Abstract
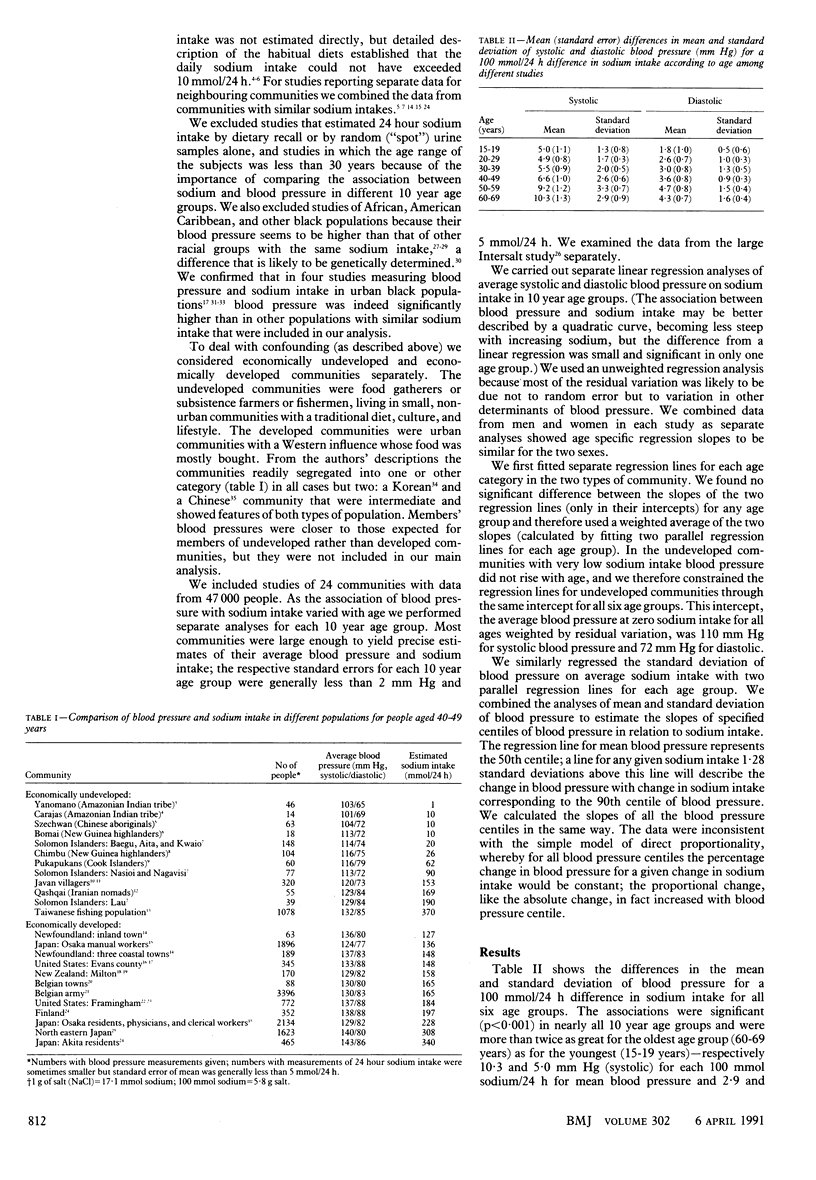
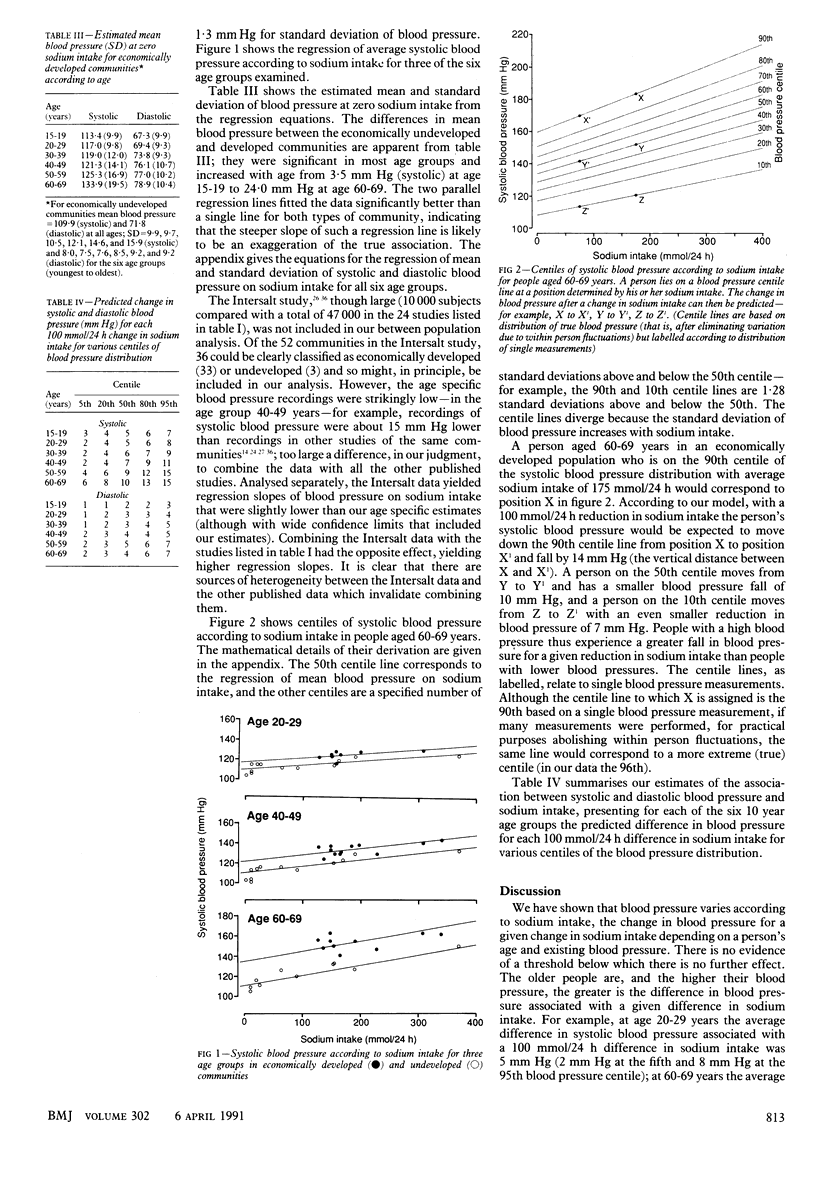
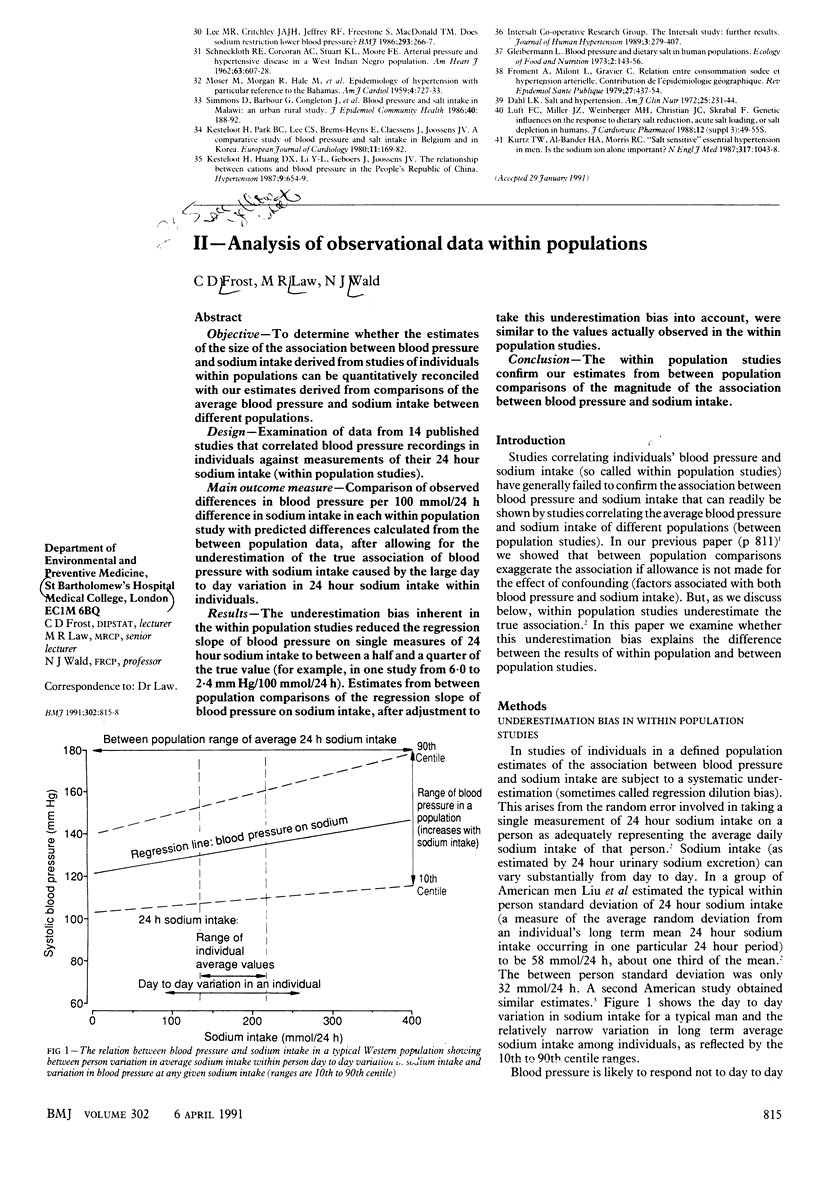
OBJECTIVE--To estimate the quantitative relation between blood pressure and sodium intake. DESIGN--Data were analysed from published reports of blood pressure and sodium intake for 24 different communities (47 000 people) throughout the world. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE--Difference in blood pressure for a 100 mmol/24 h difference in sodium intake. Allowance was made for differences in blood pressure between economically developed and undeveloped communities to minimise overestimation of the association through confounding with other determinants of blood pressure. RESULTS--Blood pressure was higher on average in the developed communities, but the association with sodium intake was similar in both types of community. A difference in sodium intake of 100 mmol/24 h was associated with an average difference in systolic blood pressure that ranged from 5 mm Hg at age 15-19 years to 10 mm Hg at age 60-69. The differences in diastolic blood pressure were about half as great. The standard deviation of blood pressure increased with sodium intake implying that the association of blood pressure with sodium intake in individuals was related to the initial blood pressure--the higher the blood pressure the greater the expected reduction in blood pressure for the same reduction in sodium intake. For example, at age 60-69 the estimated systolic blood pressure reduction in response to a 100 mmol/24 h reduction in sodium intake was on average 10 mm Hg but varied from 6 mm Hg for those on the fifth blood pressure centile to 15 mm Hg for those on the 95th centile. CONCLUSIONS--The association of blood pressure with sodium intake is substantially larger than is generally appreciated and increases with age and initial blood pressure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAILEY K. V. BLOOD-PRESSURE IN UNDERNOURISHED JAVANESE. Br Med J. 1963 Sep 28;2(5360):775–776. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5360.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES R. COMPARISONS OF BLOOD PRESSURES AND BLOOD CHOLESTEROL LEVELS OF NEW GUINEANS AND AUSTRALIANS. Med J Aust. 1965 Apr 24;1(17):611–617. