Abstract
1 Isolated rings of hamster aorta produced an unstable substance which inhibited platelet aggregation in vitro and had the same characteristics as prostacyclin. 2 Prostacyclin inhibited adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced aggregation of hamster platelets in vitro. 3 The effects of prostacyclin on ADP-induced platelet thrombi in the microcirculation of the hamster cheek pouch were studied with a television microscope. 4 Prostacyclin caused a dose-dependent increase in the time of iontophoretic application of ADP which was required to induce platelet thrombi formation and embolization in venules (30 to 40 micron diameter). 5 Prostacyclin caused a dose-dependent reduction in the total time during which ADP-induced thrombi were observed following local electrical damage to arterioles (40 to 80 micron diameter). 6 Thrombus formation in venules and arterioles was abolished by 500 ng/ml prostacyclin in the Krebs solution superfusing the hamster cheek pouch. 7 Prostacyclin was approximately twenty times more potent than prostaglandin E1 in preventing thrombus formation in the microcirculation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
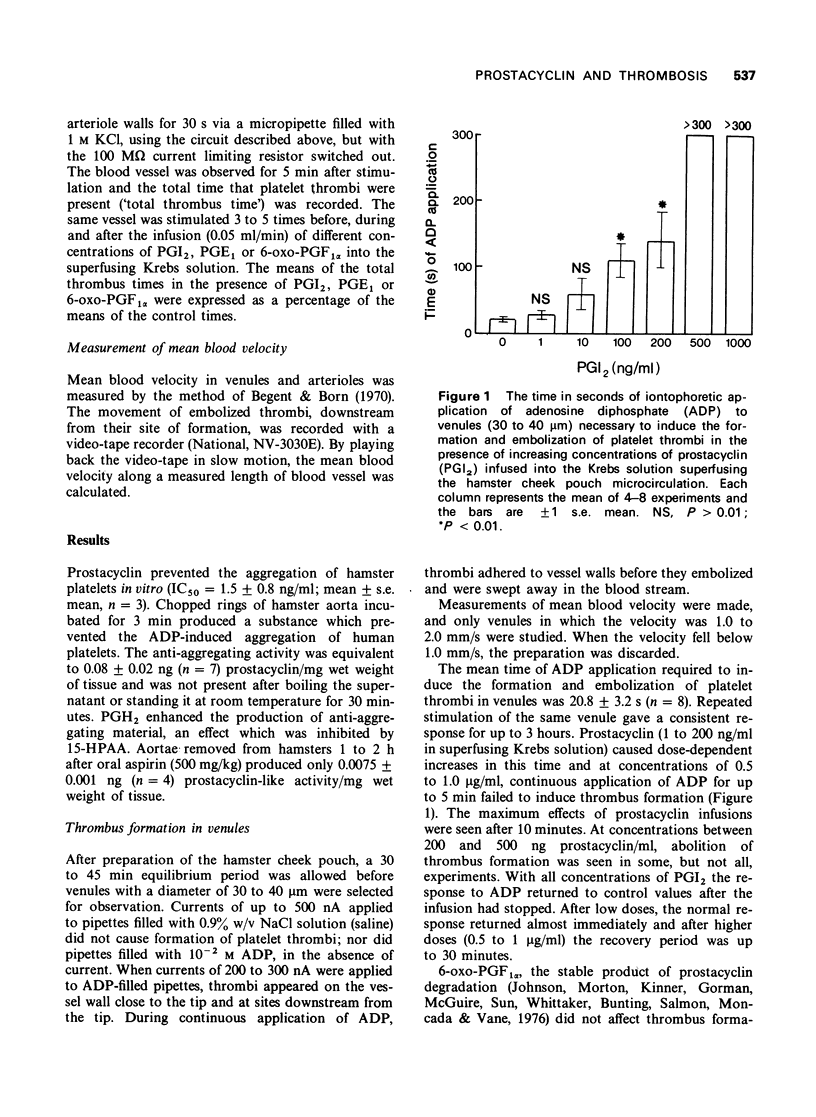
- Begent N. A., Born G. V., Sharp D. E. The initiation of platelet thrombi in normal venules and its acceleration by histamine. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):229–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begent N., Born G. V. Growth rate in vivo of platelet thrombi, produced by iontophoresis of ADP, as a function of mean blood flow velocity. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):926–930. doi: 10.1038/227926a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons P. R., Hampton J. R., Harrison M. J., Honour A. J., Mitchell J. R. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on platelet behaviour in vitro and in vivo. Br Med J. 1967 May 20;2(5550):468–472. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5550.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Wakabayashi T., Samuelsson B. Isolation and structure of two prostaglandin endoperoxides that cause platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostacyclin (PGI2) inhibits the formation of platelet thrombi induced by adenosine diphosphate (ADP) in vivo [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):137P–137P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostacyclin as a potent dilator of arterioles in the hamster cheek pouch [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:30P–31P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Lincoln F. H., Thompson J. L., Nidy E. G., Mizak S. A., Axen U. Synthesis and sterochemistry of prostacyclin and synthesis of 6-ketoprostagliandin F1alpha. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Jun 8;99(12):4182–4184. doi: 10.1021/ja00454a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R. J., Bunting S., Vane J. R. A lipid peroxide inhibits the enzyme in blood vessel microsomes that generates from prostaglandin endoperoxides the substance (prostaglandin X) which prevents platelet aggregation. Prostaglandins. 1976 Nov;12(5):715–737. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A., Vane J. R. Human arterial and venous tissues generate prostacyclin (prostaglandin x), a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):18–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Vane J. R., Whittle B. J. Relative potency of prostacyclin, prostaglandin E1 and D2 as inhibitors of platelet aggregation in several species [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):2P–4P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Moncada S., Bunting S., Vane J. R., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Identification of an enzyme in platelet microsomes which generates thromboxane A2 from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):558–560. doi: 10.1038/261558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Ingerman C. M., Kocsis J. J. Prostaglandin D2 inhibits the aggregation of human platelets. Thromb Res. 1974 Sep;5(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwick J. Modulation of thrombus formation in vivo by prostaglandins [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):138P–139P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker N., Bunting S., Salmon J., Moncada S., Vane J. R., Johnson R. A., Morton D. R., Kinner J. H., Gorman R. R., McGuire J. C. The chemical structure of prostaglandin X (prostacyclin). Prostaglandins. 1976 Dec;12(6):915–928. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



