Abstract
1 The actions of morphine, methionine and leucine enkephalin, administered electrophoretically, were studied on supraspinal neurones in the cortex and brainstem of the rat anaesthetized with urethane and on spinal Renshaw cells and dorsal horn interneurones in the cat anaesthetized with pentobarbitone.
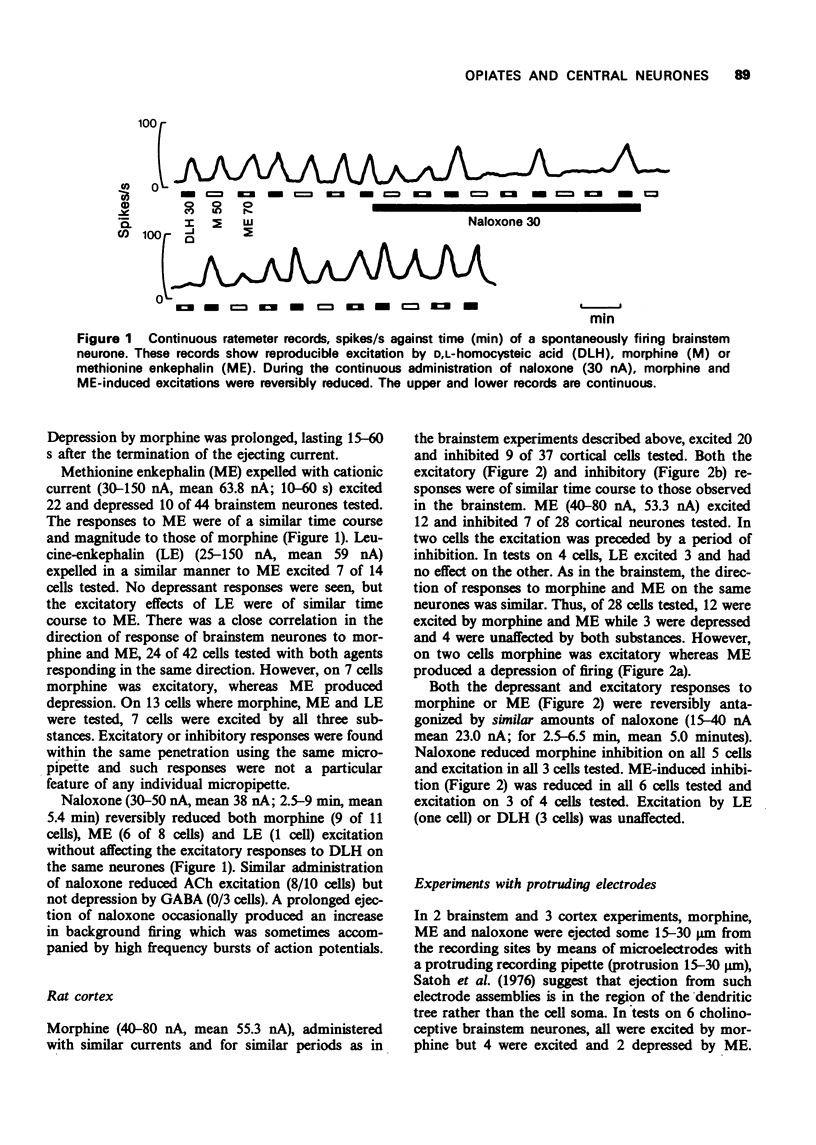
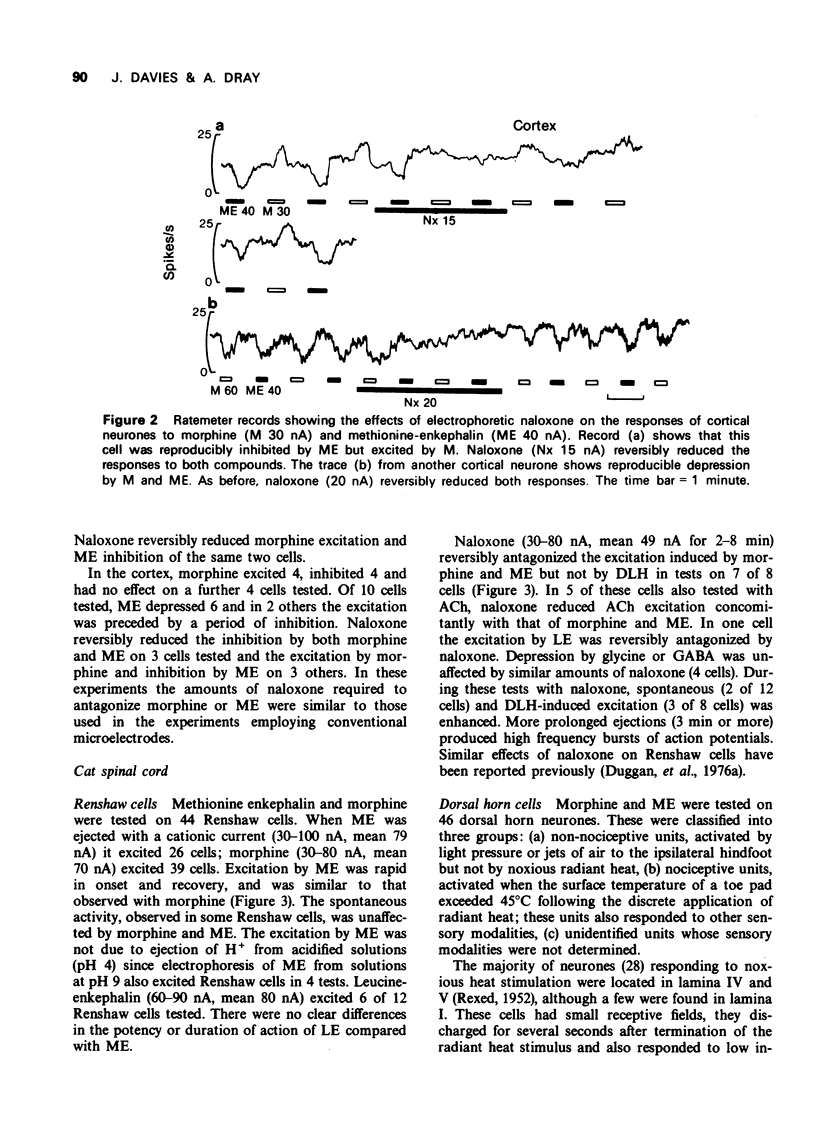
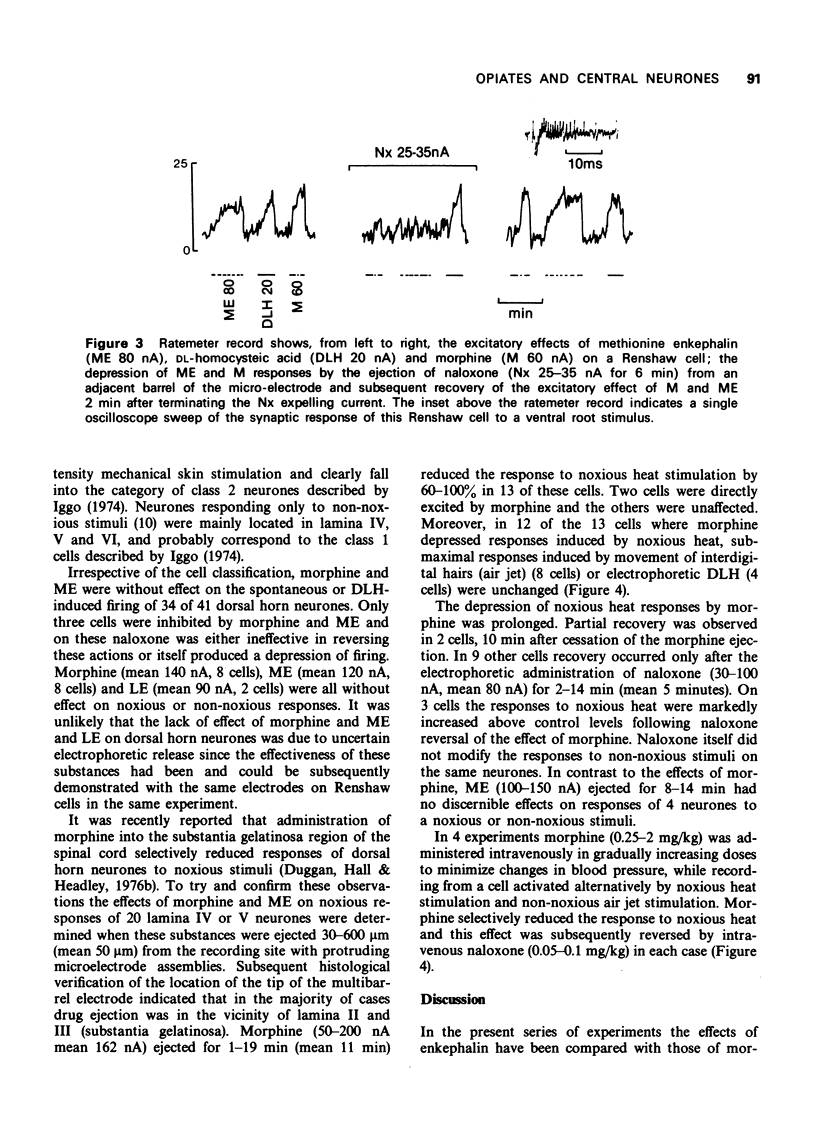
2 The majority of Renshaw cells and cortical and brainstem neurones were excited by all three compounds although some supraspinal neurones were depressed.
