Abstract
1 The vascular bed of the tongue in situ was perfused with blood through the lingual arteries at a constant pressure in anaesthetized dogs. All drugs except for SQ 14,225 were administered intra-arterially.
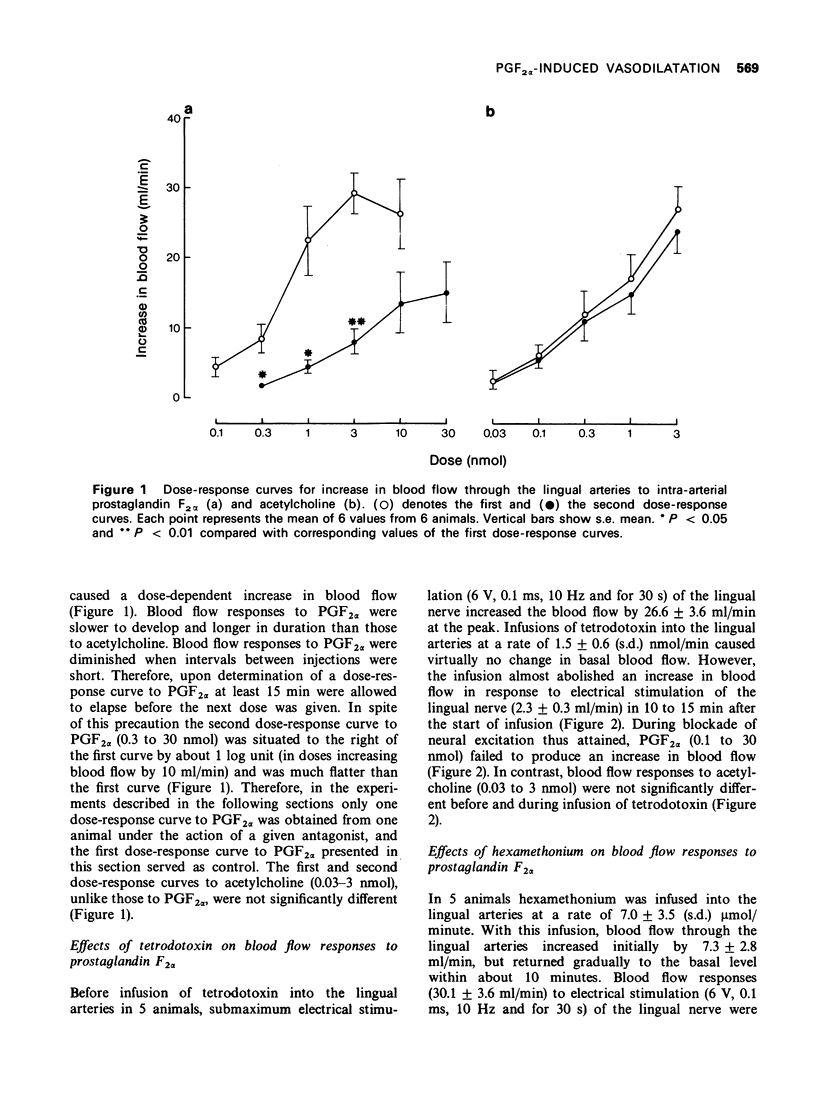
2 Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) produced a dose-dependent increase in blood flow through the lingual arteries (vasodilatation).
3 Marked desensitization was observed on the vasodilator responses to repeated administration of PGF2α.
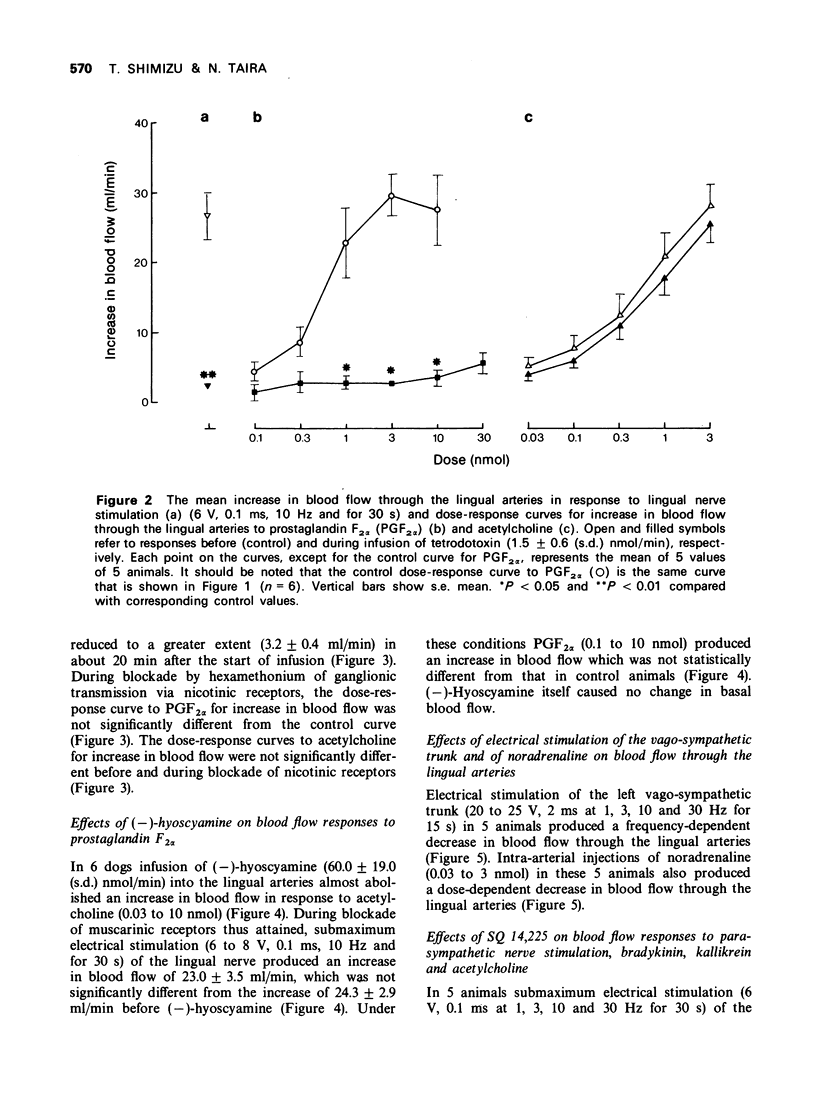
4 The vasodilator response to PGF2α was abolished by tetrodotoxin in doses that abolished the vasodilator response to electrical stimulation of the lingual nerve.
