Abstract
1 Effects of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on single neurones in slices of guinea-pig olfactory cortex maintained in vitro were recorded with single intracellular microelectrodes. The average resting potential of 52 cells was -75 mV and apparent input resistance ranged from 20 to 200 MΩ.
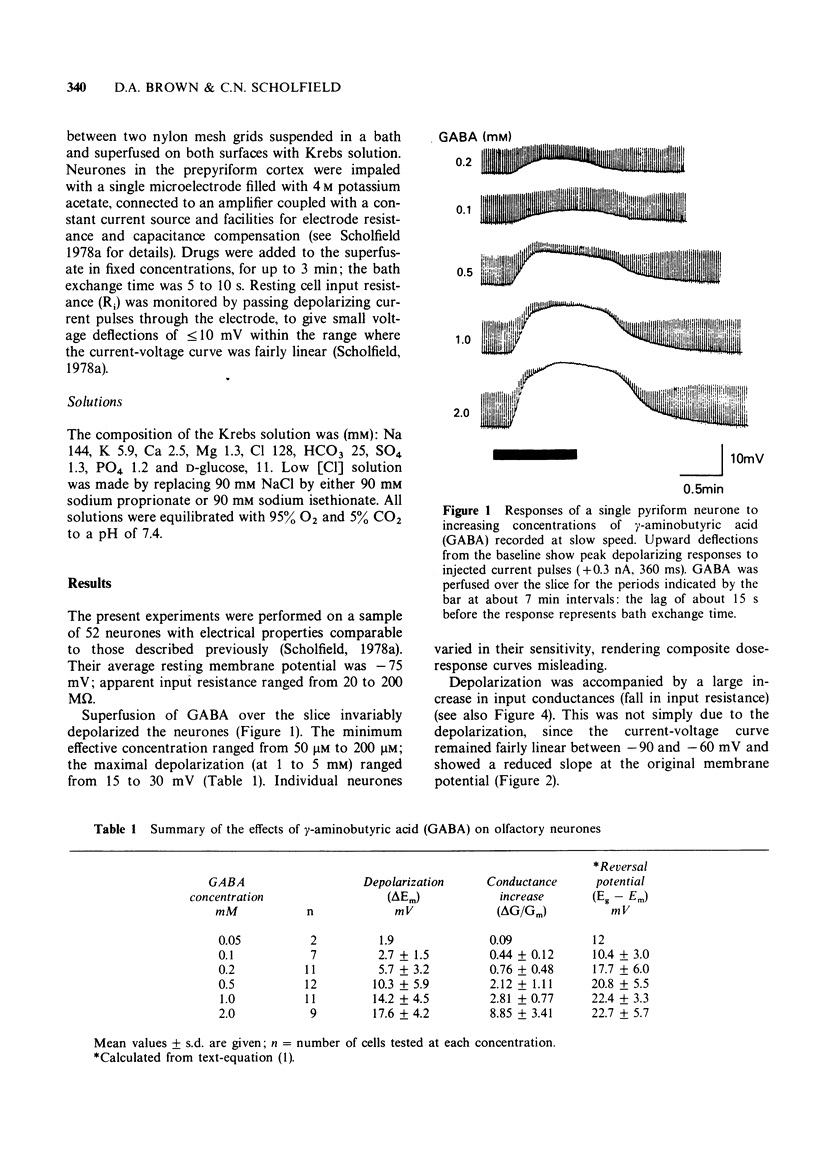
2 Superfusions of GABA over the slice invariably depolarized the neurones and reduced their input resistance. The minimum effective concentration was 50 to 200 μM.