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1965.tb71999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. K. Salt and hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Feb;25(2):231–244. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froment A., Milon H., Gravier C. Relation entre consommation sodée et hypertension artérielle. Contribution de l'épidémiologie géographique. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 1979;27(5-6):437–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum R. F., Grant C. T. Coronary heart disease in black populations. II. Risk factors. Am Heart J. 1982 Oct;104(4 Pt 1):852–864. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum R. F. Pathophysiology of hypertension in blacks and whites. A review of the basis of racial blood pressure differences. Hypertension. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):468–475. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.5.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grim C. E., Luft F. C., Miller J. Z., Meneely G. R., Battarbee H. D., Hames C. G., Dahl L. K. Racial differences in blood pressure in Evans County, Georgia: relationship to sodium and potassium intake and plasma renin activity. J Chronic Dis. 1980;33(2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(80)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANNEL W. B., DAWBER T. R., KAGAN A., REVOTSKIE N., STOKES J., 3rd Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease--six year follow-up experience. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Jul;55:33–50. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot H., Huang D. X., Li Y. L., Geboers J., Joossens J. V. The relationship between cations and blood pressure in the People's Republic of China. Hypertension. 1987 Jun;9(6):654–659. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.6.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot H., Park B. C., Lee C. S., Brems-Heyns E., Claessens J., Joossens J. V. A comparative study of blood pressure and sodium intake in Belgium and in Korea. Eur J Cardiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):169–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot H. Urinary cations and blood pressure--population studies. Ann Clin Res. 1984;16 (Suppl 43):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komachi Y., Iida M., Shimamoto T., Chikayama Y., Takahashi H. Geographic and occupational comparisons of risk factors in cardiovascular diseases in Japan. Jpn Circ J. 1971 Feb;35(2):189–207. doi: 10.1253/jcj.35.