Abstract
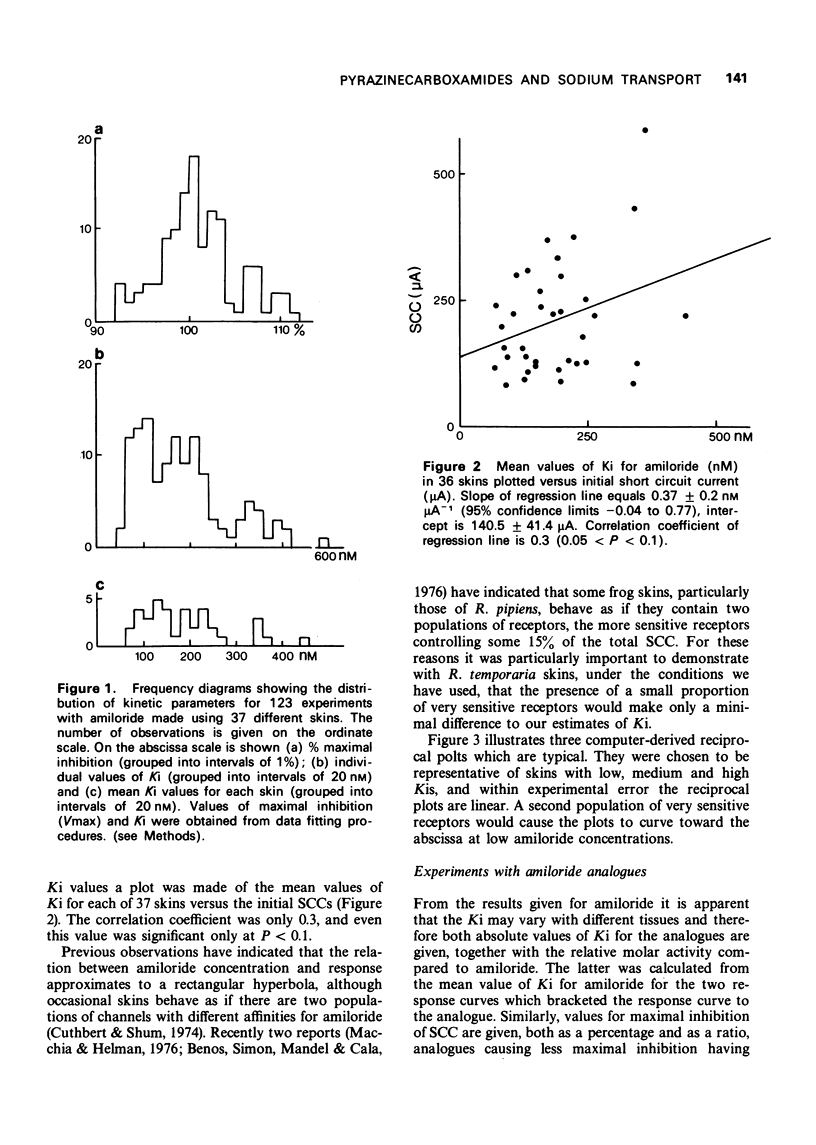
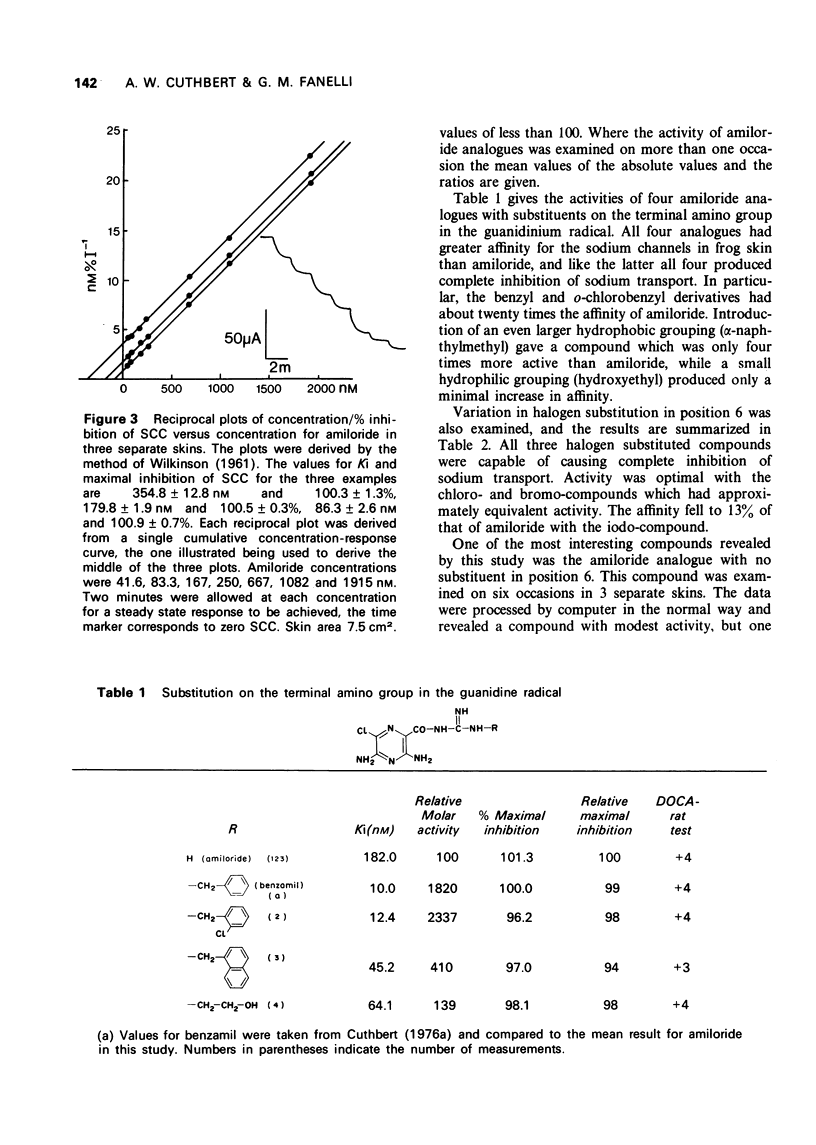
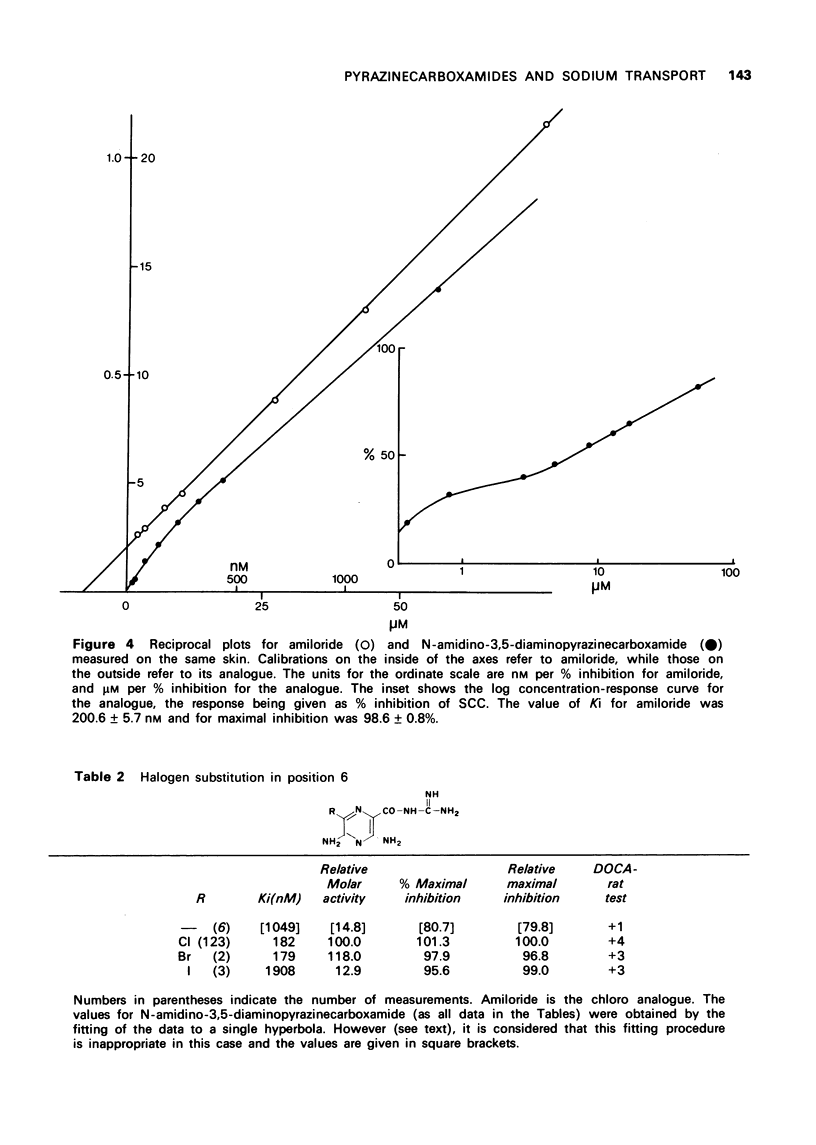
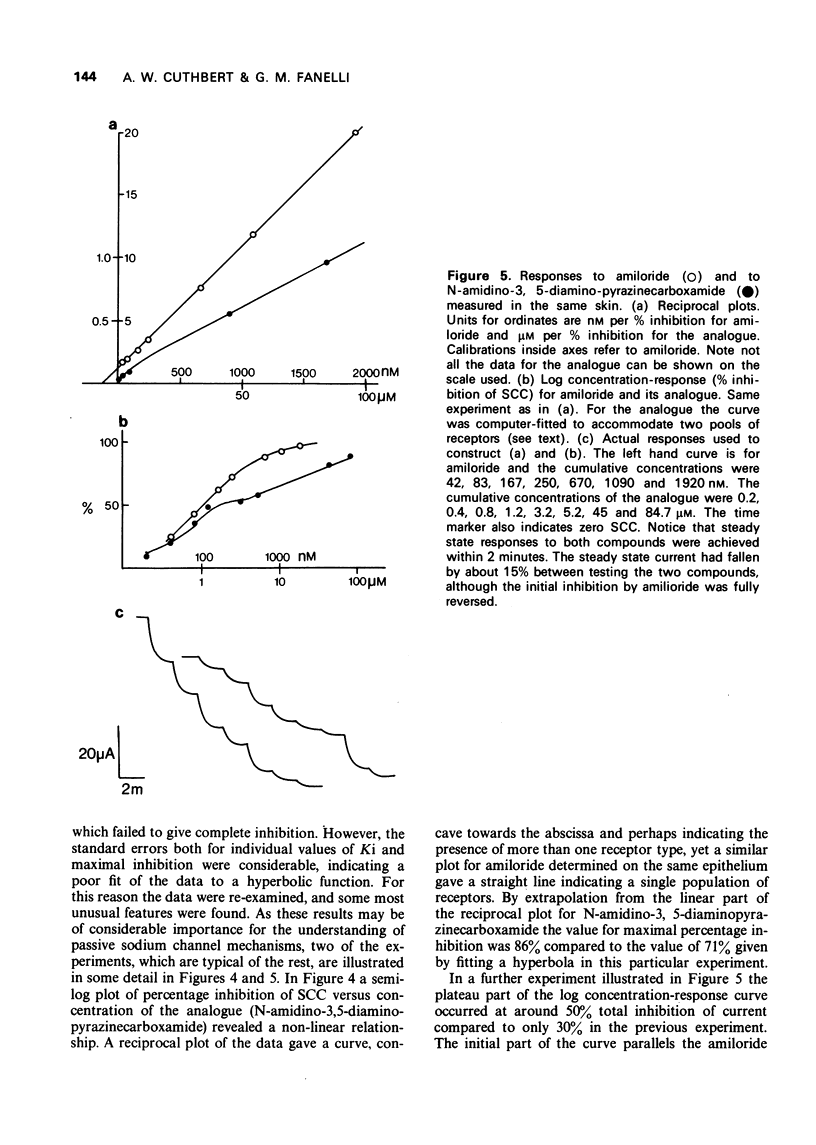
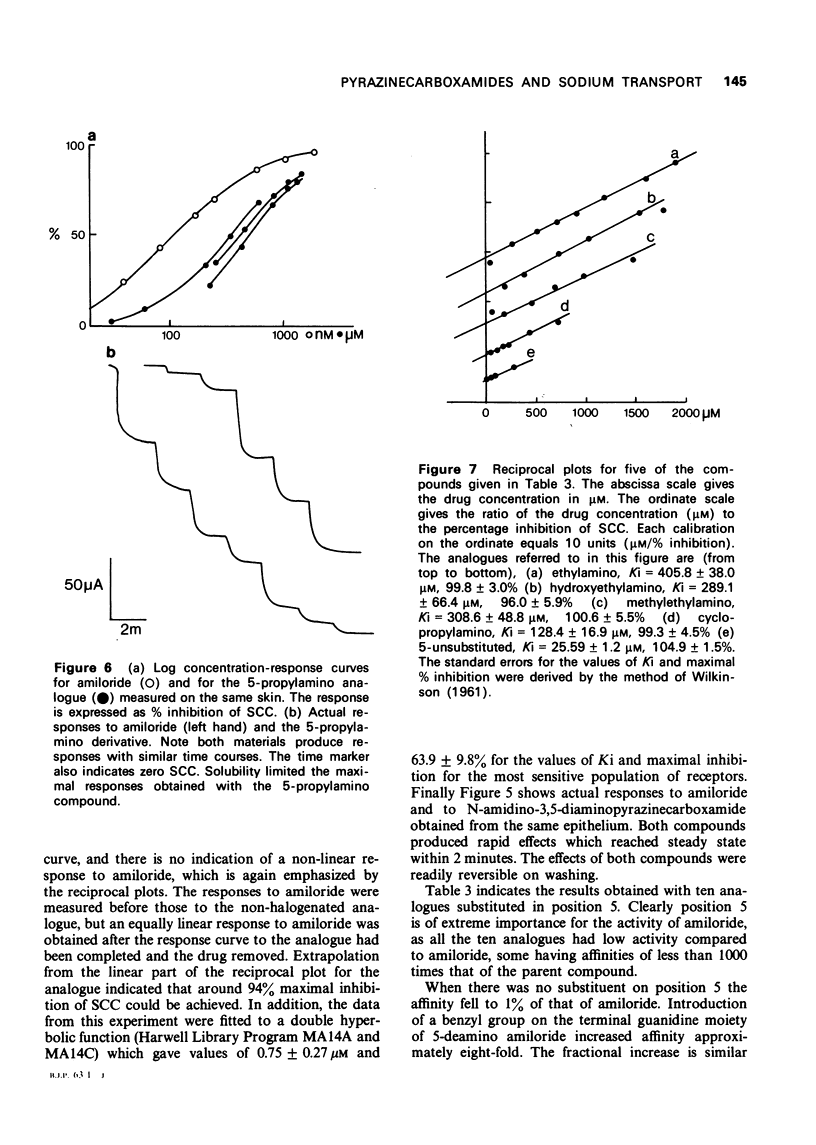
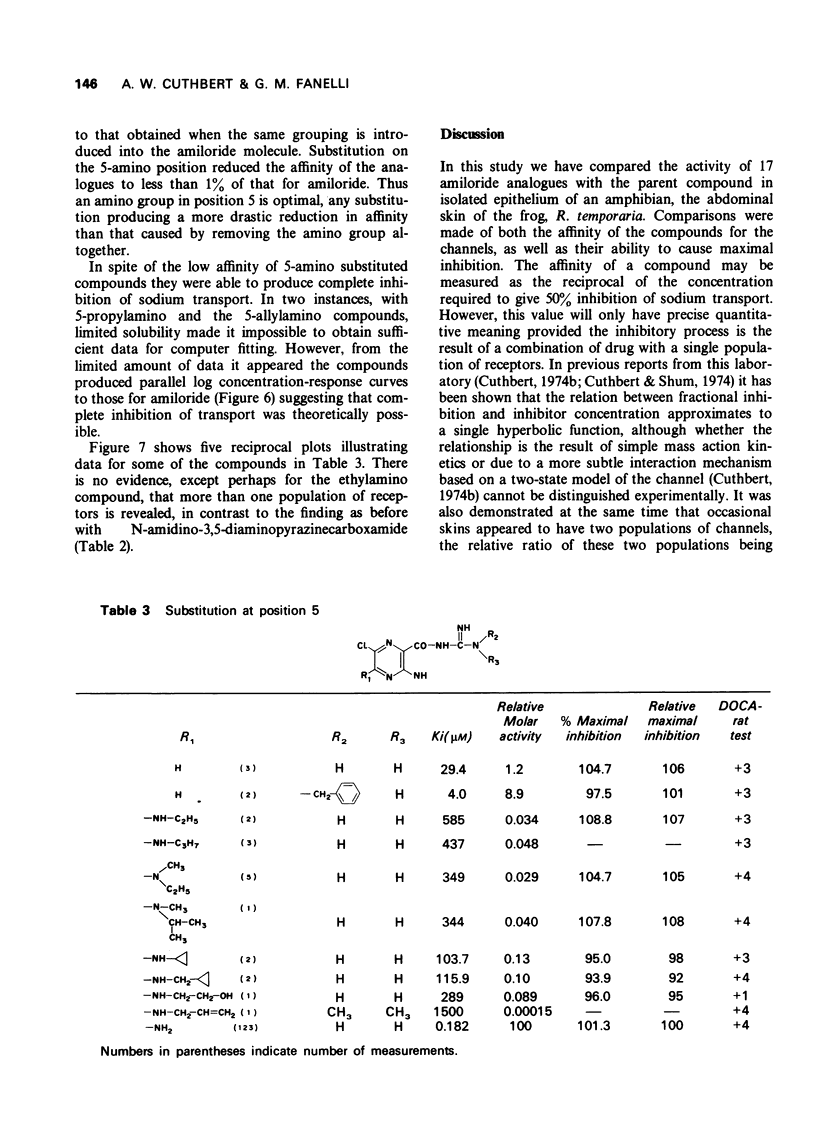
1 The inhibitory effect of amiloride (N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide) on sodium transport in isolated skin of frog has been compared with 17 of its analogues. The dissociation constant of amiloride for passive sodium channels was 181.9 +/- 8.9 nM, and the maximal percentage inhibition of sodium transport was 101.3 +/- 0.4% (means of 123 measurements) when measured at a sodium concentration of 111 mM. 2 The N-benzylamidino and N-o-chlorobenzylamidino compounds had affinities approximately 20 times larger than those for amiloride, and produced maximal inhibition of transport. 3 Substitution of chlorine in the 6-position by other halogens showed that the bromo-compound was equally active to amiloride, whereas the iodo derivative had an affinity equal to 15% of that for amiloride. 4 Substitution in the 5-amino group in 10 compounds reduced the affinities to less than 1% of that of amiloride, without affecting their ability to produce complete inhibition of transport. 