Abstract
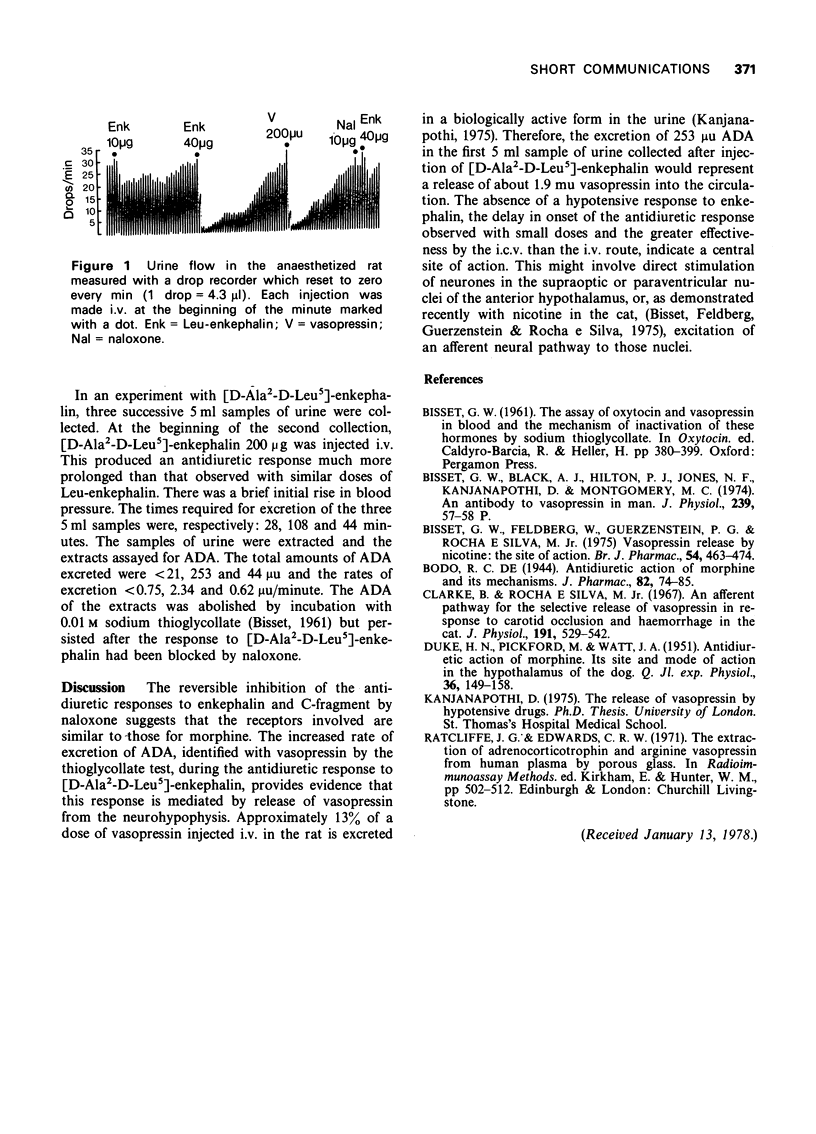
Leu-enkephalin, its stable analogue [D-Ala2-D-Leu5]-enkephalin and the C-fragment of lipotropin (beta endorphin) injected intravenously in the rat produced antidiuretic responses which were inhibited reversibly by naloxone. It was shown for Leu-enkephalin that injection into the cerebral ventricles was at least ten times more effective than intravenous injection and for [D-Ala2-D-Leu5]-enkephalin that the antidiuretic response was associated with increased excretion of vaspressin in the urine.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark B. J., Silva MR Jr E. An afferent pathway for the selective release of vasopressin in response to carotid occlusion and haemorrhage in the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):529–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Guertzenstein P. G., Rocha e Silva M., Jr Vasopressin release by nicotine: the site of action. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;54(4):463–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