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz T. W., Al-Bander H. A., Morris R. C., Jr "Salt-sensitive" essential hypertension in men. Is the sodium ion alone important? N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 22;317(17):1043–1048. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710223171702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. R., Frost C. D., Wald N. J. By how much does dietary salt reduction lower blood pressure? III--Analysis of data from trials of salt reduction. BMJ. 1991 Apr 6;302(6780):819–824. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6780.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. R., Critchley J. A., Jeffrey R. F., Freestone S., MacDonald T. M. Does sodium restriction lower blood pressure? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jul 26;293(6541):266–267. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6541.266-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH J. R., GARRISON G. E., HAMES C. G. BLOOD PRESSURE AND HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE AMONG NEGROES AND WHITES; A STUDY IN EVANS COUNTY, GEORGIA. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Aug;61:208–228. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-2-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver W. J., Cohen E. L., Neel J. V. Blood pressure, sodium intake, and sodium related hormones in the Yanomamo Indians, a "no-salt" culture. Circulation. 1975 Jul;52(1):146–151. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.1.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page L. B., Damon A., Moellering R. C., Jr Antecedents of cardiovascular disease in six Solomon Islands societies. Circulation. 1974 Jun;49(6):1132–1146. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.49.6.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page L. B., Vandevert D. E., Nader K., Lubin N. K., Page J. R. Blood pressure of Qash'qai pastoral nomads in Iran in relation to culture, diet, and body form. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Apr;34(4):527–538. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASAKI N. High blood pressure and the salt intake of the Japanese. Jpn Heart J. 1962 Jul;3:313–324. doi: 10.1536/ihj.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNECKLOTH R. E., CORCORAN A. C., STUART K. L., MOORE F. E. Arterial pressure and hypertensive disease in a West Indian Negro population. Report of survey in St. Kitts, West Indies. Am Heart J. 1962 May;63:607–628. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(62)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Barbour G., Congleton J., Levy J., Meacher P., Saul H., Sowerby T. Blood pressure and salt intake in Malawi: an urban rural study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1986 Jun;40(2):188–192. doi: 10.1136/jech.40.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. O., Paulin J. M., Phelan E. L., Thaler B. I., Waal-Manning H. J., Nye E. R., Herbison G. P. Further surveys in Milton, 1978 and 1981: blood pressure, height, weight and 24-hour excretion of sodium and potassium. N Z Med J. 1982 Dec 22;95(722):873–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J., Fagard R., Lijnen P., Amery A., Bulpitt C., Joossens J. V. Salt and blood pressure in Belgium. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1981 Dec;35(4):256–261. doi: 10.1136/jech.35.4.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Stamler R., Riedlinger W. F., Algera G., Roberts R. H. Hypertension screening of 1 million Americans. Community Hypertension Evaluation Clinic (CHEC) program, 1973 through 1975. JAMA. 1976 May 24;235(21):2299–2306. doi: 10.1001/jama.235.21.2299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng W. P. Blood pressure and hypertension in an agricultural and a fishing population in Taiwan. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Nov;86(3):513–525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto J., Puska P., Tanskanen A., Karppanen H., Pietinen P., Nissinen A., Enlund H., Ruotsalainen P. A community-based intervention study on the feasibility and effects of the reduction of salt intake in North Karelia, Finland. Acta Cardiol. 1981;36(2):83–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