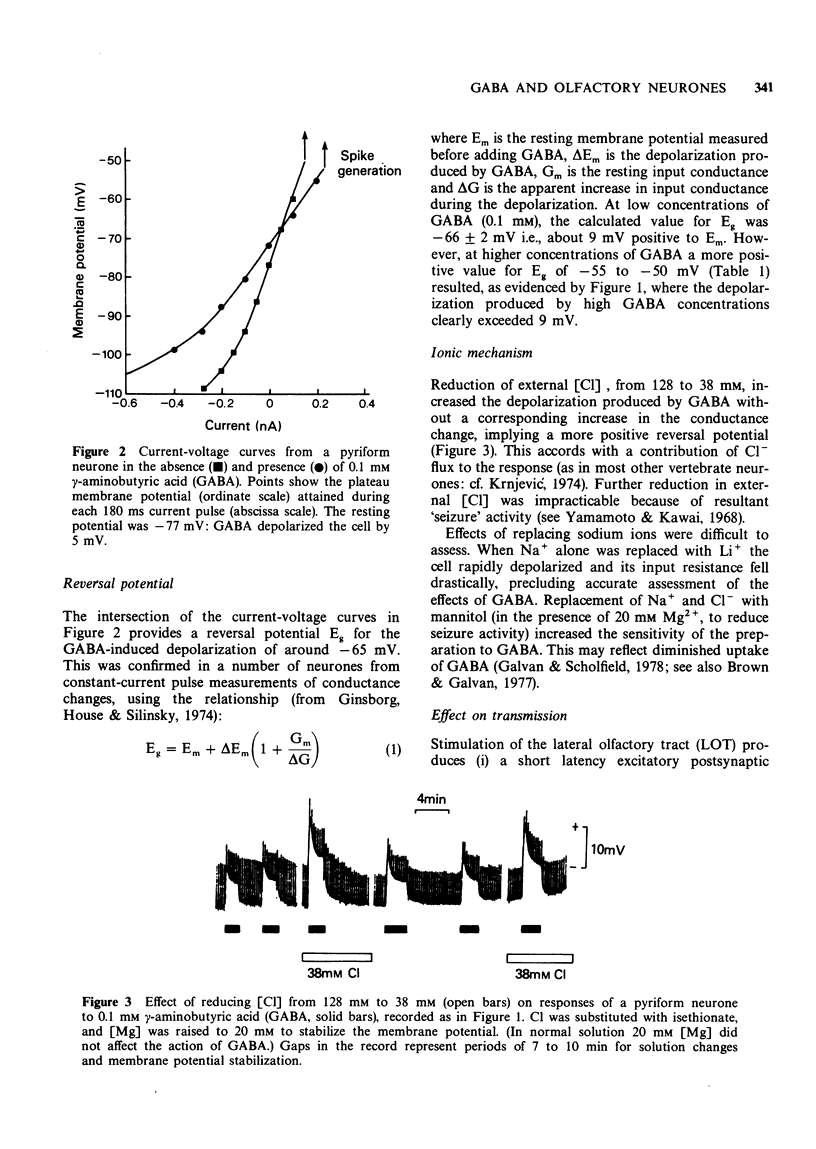
3 The reversal potential for the depolarization produced by 0.1 mM GABA (Eg) was -66 ± 2 mV. At concentrations >0.1 mM the reversal potential became progressively more positive (-55 to -50 mV).
4 Reduction of external chloride, with isethionate as the substitute anion, increased the amplitude of the depolarization.