3 Naloxone reversibly antagonized both excitatory and depressant actions of morphine and enkephalin. Acetylcholine-induced excitation but not amino acid-induced excitation was also antagonized by naloxone.
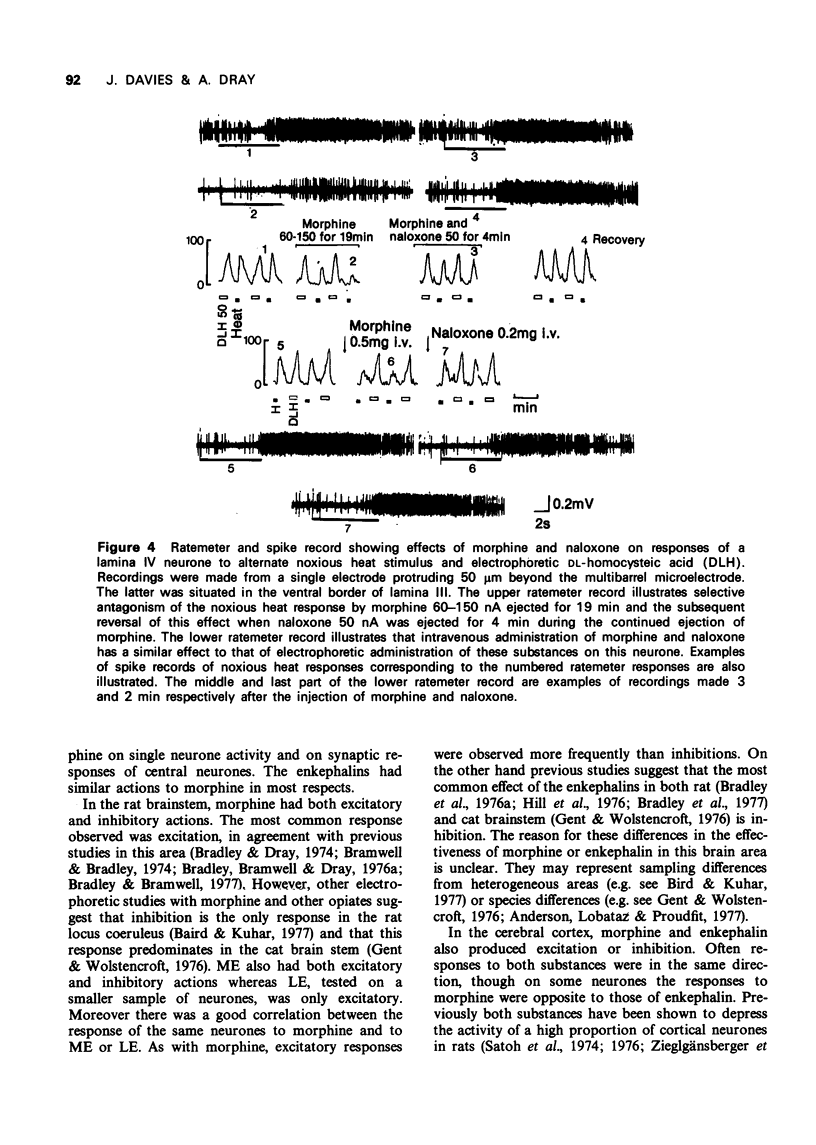
4 Neither morphine nor the enkephalins had any naloxone-reversible action on dorsal horn neurones when ejected from conventional multibarrelled electrodes. However, morphine but not enkephalin, administered into the substantia gelatinosa region of the spinal cord selectively reduced responses to noxious stimuli of neurones in deeper laminae. Naloxone administered into the same region antagonized this action of morphine.
5 Intravenous morphine also antagonized responses of dorsal horn neurones to noxious stimuli and subsequent intravenous naloxone reversed this effect.
