Abstract
1 High-speed cytoplasmic supernatants of rat, rabbit, pig and guinea-pig kidneys were prepared and the metabolism of 10 μg/ml prostaglandin F2α labelled with [3H1-9β]-prostaglandin F2α studied by thin layer radiochromatography and bioassay.
2 The metabolism of prostaglandin F2α measured by radiochromatography parallels biological inactivation in all species except the rabbit.
3 Kidneys metabolize prostaglandin F2α by two divergent pathways, yielding a mixture of prostaglandin E and F metabolites.
4 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase and prostaglandin Δ-13 reductase are present in all species in characteristic proportions. Thus prostaglandin F2α is metabolized sequentially to 15-keto prostaglandin F2α and 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2α. The rate and profile of formation of these metabolites is species-dependent.
5 13,14-Dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2α is the principal prostaglandin F series metabolite in all species.
6 Pig and guinea-pig kidney contain an unidentified enzyme which converts 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2α to 13,14-dihydro prostaglandin F2α.
7 Rat kidney contains a high concentration of a prostaglandin 9-hydroxy dehydrogenase which converts 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2α to 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin E2.
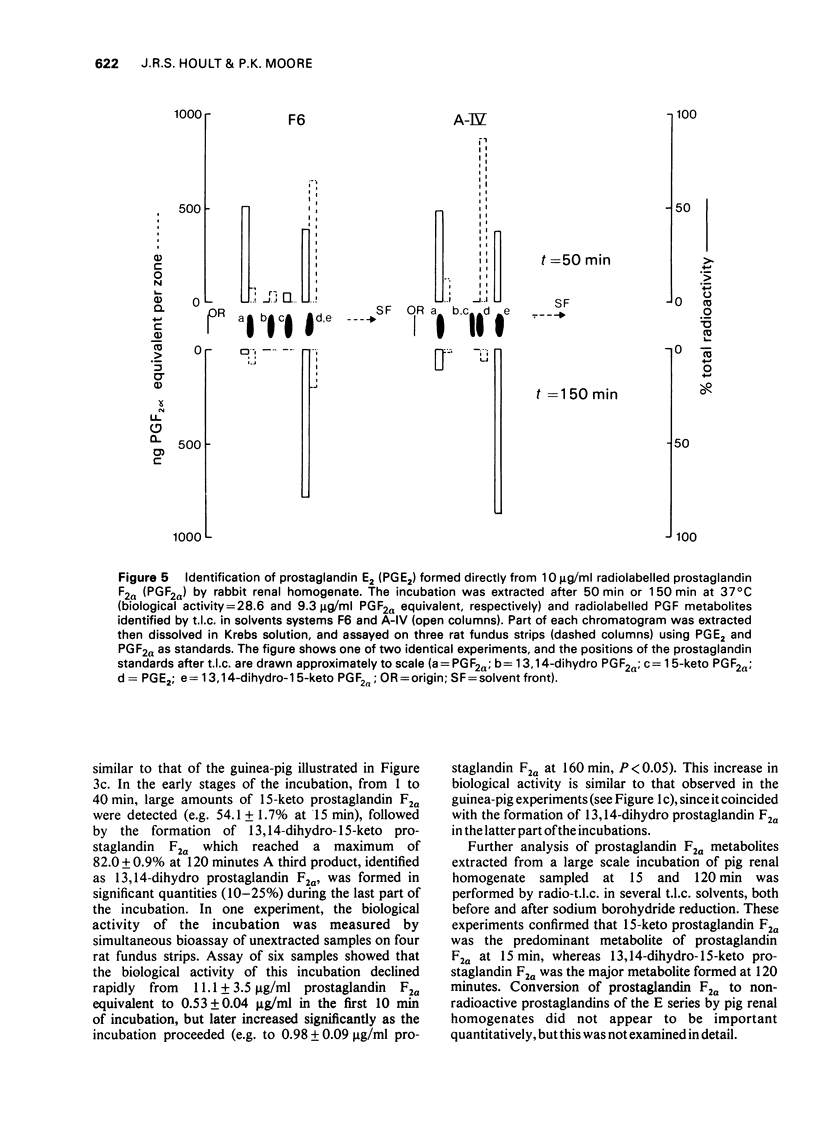
8 Rabbit kidney contains a novel 9-hydroxydehydrogenase which oxidises prostaglandin F2α directly to E2, thus producing a compound with more potent renal actions. The possible implications of this enzyme for kidney homeostasis are discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders N. H. Preparative thin-layer and column chromatography of prostaglandins. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):316–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E., Larsson C., Samuelsson B. The distribution of 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase and prostaglandin-delta 13-reductase in tissues of the swine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):396–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E., Larsson C. The sequence of the early steps in the metabolism of prostaglandin E1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971;14(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E. The biological activities of three metabolites of prostaglandin E 1. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Apr;66(4):509–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley D. J., Piper P. J. Comparative bioassay of prostaglandin E2 and its three pulmonary metabolites. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;54(3):397–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley D. J., Piper P. J. The behaviour of the pulmonary metabolites of prostaglandins in several simple thin-layer chromatography and bioassay systems. Prostaglandins. 1976 Jun;11(6):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W., Leach B. E., Muirhead E. E. Identification of prostaglandin E2 as the principal vasodepressor lipid of rabbit renal medulla. Nature. 1967 Sep 16;215(5107):1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2151298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. A., Horton E. W. Output of prostaglandins from the rabbit kidney, its increase on renal nerve stimulation and its inhibition by indomethacin. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):658–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the renal medulla of rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Israelsson U. Metabolism of prostaglandin E2 in guinea pig liver. I. Identification of seven metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5107–5114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of prostaglandin E2 in guinea pig liver. II. Pathways in the formation of the major metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1073–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L. 15-hydroxy-9-oxoprosta-11, 13-dienoic acid as the product of a prostaglandin isomerase. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. B., Ferguson J. F. Prostaglandins and natriuresis: the effect of renal prostaglandins on PAH uptake by kidney cortex. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1185–1186. doi: 10.1038/2221185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Levine L. Prostaglandin metabolism. I. Cytoplasmic reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent and microsomal reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent prostaglandin E 9-ketoreductase activities in monkey and pigeon tissues. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Pong S. S., Katzen D., Wu K. Y., Levine L. Distribution of prostaglandin E 9-KETOREDUCTASE AND TYPES I and II 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in swine kidney medulla and cortex. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):142–145. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. A., Levine L. Evidence for the presence of a prostaglandin E 2 -9-keto reductase in rat organs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90996-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrazzi M. A., Shaw J. E., Tao F. T., Matschinsky F. M. Reversibility of 15-OH prostaglandin dehydrogenase from swine lung. Prostaglandins. 1972 May;1(5):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Differential effect of noradrenaline and renal nerve stimulation on vascular resistance in the dog kidney and the release of a prostaglandin E-like substance. Clin Sci. 1972 Feb;42(2):223–233. doi: 10.1042/cs0420223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J. Effects of prostaglandins E1, A1 and F2a on the coronary and peripheral circulations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1160–1163. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak C. Activity profiles of prostaglandin 15- and 9-hydroxydehydrogenase and 13-reductase in the developing rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2795–2800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak C., Miller D. Prostaglandins during development. II. Identification of prostaglandin 9-hydroxy dehydrogenase activity in adult rat kidney homogenates. Experientia. 1974 Jun 15;30(6):590–592. doi: 10.1007/BF01921489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak C. Prostaglandin 9-hydroxydehydrogenase activity in the adult rat kidney. Identification, assay, pathway, and some enzyme properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2789–2794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins. Fed Proc. 1972 Sep-Oct;31(5):1442–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. J., Hart M. Prostaglandin-E2-9-ketoreductase in rabbit kidney. Prostaglandins. 1975 Aug;10(2):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun F. F., Armour S. B. Prostaglandin 15-hydroxy dehydrogenase and delta13 reductase levels in the lungs of maternal, fetal and neonatal rabbits. Prostaglandins. 1974 Aug 25;7(4):327–338. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Nasjletti A., Terragno D. A., McGiff J. C. Renal prostaglandins. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1976;2:561–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



