Abstract
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides (Nod factors) are produced by symbiotic Rhizobium sp. bacteria to elicit Nod responses on their legume hosts. One of the earliest responses is the formation of phosphatidic acid (PA), a novel second messenger in plant cells. Remarkably, pathogens have also been reported to trigger the formation of PA in nonlegume plants. To investigate how host plants can distinguish between symbionts and pathogens, the effects of Nod factor and elicitors (chitotetraose and xylanase) on the formation of PA were investigated in suspension-cultured alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cells. Theoretically, PA can be synthesized via two signaling pathways, i.e. via phospholipase D (PLD) and via phospholipase C in combination with diacylglycerol (DAG) kinase. Therefore, a strategy involving differential radiolabeling with [32P]orthophosphate was used to determine the contribution of each pathway to PA formation. In support, PLD activity was specifically measured by using the ability of the enzyme to transfer the phosphatidyl group of its substrate to a primary alcohol. In practice, Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase induced the formation of PA and its phosphorylated product DAG pyrophosphate within 2 min of treatment. However, whereas phospholipase C and DAG kinase were activated during treatment with all three different compounds, PLD was only activated by Nod factor. No evidence was obtained for the activation of phospholipase A2.
Leguminous plants can form a symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium sp. bacteria. These gram-negative soil bacteria can invade the host's roots and trigger the formation of a new organ, the root nodule. There, they benefit from the proper environment to fix atmospheric nitrogen from which their host profits, while the host supplies Rhizobium sp. with sugars. An exchange of signals between the plant and the bacterium initiates symbiosis. During the first interactions, nodulation (Nod) factors are secreted by Rhizobium sp. They are lipo-chitooligosaccharide signals that are essential for initiating early plant responses during nodulation (for review, see Geurts and Bisseling, 2002).
Plants can also recognize the presence of pathogens. Perception of elicitors derived from the cell surface of pathogenic microorganisms initiate a hypersensitive response, phytoalexin production, and other defense responses. It is not understood how plants distinguish between symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms. Besides the responses that typify Nod or defense, much faster responses are known. Changes in cytosolic calcium concentration are triggered within minutes by elicitors and Nod factor (for review, see Grant and Mansfield, 1999; Cullimore et al., 2001), whereas more recently, we showed that phosphatidic acid (PA) was formed when common vetch (Vicia sativa) roots were treated with Nod factor (den Hartog et al., 2001) and when tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cell suspensions were treated with xylanase or chitin fragments (Van der Luit et al., 2000).
The importance of PA as a second messenger in plants has been documented (Munnik, 2001). It can be generated via two signaling pathways. Phospholipase C (PLC) can hydrolyze the phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol (DAG). The latter is then rapidly phosphorylated by DAG kinase (DGK) to PA (Munnik et al., 1998a; Munnik, 2001). 1,4,5-Trisphosphate is able to release Ca2+ from internal stores, increasing the activity of a range of effector enzymes such as Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Second, PA is the direct product of phospholipase D (PLD), which hydrolyzes structural lipids such as phosphatidylcholine. To attenuate PA signals, plants convert PA into DAG pyrophosphate (DGPP) via PA kinase (Munnik et al., 1996; Meijer and Munnik, 2003).
One of the key questions concerning Rhizobium sp.-legume symbiosis is how the host discriminates between symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms. In this study, we investigated phospholipid signaling in suspension-cultured alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cells during treatments with Nod factor and elicitors (xylanase and chitin fragments). Recently, we used 32P-labeled intact seedlings to show that Nod factor induces the activation of PLD and PLC in combination with DGK in the root of common vetch (den Hartog et al., 2001). However, intact plants are not suitable for studying the finer details of phospholipid turnover, because most cells are not in direct contact with the medium. Consequently, different cell layers are labeled asynchronously and perceive the agonists asynchronously, resulting in lipid turnover data that are averages of cells expressing widely different kinetics. Therefore a suspension of alfalfa cells was used to favor synchronic labeling and treatment. We demonstrate that both Nod factor and the elicitors stimulate PA formation. Nonetheless, whereas the PLC pathway is activated during treatment with all three different compounds, PLD is only activated by Nod factor.
