Abstract
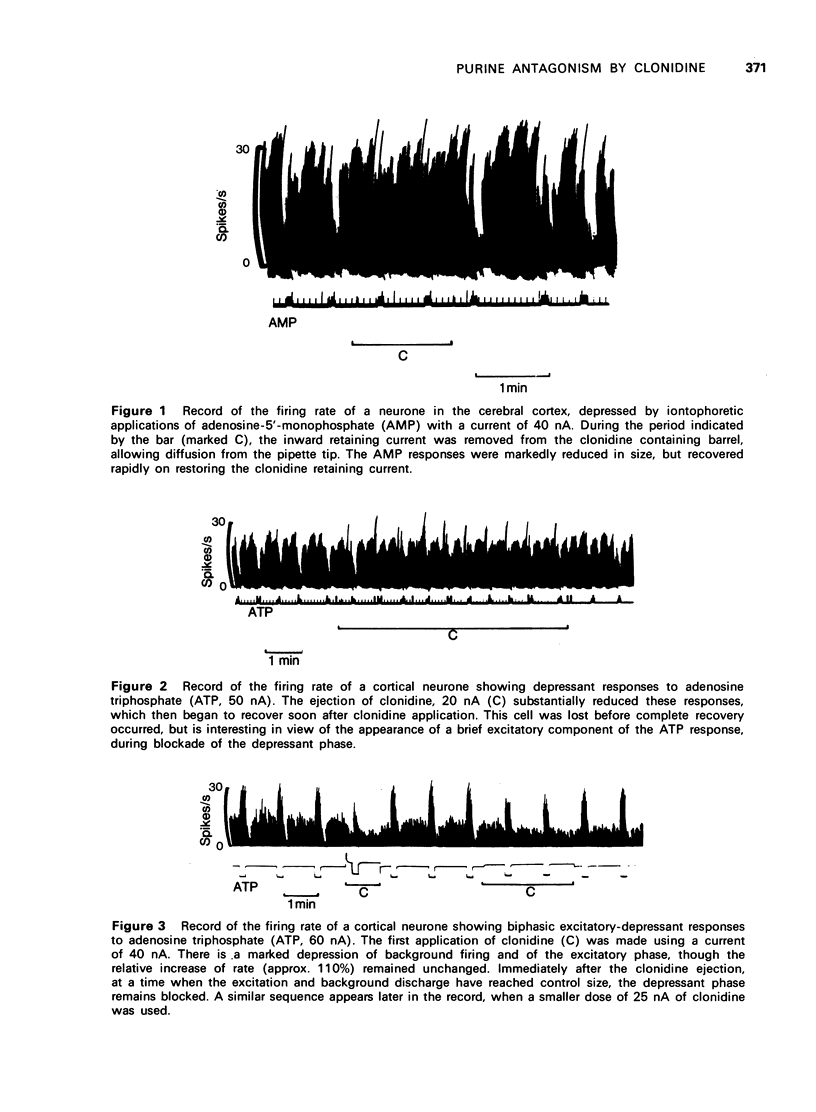
1. Adenosine and its nucleotides adenosine-5'-monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) have been applied by microiontophoresis to neurones in the cerebral cortex of rats anesthetized with urethane. The firing rate of most neurones was depressed, though two cells were encountered which showed biphasic responses to ATP consisting of an initial excitation succeeded by depression. 2. The application of clonidine with iontophoretic currents of less than 25 nA resulted in blockade of the depressant responses to the purines, without affecting responses to noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine or gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). At much higher doses of clonidine, direct depression of cell firing occurred and occasional interaction with noradrenaline was noted. 3. In the case of the biphasic responses to ATP, clonidine seemed to block only the depressant phase. Reduction of the excitatory component paralleled changes of background firing. 4. It is concluded that, in common with some other 2-substituted imidazoline derivatives, clonidine possesses the ability to block responses to purine compounds.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C., Stone T. W. On the mechanism of action of clonidine: effects on single central neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;51(3):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb10670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanachan A. S., Johns A., Paton D. M. Presynaptic inhibitory actions of adenine nucleotides and adenosine on neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1977;2(4):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Reid J. L. Central noradrenergic neurones and the cardiovascular actions of clonidine in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):206–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Hirst G. D. The effect of adenosine on the release of the transmitter from the phrenic nerve of the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):629–645. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B. Effects of adenosine on adrenergic neurotransmission; prejunctional inhibition and postjunctional enhancement. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;293(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00507344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulos G. K., Phillis J. W. Purinergic depression of neurons in different areas of the rat brain. Exp Neurol. 1977 Jun;55(3 Pt 1):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. Regulatory significance of the release and action of adenine derivatives in cerebral systems. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(36):69–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Kostopoulos G. K., Limacher J. J. Depression of corticospinal cells by various purines and pyrimidines. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(6):1226–1229. doi: 10.1139/y74-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Adenine derivatives as neurohumoral agents in the brain. The quantities liberated on excitation of superfused cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):975–981. doi: 10.1042/bj1300975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchell D., Burnstock G., Dann P. Antagonism of the effects of purinergic nerve stimulation and exogenously applied ATP on the guinea-pig taenia coli by 2-substituted imidazolines and related compounds. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;23(3):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Daly J. W. Effect of depolarizing agents on accumulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in cerebral cortical slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;17(2):240–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Daly J. W. Interaction of clonidine with pre- and post-synaptic adrenergic receptors of rat brain: effects on cyclic AMP-generating systems. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;39(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Cholinergic mechanisms in the rat somatosensory cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):485–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Cortical pyramidal tract interneurones and their sensitivity to L-glutamic acid. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):211–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Cortical responses to pyramidal tract stimulation in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1972 Jun;35(3):492–502. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Taylor D. A. An electrophysiological demonstration of a synergistic interaction between norepinephrine and adenosine in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1978 May 26;147(2):396–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90851-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Taylor D. A. Microiontophoretic studies of the effects of cylic nucleotides on excitability of neurones in the rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):523–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Stone T. W. Neuronal responses to extracellularly applied cyclic AMP:Role of the adenosine receptor. Experientia. 1978 Apr 15;34(4):481–482. doi: 10.1007/BF01935940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Knoll J. The inhibitory effect of adenosine and related nucleotides on the release of acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1976;1(5):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