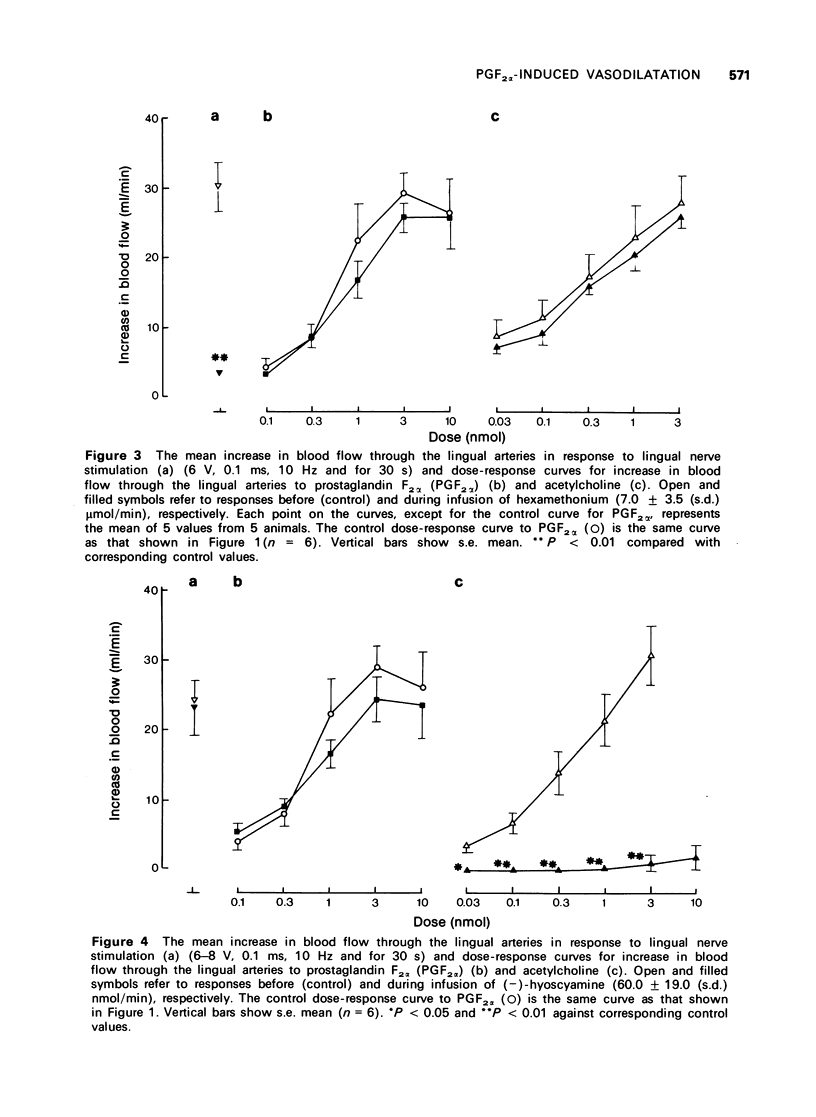
5 The vasodilator response to PGF2α was not affected by hexamethonium in doses that almost abolished the vasodilator response to lingual nerve stimulation.
6 The vasodilator responses to PGF2α and to lingual nerve stimulation were scarcely modified by (-)-hyoscyamine in doses that fully antagonized the vasodilator response to acetylcholine.