6 It was concluded that the excitatory and inhibitory effects of morphine and enkephalin on central neurones may be mediated by actions on different opiate receptors and that depression of noxious responses of dorsal horn neurones may be relevant to the analgesic action of morphine.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. D., Basbaum A. I., Fields H. L. Response of medullary raphe neurons to peripheral stimulation and to systemic opiates. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 11;123(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter M. G., Goff D., Miller A. A., Saunders I. A. Effect of a potent synthetic opioid pentapeptide in some anti-nociceptive and behavioural tests in mice and rats [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):455P–456P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi J. D., Grant N., Garsky V., Sarantakis D., Wise C. D., Stein L. Analgesia induced in vivo by central administration of enkephalin in rat. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):625–626. doi: 10.1038/260625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird S. J., Kuhar M. J. Iontophoretic application of opiates to the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Bramwell G. J. Stereoscpecific actions of morphine on single neurones in the brain stem of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Jul-Aug;16(7-8):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Gayton R. J., Lambert L. A. Effects of microiontophoretically applied methionine-enkephalin on single neurones in rat brain. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):425–426. doi: 10.1038/261425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dray A. Modification of the responses of brain stem neurones to transmitter substances by anaesthetic agents. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;48(2):212–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb06907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dray A. Morphine and neurotransmitter substances: Microiontophoretic study in the rat brain stem. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramwell G. J., Bradley P. B. Actions and interactions of narcotic agonists and antagonists on brain stem neurones. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buscher H. H., Hill R. C., Römer D., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Pless J. Evidence for analgesic activity of enkephalin in the mouse. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):423–425. doi: 10.1038/261423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvillo O., Henry J. L., Neuman R. S. Effects of morphine and naloxone on dorsal horn neurones in the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(6):1207–1211. doi: 10.1139/y74-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou D. T., Wang S. C. Unit activity of amygdala and hippocampal neurons: effects of morphine and benzodiazepines. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):427–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90595-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Actions of enkephalin and morphine on spinal cord and brain stem neurones [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):458P–459P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Effects of enkephalin and morphine on Renshaw cells in feline spinal cord. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):603–604. doi: 10.1038/262603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Duggan A. W. Opiate agonist-antagonist effects on Renshaw cells and spinal interneurones. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):70–71. doi: 10.1038/250070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Effects of morphine and naloxone on Renshaw cells and spinal interneurones in morphine dependent and non-dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;113(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90943-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostrovsky J. O., Pomeranz B. Interaction of iontophoretically applied morphine with responses of interneurons in cat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 1976 Aug;52(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostrovsky J., Pomeranz B. Morphine blockade of amino acid putative transmitters on cat spinal cord sensory interneurones. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):222–224. doi: 10.1038/newbio246222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Davies J., Hall J. G. Effects of opiate agonists and antagonists on central neurons of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Morphine, enkephalin and the substantia gelatinosa. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):456–458. doi: 10.1038/264456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Suppression of transmission of nociceptive impulses by morphine: selective effects of morphine administered in the region of the substantia gelatinosa. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):65–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent J. P., Wolstencroft J. H. Effects of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin compared with those of morphine on brainstem neurones in cat. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):426–427. doi: 10.1038/261426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Szekely J. I., Ronai A. Z., Dunai-Kovacs Z., Bajusz S. Comparative study on analgesic effect of Met5-enkephalin and related lipotropin fragments. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):240–242. doi: 10.1038/263240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambrook J. M., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Mode of deactivation of the enkephalins by rat and human plasma and rat brain homogenates. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):782–783. doi: 10.1038/262782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Pepper C. M., Mitchell J. F. Depression of nociceptive and other neurones in the brain by iontophoretically applied met-enkephalin. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):604–606. doi: 10.1038/262604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Hughes J. Some thoughts on the significance of enkephalin, the endogenous ligand. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars D., Menétrey D., Conseiller C., Besson J. M. Depressive effects of morphine upon lamina V cells activities in the dorsal horn of the spinal cat. Brain Res. 1975 Nov 14;98(2):261–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Siggins G. R., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Neuronal actions of endorphins and enkephalins among brain regions: a comparative microiontophoretic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. Enkephalin inhibits firing of myenteric neurones. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):460–461. doi: 10.1038/264460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Autoradiograhic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1849–1853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Zieglgänsberger W., Fries W., Herz A. Opiate agonist-antagonist interaction at cortical neurones of naive and tolerant/dependent rats. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 27;82(2):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Zieglgänsberger W., Herz A. Actions of opiates upon single unit activity in the cortex of naive and tolerant rats. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90825-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Morphine and enkephalin interactions with putative neurotransmitters in rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Sep;16(9):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. The regional distribution of a morphine-like factors enkephalin in monkey brain. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. A morphine-like factor 'enkephalin' in rat brain: subcellular localization. Brain Res. 1976 May 14;107(3):650–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder H. Isolation and structure identification of a morphine-like peptide "enkephalin" in bovine brain. Life Sci. 1976 Apr 15;18(8):781–787. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L., Wahlström A. Search for an endogenous ligand for the opiate receptor. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 May;94(1):74–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. E. Somaesthetic pathways. Br Med Bull. 1977 May;33(2):113–120. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Studies on the direct spinal action of narcotics in the production of analgesia in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):411–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Bayerl H. The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90826-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Fry J. P., Herz A., Moroder L., Wünsch E. Enkephalin-induced inhibition of cortical neurones and the lack of this effect in morphine tolerant/dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