5 N-Amidino-3,5-diaminopyrazinecarboxamide was unique in that it produced an unusual concentration-response relationship.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benos D. J., Simon S. A., Mandel L. J., Cala P. M. Effect of amiloride and some of its analogues of cation transport in isolated frog skin and thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jul;68(1):43–63. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber T. U. Effect of changes in transepithelial transport on the uptake of sodium across the outer surface of the frog skin. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Aug;58(2):131–144. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicking J. B., Robb C. M., Kwong S. F., Cragoe E. J., Jr Pyrazine diuretics. 3. 5- and 6-alkyl, -cycloalkyl, and -aryl derivatives of n-amidino-3-aminopyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Jul;10(4):598–602. doi: 10.1021/jm00316a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragoe E. J., Jr, Woltersdorf O. W., Jr, Bicking J. B., Kwong S. F., Jones J. H. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Jan;10(1):66–75. doi: 10.1021/jm00313a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in frog skin epithelium. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):681–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. Evidence for multiple forms of receptors for amiloride in transporting epithelia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;23(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. Importance of guanidinium groups of blocking sodium channels in epithelia. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):945–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Okpako D., Shwm W. K. Proceedings: Aldosterone, moulting and the number of sodium channels in frog skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 May;51(1):128P–129P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Shum W. K. Characteristics of the entry process for sodium in transporting epithelia as revealed with amiloride. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):587–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Shum W. K. Effects of vasopressin and aldosterone on amiloride binding in toad bladder epithelial cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 17;189(1097):543–575. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Shum W. K. Estimation of the lifespan of amiloride binding sites in the membranes of toad bladder epithelial cells. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):605–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Shum W. K. Induction of transporting sites in a sodium transporting epithelium. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;260(1):223–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörge A., Nagel W. Effect of amiloride on sodium transport in frog skin. II. Sodium transport pool and unidirectional fluxes. Pflugers Arch. 1970;321(2):91–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00586365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich E. N., Crabbé J. The mechanism of action of amipramizide. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):79–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00586783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. H., Bicking J. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr Pyrazine diuretics. IV. N-amidino-3-amino-6-substituted pyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Sep;10(5):899–903. doi: 10.1021/jm00317a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS F., ROMANOFF L. P., PINCUS G. The electrolyte-excreting activity of adrenocortical substances. Endocrinology. 1952 Mar;50(3):286–293. doi: 10.1210/endo-50-3-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Tomilson R. W. The effect of amiloride on sodium transport in the normal and moulting frog skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Jun;79(2):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salako L. A., Smith A. J. Effects of amiloride on active sodium transport by the isolated frog skin: evidence concerning site of action. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;38(4):702–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Yeung C. H. Inhibition by amiloride of sodium-dependent fluid reabsorption in the rat isolated caudal epididymis. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;58(4):529–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb08620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


