Abstract
1. Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Single myenteric ganglia were maintained in vitro and drugs were applied by adding them to the perfusing solution. 2. Narcotic analgesics hyperpolarized the membrane of a proportion of neurones in the myenteric plexus. 3. The membrane hyperpolarization was sometimes associated with a decrease in input resistance. These effects reduced the excitability of myenteric neurones. 4. The effects of narcotics occurred at low concentrations (10 nM to 1 micrometer), were stereospecific and were reversed by naloxone. 5. It is proposed that the morphine-sensitive neurones may be the cholinergic efferents to the muscle layers. By hyperpolarizing these neurones, morphine may prevent their excitation by electric field stimulation. This may explain why narcotic analgesics reduce the output of acetylcholine and the contractile response of this preparation when it is excited by field stimulation.
Full text
PDF

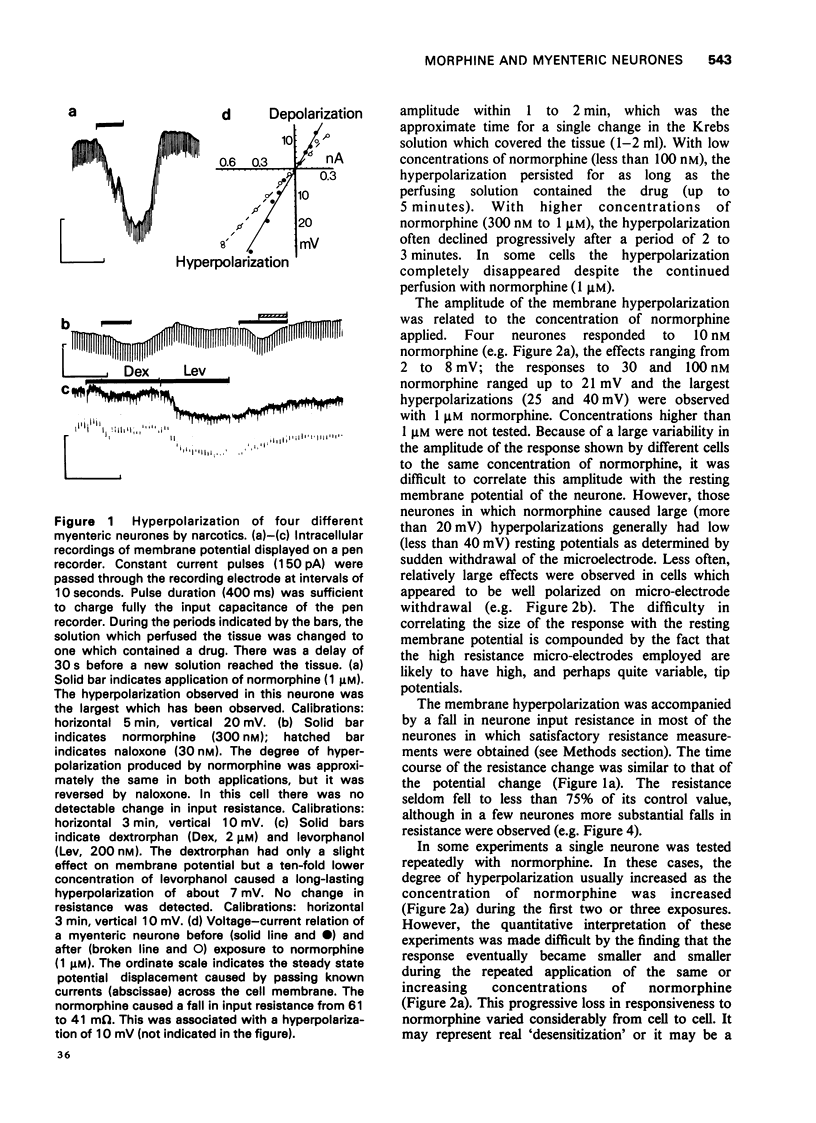
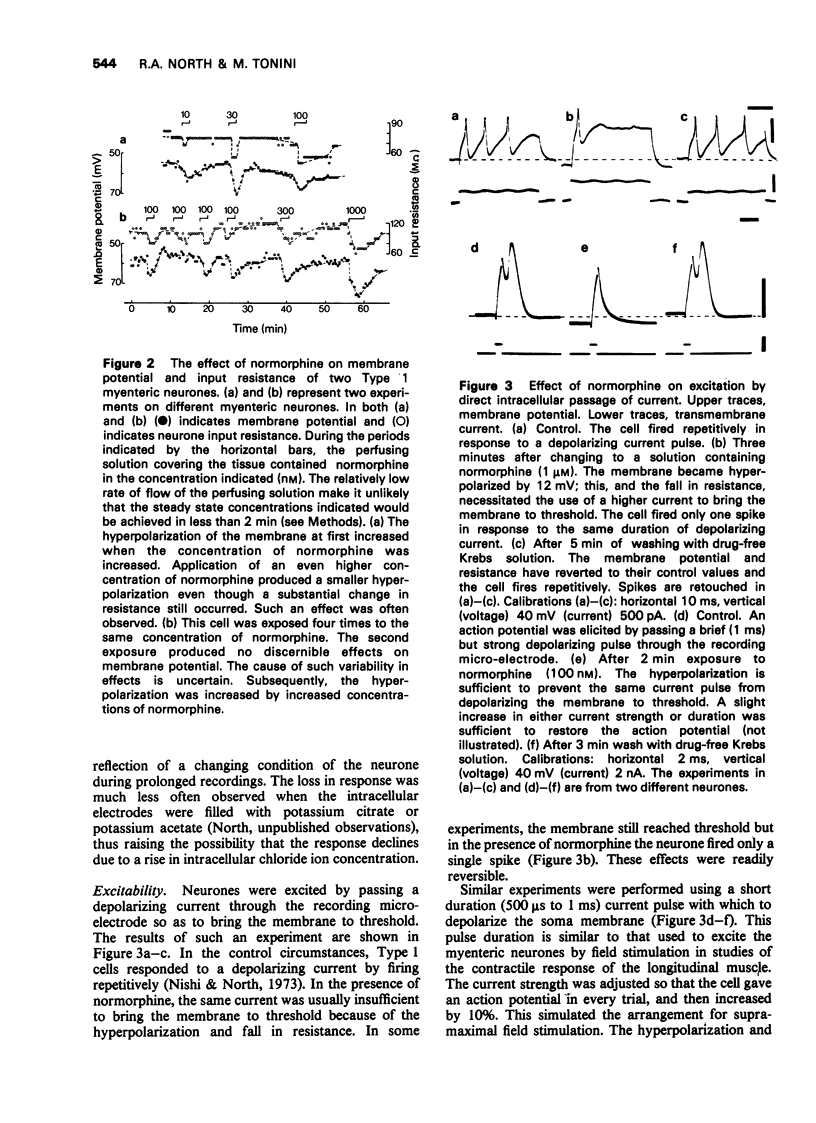





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox B. M., Weinstock M. The effect of analgesic drugs on the release of acetylcholine from electrically stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Snyder S. H. Receptor binding and pharmacological activity of opiates in the guinea-pig intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jul;194(1):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diab I. M., Dinerstein R. J., Watanabe M., Roth L. J. (3H)morphine localization in myenteric plexus. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):689–691. doi: 10.1126/science.948744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A. Effect of synaptic transmission blockade on morphine action in the guinea-pig myenteric plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A., Kendig J. Effects of narcotic opiates and serotonin on the electrical behavior of neurons in the guinea pig myenteric plexus. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 1;14(11):2299–2309. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A. Single neuron studies of opiate action in the guinea pig myenteric plexus. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennessy M. R., Heimans R. L., Rand M. J. Comparison of effect of morphine-like analgesics on transmurally stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;37(2):436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb10580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYANG E. A., KOSTERLITZ H. W., LEES G. M. THE INHIBITION OF AUTONOMIC NEURO-EFFECTOR TRANSMISSION BY MORPHINE-LIKE DRUGS AND ITS USE AS A SCREENING TEST FOR NARCOTIC ANALGESIC DRUGS . Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 May 25;248:231–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00348594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G. Fine structure of the myenteric plexus in the guinea-pig ileum. J Anat. 1972 Jan;111(Pt 1):69–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R., Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. The effects of hexamethonium, morphine and adrenaline on the output of acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle preparation of the ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):553P–554P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyand E. A., Kosterlitz H. W. Agonist and antagonist actions of morphine-like drugs on the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Sep;27(3):514–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. A nervous mechanism for descending inhibition in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):129–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. In vitro models in the study of structure-activity relationships of narcotic analgesics. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:29–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Kinetic parameters of narcotic agonists and antagonists, with particular reference to N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Effects of morphine on myenteric plexus neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Nov;15(11):719–721. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Henderson G. Action of morphine on guinea-pig myenteric plexus and mouse vas deferens studied by intracellular recording. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Influence of atropine and morphine on the liberation of acetylcholine from the guinea pig's intestine. Nature. 1956 Nov 17;178(4542):1121–1122. doi: 10.1038/1781121b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Inhibition by morphine of the release of acetylcholine from the intestine of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):115–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Takayanagi I., Takagi K. Pharmacological properties of electrical activities obtained from neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;23(5):665–671. doi: 10.1254/jjp.23.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Essen D. C. The contribution of membrane hyperpolarization to adaptation and conduction block in sensory neurones of the leech. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):509–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