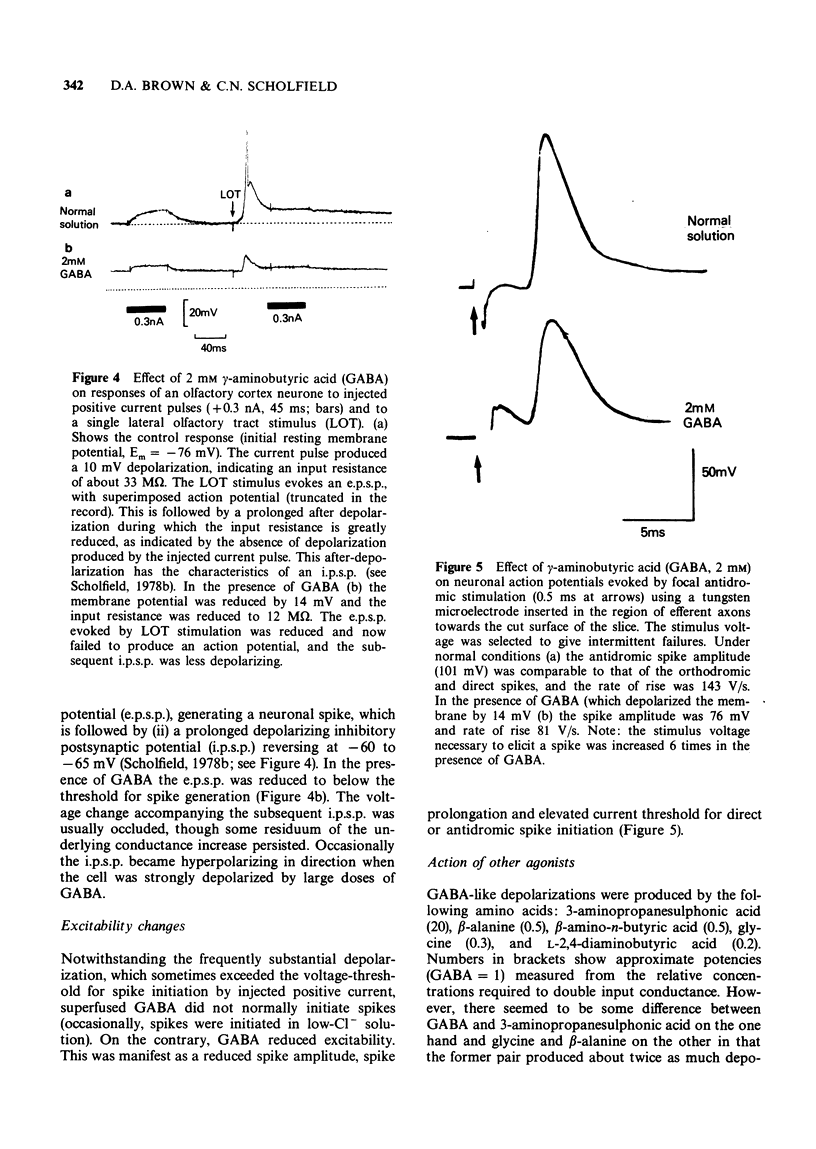
5 GABA reduced the amplitude of the excitatory postsynaptic potential produced by lateral olfactory tract stimulation, and occluded or reversed the subsequent depolarizing recurrent inhibitory postsynaptic potential.
6 Action potentials elicited by injection of depolarizing current or by focal antidromic stimulation were slowed and reduced in amplitude by GABA.
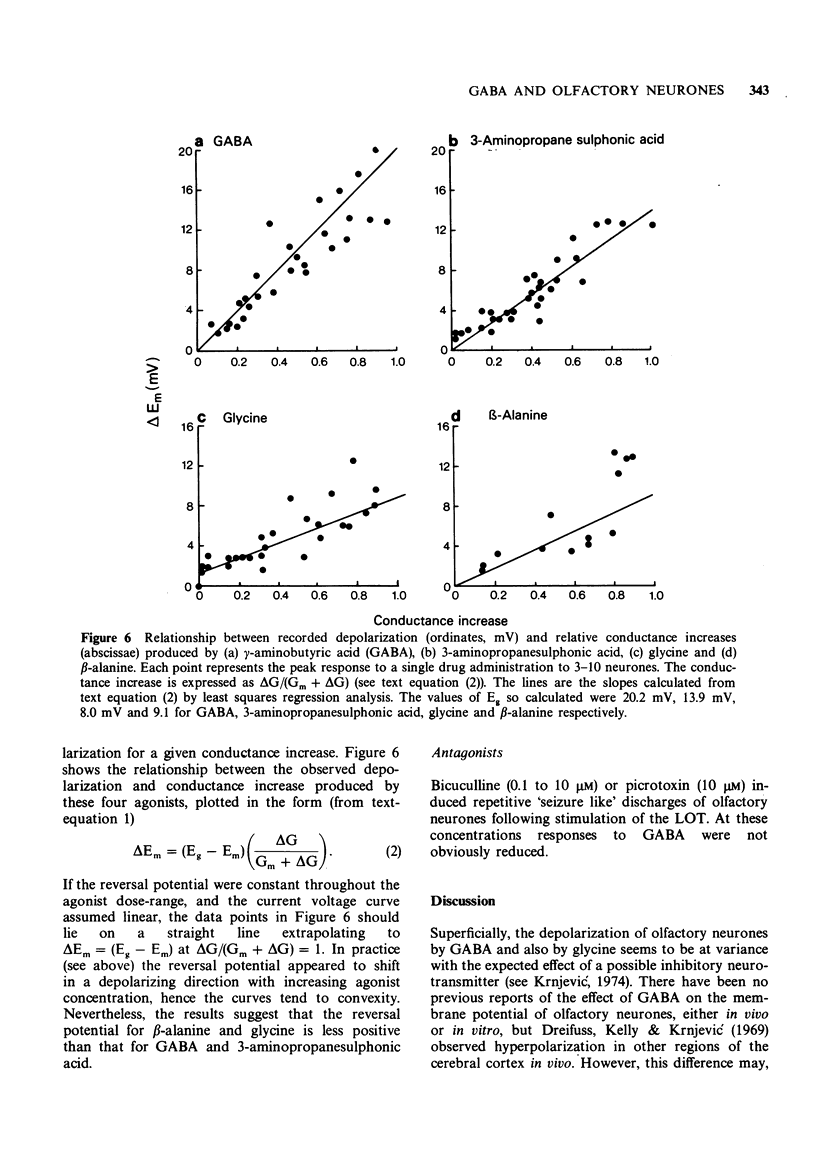
7 The effects of GABA on membrane conductance (potency = 1) were duplicated by 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid (potency = 20), β-alanine (0.5), β-amino-n-butyric acid (0.5), glycine (0.3) and L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid (0.2). For a given conductance change, 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid, glycine and β-alanine produced less depolarization than did GABA.
8 It is concluded that the action of GABA on the neurones is compatible with a role in mediating recurrent postsynaptic inhibition.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):85–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Galvan M. Influence of neuroglial transport on the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on mammalian ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A., Johnston I. H. The hyperpolarization of spinal motoneurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(3):235–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00238666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes M., Feltz P. GABA-induced rise of extracellular potassium in rat dorsal root ganglia: an electrophysiological study in vivo. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):494–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes M., Feltz P., Lamour Y. A model for an estimate in vivo of the ionic basis of presynaptic inhibition: an intracellular analysis of the GABA-induced depolarization in rat dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):486–493. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. Cortical inhibition and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00238327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. P., Higashi H., Nishi S. Characterization and ionic basis of GABA-induced depolarizations recorded in vitro from cat primary afferent neurones. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:263–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., House C. R., Silinsky E. M. Conductance changes associated with the secretory potential in the cockroach salivary gland. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):723–731. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L. Ion movements in junctional transmission. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):289–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. A., Scholfield C. N., Brown D. A. Evoked surface-positive potentials in isolated mammalian olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 16;76(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. GABA and glycine actions on spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):658–669. doi: 10.1139/y77-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legge K. F., Randic M., Straughan D. W. The pharmacology of neurones in the pyriform cortex. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Jan;26(1):87–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata K. Transmitter sensitivities of some nerve and muscle cells in culture. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):71–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. III. Neuronal chemosensitivity and its relationship to synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1163–1177. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Sercombe R. Electrical activity observed in guinea-pig olfactory cortex maintained in vitro. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):667–683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. A barbiturate induced intensification of the inhibitory potential in slices of guinea-pig olfactory cortex. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:559–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. A depolarizing inhibitory potential in neurones of the olfactory cortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:547–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. Electrical properties of neurones in the olfactory cortex slice in vitro. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:535–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., Kawai N. Generation of the seizure discharge in thin sections from the guinea pig brain in chloride-free medium in vitro. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Oct 15;18(5):620–631. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., McIlwain H. Electrical activities in thin sections from the mammalian brain maintained in chemically-defined media in vitro. J Neurochem. 1966 Dec;13(12):1333–1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


