Abstract
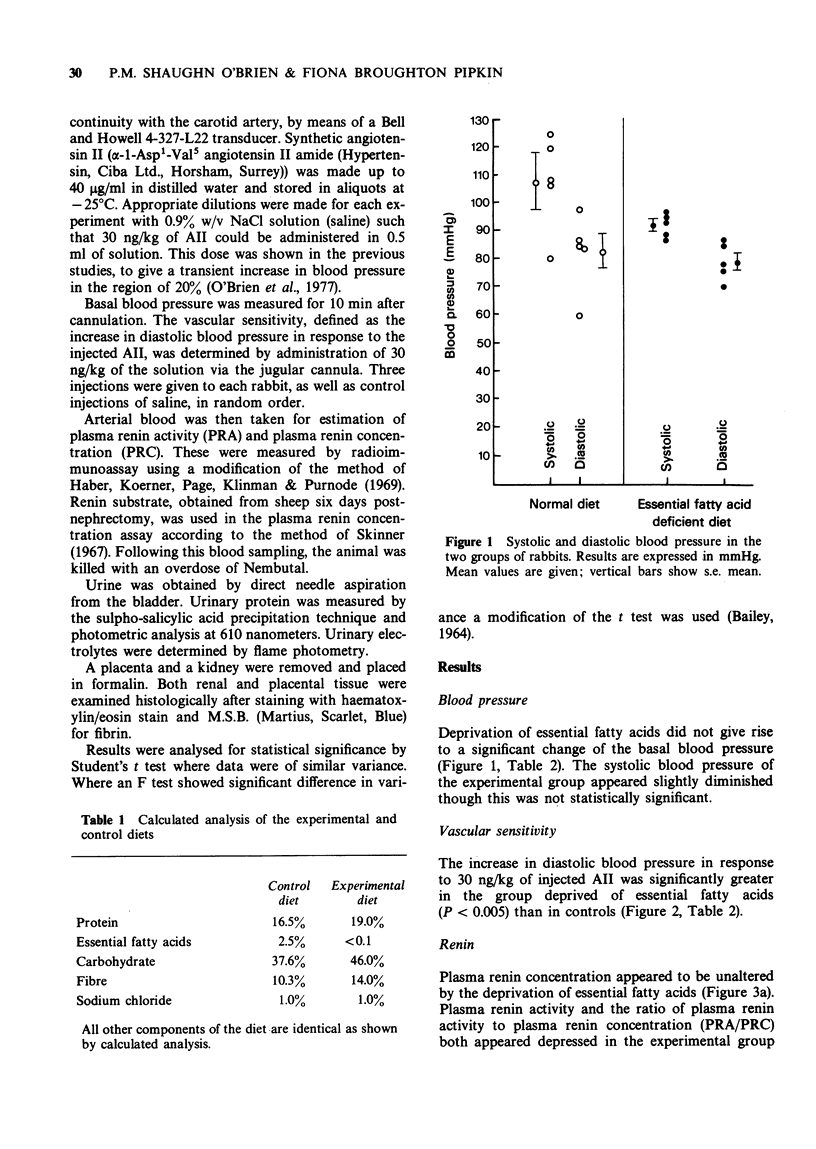
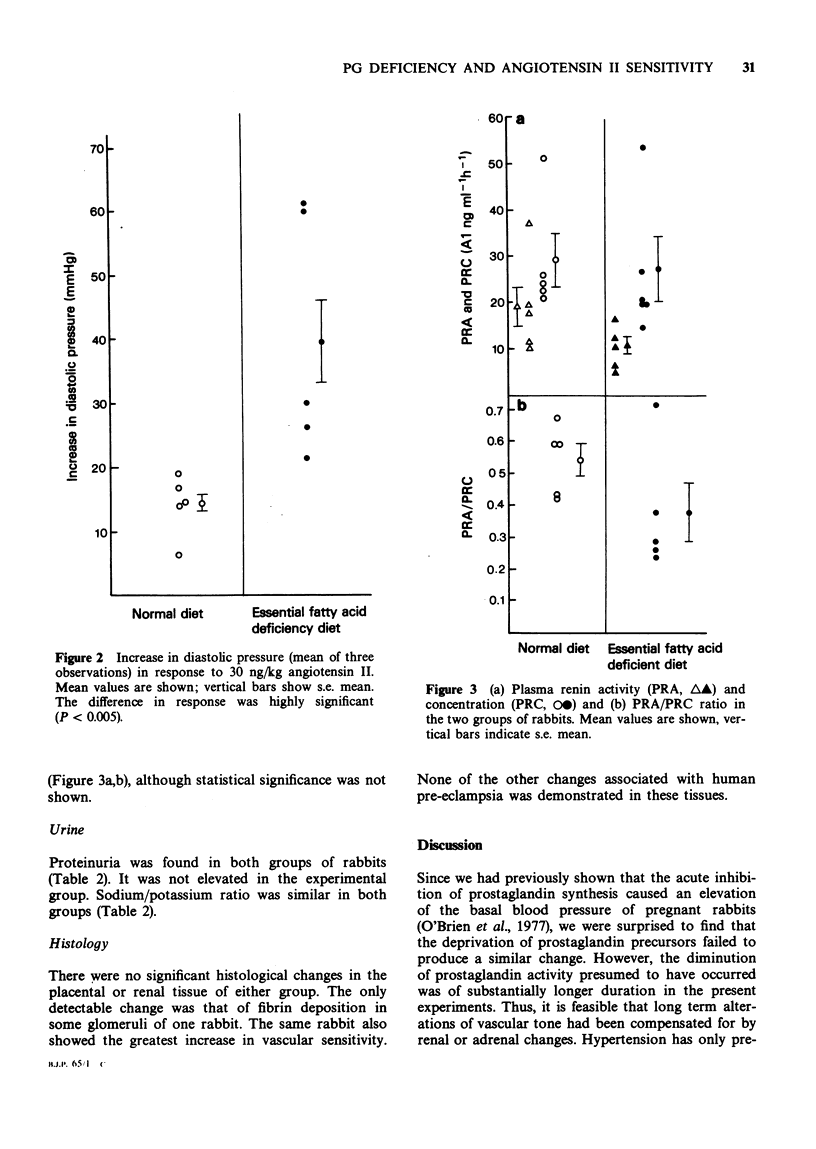
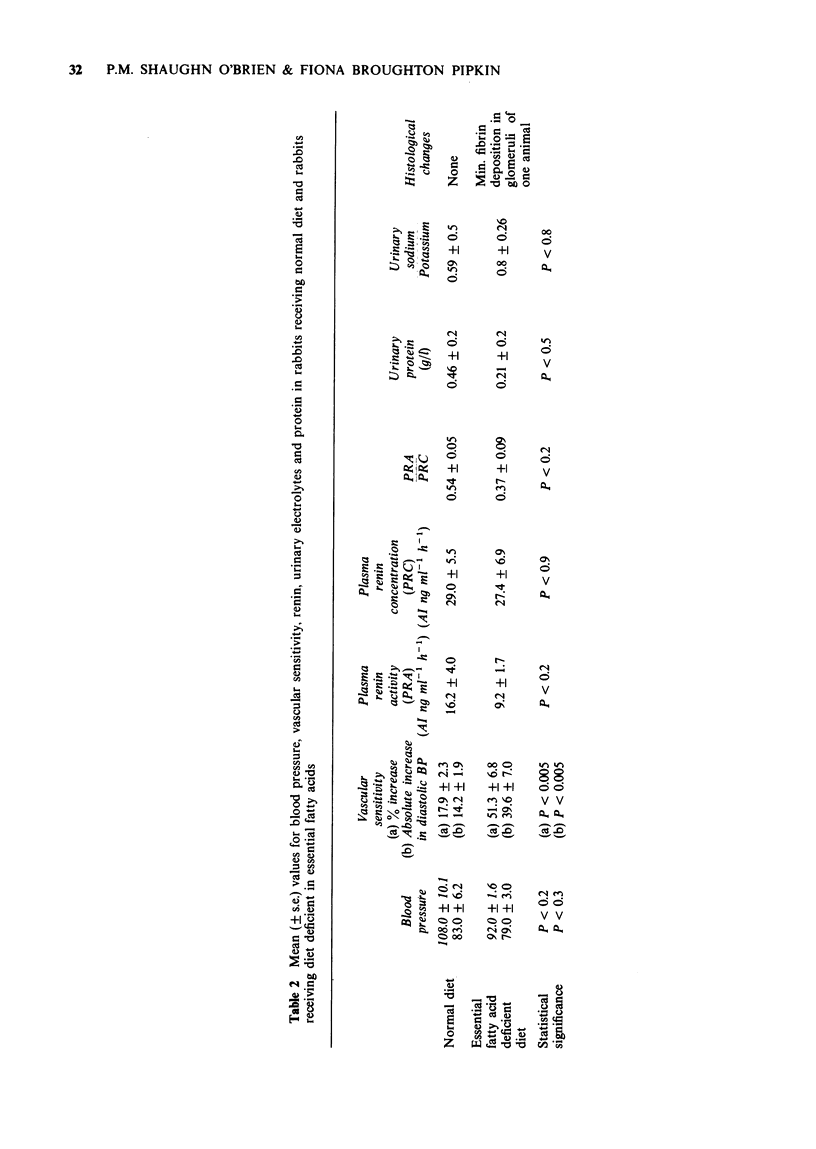
1 Pregnant rabbits were deprived of essential fatty acids from day ten of pregnancy, and results compared with a control group on a normal diet. 2 At term, cannulation of jugular and carotid vessels was performed under anaesthesia, to study the vascular sensitivity to angiotensin II and basal blood pressure. 3 Plasma renin levels, urinary electrolytes and protein were measured. 4 Placental and renal tissue was examined histologically. 5 Though no changes were found in tissues, blood or urine, a markedly significant increase in response to angiotensin II was found in the group deprived of essential fatty acids. This parallels the findings in vascular response in human pre-eclampsia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dazord A., Morera A. M., Bertrand J., Saez J. M. Prostaglandin receptors in human and ovine adrenal glands: binding and stimulation of adenyl cyclase in subcellular preparations. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):352–359. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES S. W., HORTON E. W., MAIN I. H. THE EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 ON RESPONSES OF SMOOTH MUSCLE TO CATECHOL AMINES, ANGIOTENSIN AND VASOPRESSIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:538–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaa E. In vitro biosynthesis of prostaglandin E2 by kidney medulla of essential fatty acid deficient rats. Lipids. 1976 Sep;11(9):693–696. doi: 10.1007/BF02532889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Weber P., Anggård E. Arachidonic acid increases and indomethacin decreases plasma renin activity in the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;28(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Itskovitz H. D. Prostaglandins and renal function. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. M., Filshie G. M., Broughton Pipkin F. The effect of prostaglandin E2 on the cardiovascular response to angiotensin II in pregnant rabbits. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jan;13(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J., Simone P. G., Silbergleit A. Effects of prostaglandin deficiency on natriuresis, diuresis, and blood pressure. Prostaglandins. 1974 Mar 10;5(5):435–440. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMLER F. W. Fatal eclamptic disease of pregnant rats fed anti-vitamin E stress diet. Am J Pathol. 1959 Nov-Dec;35:1207–1231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L., Lumbers E. R., Symonds E. M. Analysis of changes in the renin-angiotensin system during pregnancy. Clin Sci. 1972 Apr;42(4):479–488. doi: 10.1042/cs0420479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speroff L. An autoregulatory role for prostaglandins in placental hemodynamics: their possible influence on blood pressure in pregnancy. J Reprod Med. 1975 Nov;15(5):181–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds E. M., Broughton Pipkin F., Craven D. J. Changes in the renin-angiotensin system in primigravidae with hypertensive disease of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1975 Aug;82(8):643–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1975.tb00700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


