Abstract
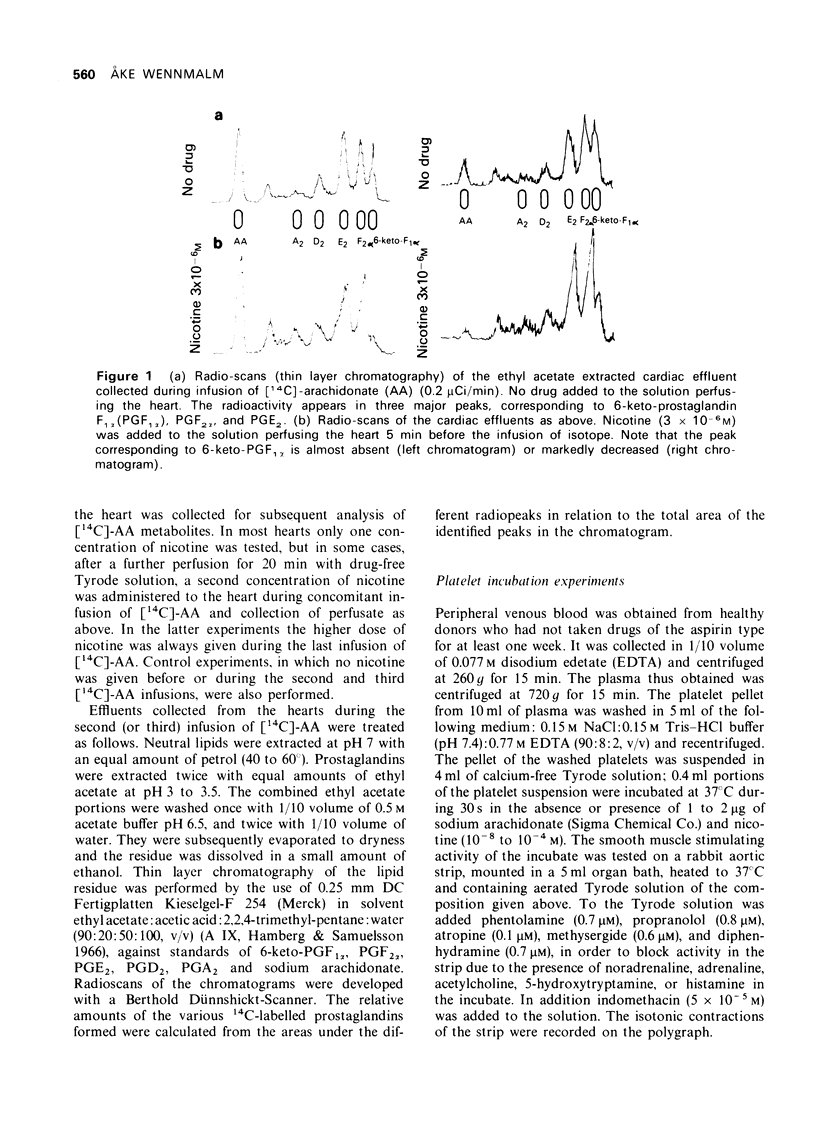
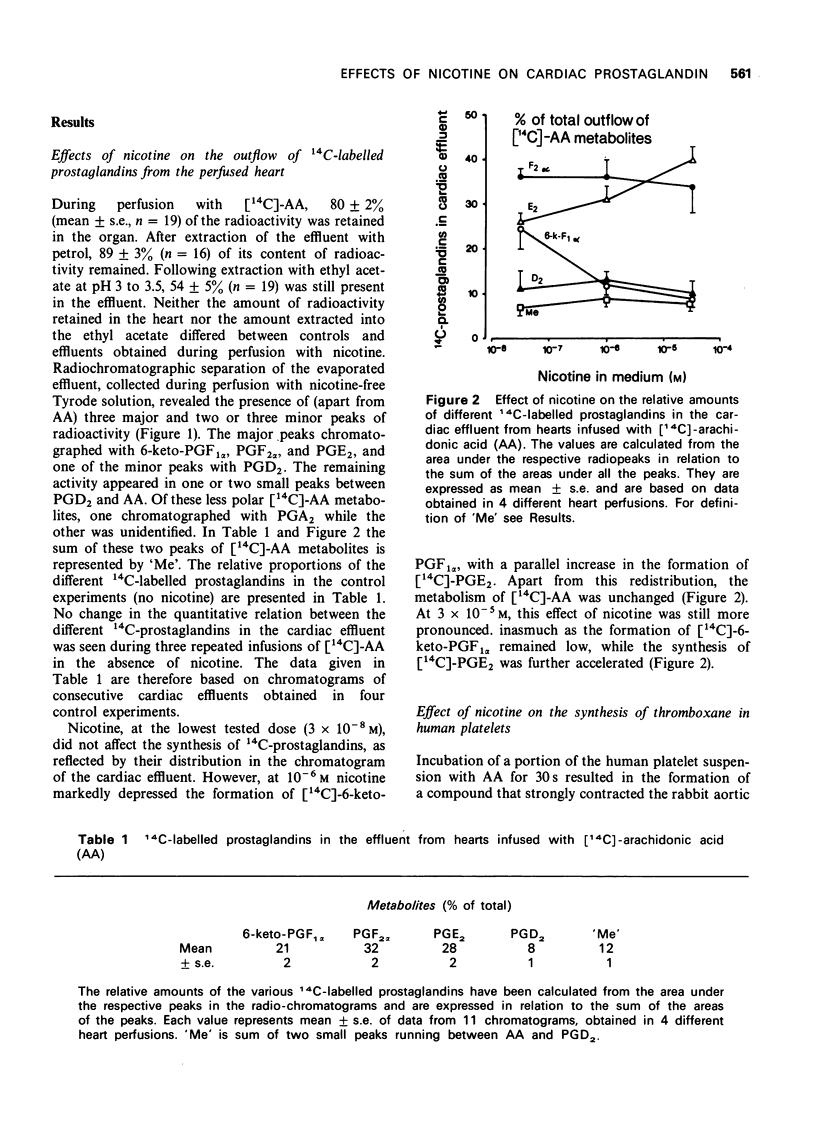
1 Rabbit hearts were perfused with a solution containing [14C]-arachidonic acid (AA) and various concentrations of nicotine (3 x 10(-8) to 3 x 10(-5) M). The venous effluent was collected and extracted for lipid acid material, which was subsequently subjected to thin layer radiochromatography. 2 Human platelets were incubated with nicotine (10(-8) to 10(-4) M), in the absence or presence of unlabelled AA. The amount of smooth muscle stimulating activity resulting from 30s of incubation was tested on a rabbit aortic strip. 3 In hearts perfused with [14C]-AA; nicotine induced a dose-related depression of the release of [14C]-6-keto-prostaglandin F1alpha, and a parallel increase of [14C]-prostaglandin E2. 4 Nicotine neither induced synthesis of thromboxane in human platelets, nor affected the platelet synthesis of thromboxane induced by AA. 5 It is suggested that nicotine affects the metabolism of prostaglandin endoperoxides in the heart by inhibiting their conversion to prostacyclin and facilitating, directly or indirectly, the formation of prostaglandin E2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Bunting S., Moncada S., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Arterial walls are protected against deposition of platelet thrombi by a substance (prostaglandin X) which they make from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Prostaglandins. 1976 Nov;12(5):685–713. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Prostaglandins in human seminal plasma. Prostaglandins and related factors 46. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junstad M., Wennmalm A. On the release of prostaglandin E2 from the rabbit heart following infusion of noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Apr;87(4):573–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin-like substance into renal venous blood in response to angiotensin II. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkes M. S., Douglas J. R., Jr, Needleman P. Prostaglandin release by the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Prostaglandins. 1973 Apr;3(4):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrör K., Moncada S., Ubatuba F. B., Vane J. R. Transformation of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin endoperoxides by the guinea pig heart. Formation of RCS and prostacyclin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan 1;47(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90380-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A., Junstad M. Nicotine mediated release of prostaglandin E from the rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Feb;96(2):281–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A. Nicotine stimulates prostaglandin formation in the rabbit heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;59(1):95–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb06981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker N., Bunting S., Salmon J., Moncada S., Vane J. R., Johnson R. A., Morton D. R., Kinner J. H., Gorman R. R., McGuire J. C. The chemical structure of prostaglandin X (prostacyclin). Prostaglandins. 1976 Dec;12(6):915–928. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


