Abstract
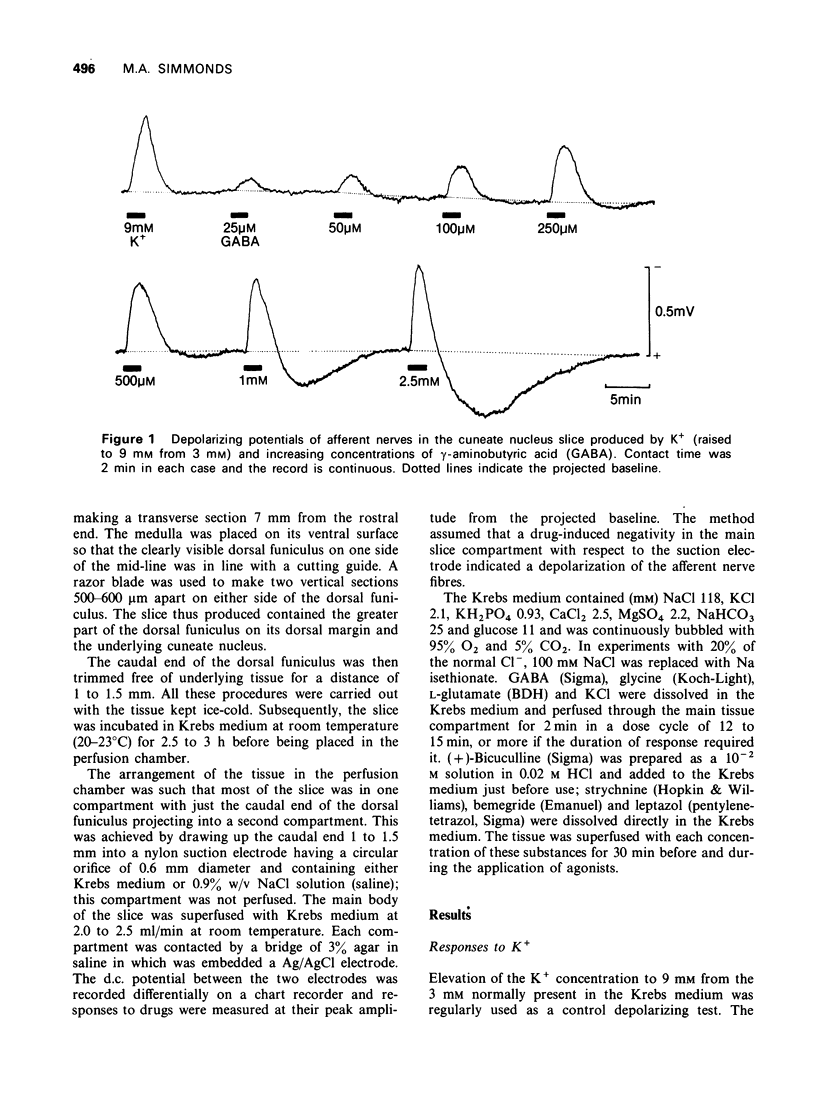
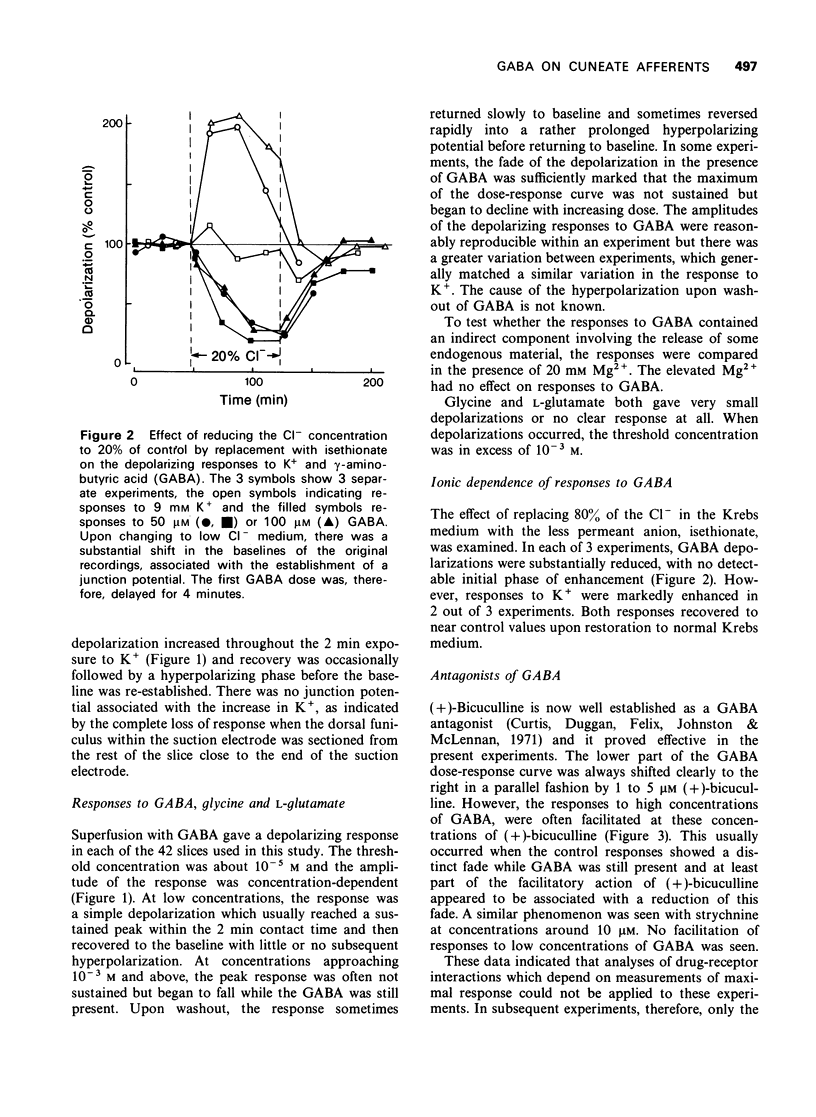
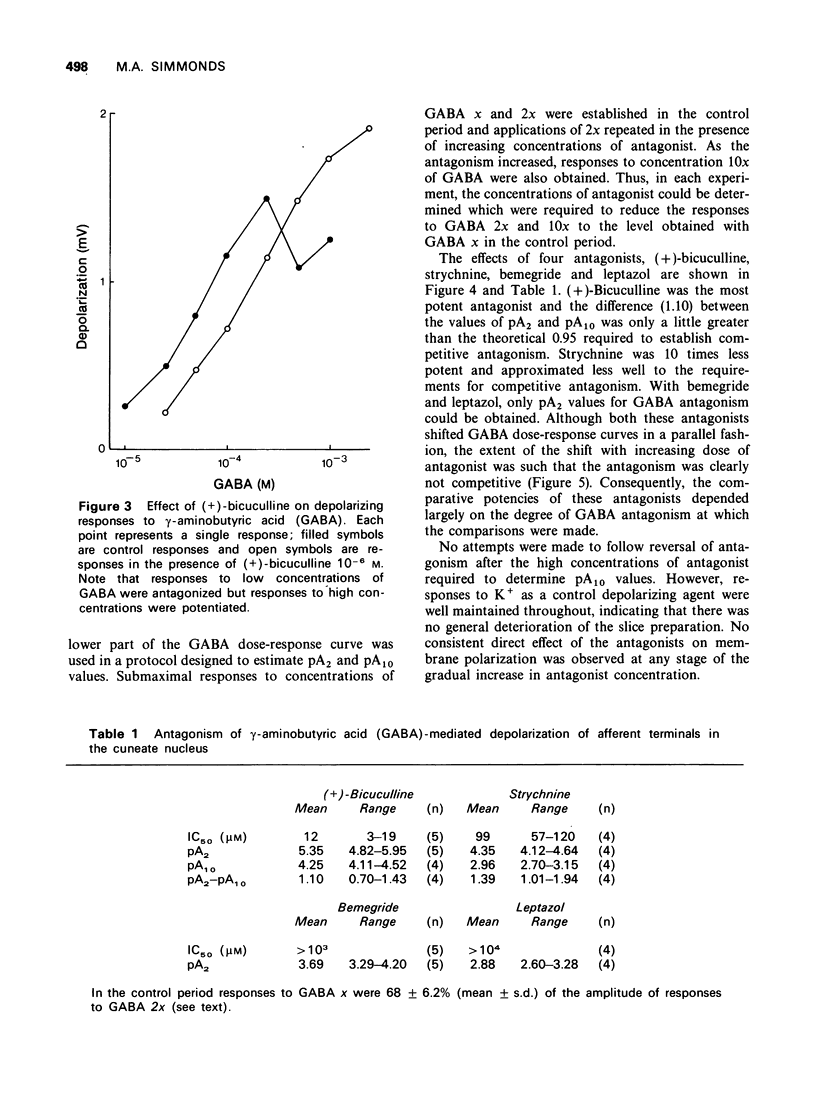
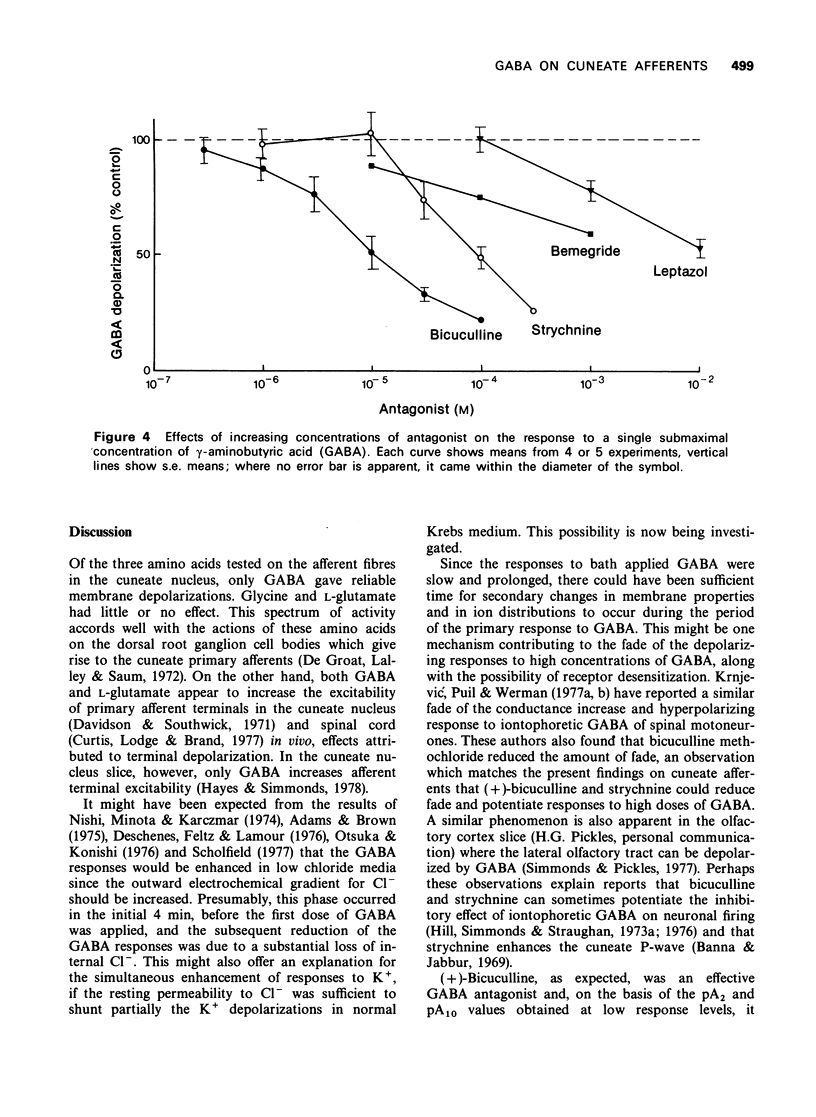
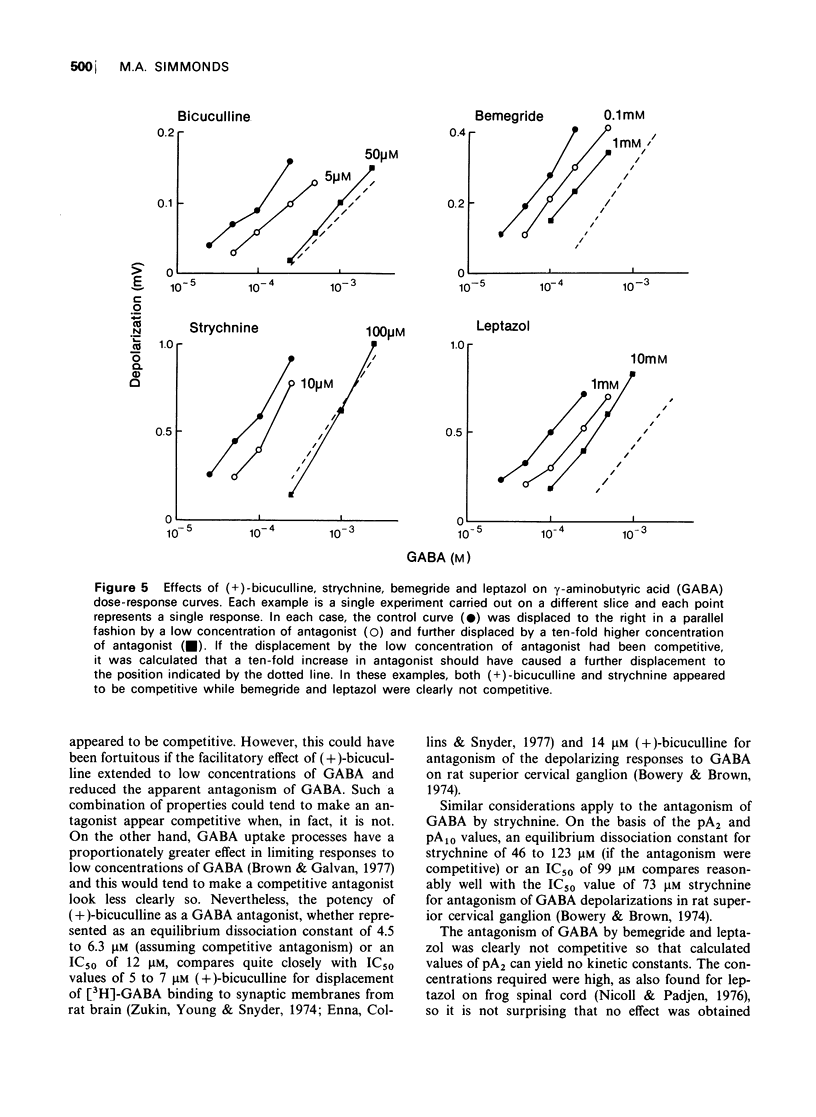
1 A slice preparation of the rat cuneate nucleus is described which is suitable for electrophysiological studies on the presynaptic action of drugs. 2. Superfusion of a slice with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) depolarized the afferent nerves in a concentration-related manner. The responses were Cl-dependent. Depolarizations to high concentrations of GABA often faded. Glycine and L-glutamate had little effect. 3 (+)-Bicuculline antagonized GABA in an apparently competitive manner (pA2 = 5.35) at low response levels. Strychnine was 10 times less potent. Responses to high concentrations of GABA were sometimes potentiated by (+)-bicuculline and strychnine. 4 Bemegride and leptazol both antagonized GABA, but with low potency and in a manner which was clearly not competitive.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., SCHMIDT R. F., YOKOTA T. DEPOLARIZATION OF PRESYNAPTIC FIBERS IN THE CUNEATE NUCLEUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jan;27:92–106. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):85–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banna N. R., Jabbur S. J. Pharmacological studies on inhibition in the cuneate nucleus of the cat. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 May;8(3):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banna N. R., Jabbur S. J. The action of bemegride on presynaptic inhibition. Neuropharmacology. 1970 Nov;9(6):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banna N. R., Naccache A., Jabbur S. J. Picrotoxin-like action of bicuculline. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;17(2):301–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A., Padjen A. Studies on convulsants in the isolated frog spinal cord. I. Antagonism of amino acid responses. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):521–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A. The pharmacology and ionic dependency of amino acid responses in the frog spinal cord. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. Depolarizing actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds on rat superior cervical ganglia in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):205–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Jones G. P. A comparison of gamma-aminobutyric acid and the semi-rigid analogues 4-aminotetrolic acid, 4-aminocrotonic acid and imidazole-4-acetic acid on the isolated superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E. S., Meritt D. A., Gardner L. C. The effect of convulsant drugs on transmission through the cuneate nucleus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Dec;154(3):398–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Galvan M. Influence of neuroglial transport on the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on mammalian ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A., McLennan H. Antagonism between bicuculline and GABA in the cat brain. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 8;33(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Brand S. J. GABA and spinal afferent terminal excitability in the cat. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 15;130(2):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90283-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N., Southwick C. A. Amino acids and presynaptic inhibition in the rat cuneate nucleus. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):689–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Lalley P. M., Saum W. R. Depolarization of dorsal root ganglia in the cat by GABA and related amino acids: antagonism by picrotoxin and bicuculline. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes M., Feltz P., Lamour Y. A model for an estimate in vivo of the ionic basis of presynaptic inhibition: an intracellular analysis of the GABA-induced depolarization in rat dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):486–493. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Collins J. F., Snyder S. H. Stereospecificity and structure--activity requirements of GABA receptor binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90878-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. Ventral root responses of the hemisected amphibian spinal cord to perfused amino acids in the presence of procaine. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):519–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Gartside I. B., Straughan D. W. Effect of four convulsants on the time course of presynaptic inhibition and the relation to seizure activity. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Nov;16(11):725–730. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Simmonds M. A. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on nerve terminal excitability in a slice preparation of cuneate nucleus. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;63(3):503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Simmonds M. A., Straughan D. W. A comparative study of some convulsant substances as gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonists in the feline cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):37–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Simmonds M. A., Straughan D. W. Antagonism of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glycine by convulsants in the cuneate nucleus of cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;56(1):9–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb06952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Simmonds M. A., Straughan D. W. Proceedings: Convulsant substances as antagonists of GABA and presynaptic inhibition in the cuneate nucleus. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):117P–117P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. Bicuculline, benzyl penicillin, and inhibitory amino acids in the spinal cord of the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1139/y77-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. GABA and glycine actions on spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):658–669. doi: 10.1139/y77-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Barker J. L. Pentylenetetrazol and penicillin are selective antagonists of GABA-mediated post-synaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):720–721. doi: 10.1038/267720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Padjen A. Pentylenetetrazol: an antagonist of GABA at primary afferents of the isolated frog spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Jan;15(1):69–71. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Minota S., Karczmar A. G. Primary afferent neurones: the ionic mechanism of GABA-mediated depolarization. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Mar;13(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