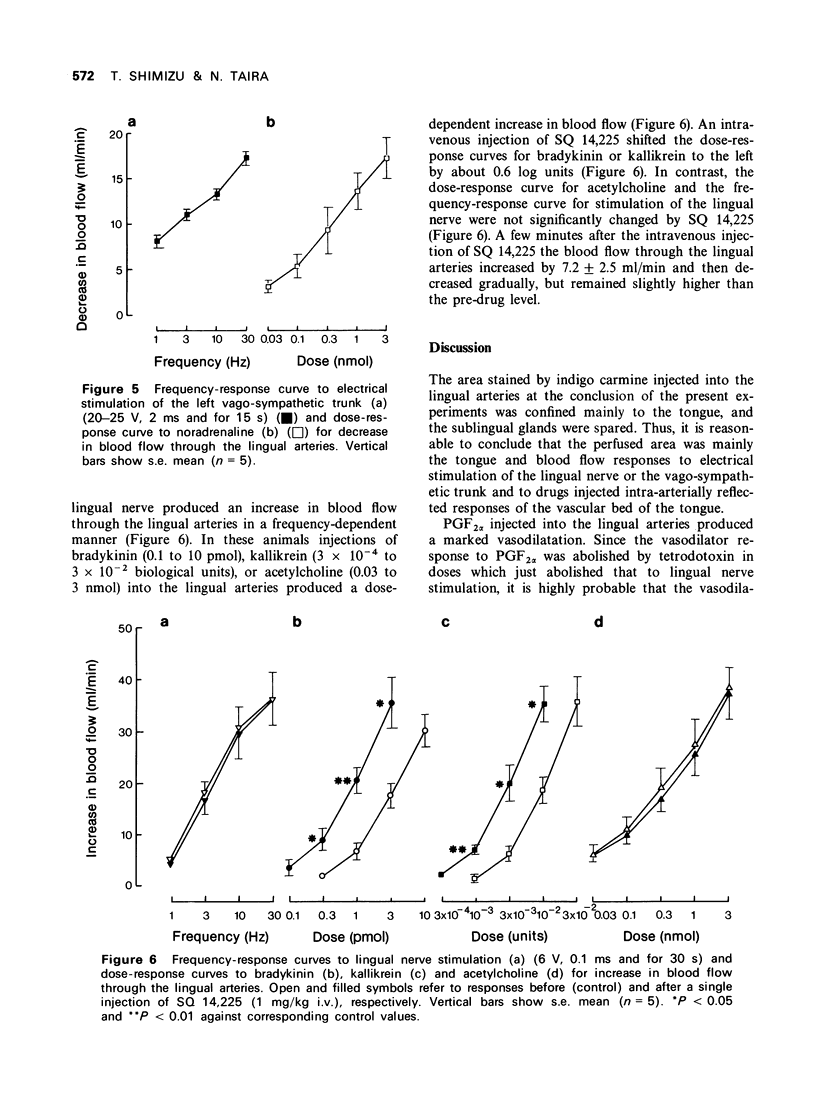
7 Electrical stimulation of the vago-sympathetic trunk and noradrenaline produced a decrease in blood flow through the lingual arteries.
8 These results indicate that the vasodilator response of the tongue to PGF2α is due exclusively to excitation of parasympathetic postganglionic neurones and that neuronal receptors involved are quite distinct from nicotinic receptors.
9 Intravenous administration of SQ 14,225, an inhibitor of angiotensin I converting enzyme or kininase II, augmented the vasodilator responses to bradykinin and kallikrein but not that to lingual nerve stimulation.
10 The results suggest that neither kallikrein nor•kinin (including bradykinin) is responsible for the parasympathetically induced vasodilatation in the tongue.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avanzino G. L., Bradley P. B., Wolstencroft J. H. Actions of prostaglandins E1, E2, and F2-alpha on brain stem neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICI I., UVNAS B. Efferent and antidromic vasodilator impulses to the tongue in the chorda-lingual nerve of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;25(1):10–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Smaje L. H. Bradykinin and functional vasodilatation in the salivary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;58(2):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb10397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. J., Alexander R. W. The intramscular ganglia of the cat's tongue. J Anat. 1969 Jul;105(Pt 1):27–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. A., Sparks H. V. Prostaglandins and consecutive vascular segments of the canine hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):567–571. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. Vasodilatation in the tongue and its relationship to plasma kinin formation. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):532–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski E., Barton S., Schachter M. Vasodilator nerve fibres to the submaxillary gland of the cat. Nature. 1971 Jul 9;232(5306):122–124. doi: 10.1038/232122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J., Cole B. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and F2-alpha on systemic, pulmonary, and splanchnic circulations in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):222–227. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J., McCurdy J. R. Hemodynamic effects of prostaglandins E1, A1 and F2-alpha in dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 May;128(1):39–42. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-32937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehadeh Z., Price W. E., Jacobson E. D. Effects of vasoactive agents on intestinal blood flow and motility in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):386–392. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N. Mode of actions of prostaglandin F2 alpha on the urinary bladder and its arterial bed in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;29(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N., Narimatsu A., Satoh S. Differential block by 1-hyoscyamine of the salivary and vascular responses of the dog mandibular gland to prostaglandin F2alpha. Life Sci. 1975 Dec 15;17(12):1869–1875. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II: angiotensin I converting enzyme). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


