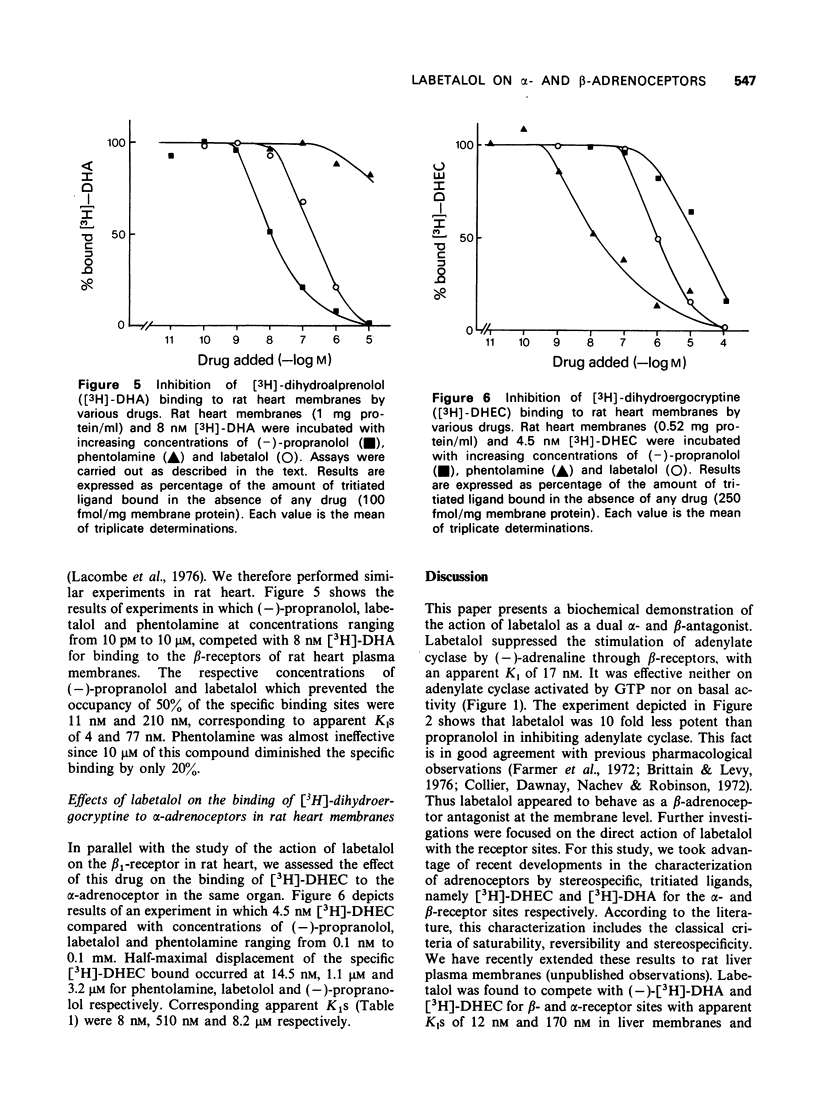
1 Labetalol (AH 5158A) inhibited the adrenaline-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity of rat liver and heart. This drug had no effect on basal or guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-activated adenylate cyclase activities. 2 Labetalol displaced the binding of the specific ligands [3H]-dihydroergocryptine and (-)-[3H]-dihydroalprenolol from their respective alpha and beta-adrenoceptors in rat heart and liver. The affinity of labetalol was 10 fold higher for the beta- than for the alpha-adrenoceptor. It appeared to be 10 to 100 times less potent than phentolamine in blocking alpha-adrenoceptors and 5 to 10 times less potent than propranolol in blocking beta-receptors. 3 It is concluded that labetalol exerts its dual alpha- and beta-antagonism by acting directly on the plasma membranes, where it binds competitively to alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. W., Williams L. T., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors by (minus) [3H]alprenolol binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1564–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain R. T., Levy G. P. A review of the animal pharmacology of labetalol, a combined alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drug. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Fedak S. A., Woodard C. J., Aurbach G. D. Beta-Adrenergic receptor interactions. Direct comparison of receptor interaction and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1239–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burges R. A., Blackburn K. J. Adenyl cyclase and the differentiation of -adrenoreceptors. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):249–250. doi: 10.1038/newbio235249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T., Marinetti G. V. Thyroxine and propylthiouracil effects of vivo on alpha and beta adrenergic receptors in rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):984–991. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. G., Dawnay N. A., Nachev C., Robinson B. F. Clinical investigation of an antagonist at alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors-AH5158A. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;44(2):286–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargie H. J., Dollery C. T., Daniel J. Labetalol in resistant hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):751–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T. Closing remarks: current status of labetalol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):823–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. B., Kennedy I., Levy G. P., Marshall R. J. Pharmacology of AH 5158; a drug which blocks both - and -adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;45(4):660–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanoune J., Lacombe M. L., Pecker F. The epinephrine-sensitive adenylate cyclase of rat liver plasma membranes. Role of guanyl nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4569–4574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanoune J., Stengel D., Lacombe M. L., Feldmann G., Coudrier E. Proteolytic activation of rat liver adenylate cyclase by a contaminant of crude collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2039–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. Combined alpha- and beta-adrenoreceptors blockade with oral labetalol in hypertensive patients with reference to haemodynamic effects at rest and during exercise. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):729–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. Haemodynamic effects of combined alpha- and beta-adrenoreceptor blockade after intravenous labetalol in hypertensive patients at rest and during exercise. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):725–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. L., Rene E., Guellaen G., Hanoune J. Transformation of the beta2 adrenoceptor in normal rat liver into a beta1 type in Zajdela hepatoma. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):70–72. doi: 10.1038/262070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Luduena F. P., Buzzo H. J. Differentiation of receptors responsive to isoproterenol. Life Sci. 1967 Nov 1;6(21):2241–2249. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leray F., Chambaut A. M., Perrenoud M. L., Hanoune J. Adenylate-cyclase activity of rat-liver plasma membranes. Hormonal stimulation and effect of adrenalectomy. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):185–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. A. Pharmacological effects of labetalol in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):721–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., OYE I., BUTCHER R. W. THE ACTION OF EPINEPHRINE AND THE ROLE OF THE ADENYL CYCLASE SYSTEM IN HORMONE ACTION. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:623–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Pochet R. In vivo labelling of beta-adrenergic receptors on rat glioma cells. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. A. Separation and purification of cyclic nucleotides by alumina column chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:41–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Mullikin D., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of alpha-adrenergic receptors in uterine smooth muscle membranes by [3H]dihydroergocryptine binding. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):6915–6923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