RESULTS
Nod Factor Treatment Activates PA, DGPP, and PBut Formation in Suspension-Cultured Alfalfa Cells
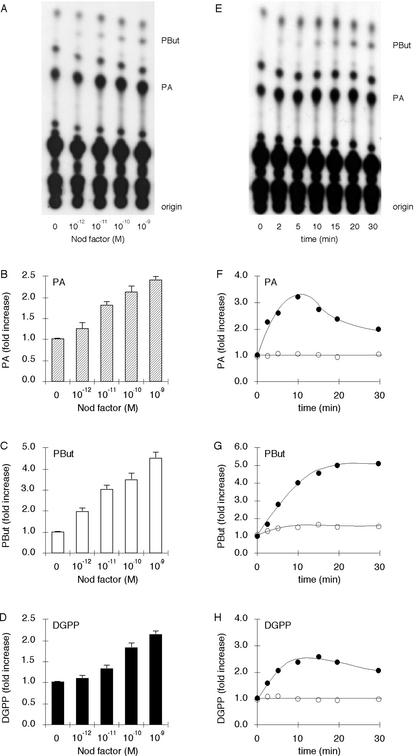
To investigate whether Nod factor triggers phospholipid signaling, suspension-cultured alfalfa cells were incubated with [32P]orthophosphate (32Pi) for 3 h to label all phospholipids. Subsequently, they were treated for 15 min with different concentrations of Nod factor in the presence of 0.5% (v/v) n-butanol to measure PLD activity. PLD has the unique ability to transfer the phosphatidyl group of its substrate to a primary butanol, forming phosphatidylbutanol (PBut; Munnik et al., 1995). After Nod factor treatment, lipids were extracted and separated by thin layer chromatography (TLC). As shown in Figure 1, A and B, Nod factor elicits the formation of PA in suspension-cultured alfalfa cells in a dose-dependent manner. At concentrations as low as 10−12 m, PA formation was already triggered with a maximum stimulation at 10−9 m Nod factor. Higher concentrations inhibited the PA response (data not shown). At least part of the PA was formed via the PLD pathway, because PBut was generated as well (Fig. 1, A and C). DGPP, the phosphorylated product of PA, also increased in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1D). No changes in lyso-phospholipids, the products of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity, were detected (Fig. 1A).
Figure 1.
Nod factor treatment activates PA, PBut, and DGPP formation in suspension-cultured alfalfa cells. A, Nod factor stimulates the formation of PA and PBut in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were prelabeled with 32Pi for 3 h and stimulated with different concentrations of Nod factor for 15 min in the presence of 0.5% (v/v) n-butanol. Treatment was stopped, and lipids were extracted, separated by TLC, and detected by autoradiography. B, Quantification of PA levels; C, quantification of PBut levels; and D, quantification of DGPP levels. The amount of radioactivity in each species was quantified by phosphor imaging and expressed as -fold stimulation compared with the control. Error bars indicate sds. E, Nod factor stimulates the formation of PA and PBut in a time-dependent manner. Cells were prelabeled with 32Pi for 3 h and stimulated with 10−9 m Nod factor for different periods in the presence of 0.5% (v/v) n-butanol. Treatment was stopped, and lipids were extracted, separated by ethyl acetate TLC, and detected by autoradiography. F, Quantification of PA levels; G, quantification of PBut levels; and H, quantification of DGPP levels. The amount of radioactivity in each species was quantified by phosphor imaging and expressed as -fold stimulation compared with the control. Error bars indicate sds.
The stimulation of PA, PBut, and DGPP syntheses were not only dose-dependent, but also time-dependent (Fig. 1, E–H). An increase in PA was detectable after 2 min, and the stimulation was maximal after 10 min (Fig. 1, E and F). PBut was also formed after 2 min (Fig. 1, E and G), implying that PLD was very rapidly activated on Nod factor treatment. PBut synthesis stopped after 20 min, indicating that PLD activation had ceased. Because PBut is an “unnatural” lipid, it is not readily metabolized and is therefore accumulated. This is in contrast to PA and DGPP, which are metabolized and therefore decline in concentration after 10 min. Because DGPP is a metabolite of PA, DGPP labeling followed the kinetics of PA labeling (Fig. 1H). Again, no evidence was obtained for the activation of PLA2 (Fig. 1E).
Chitotetraose and Xylanase Elicit PA and DGPP Formation, But Not PBut Formation
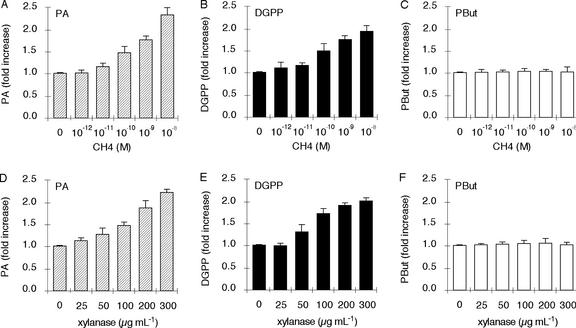
To test whether plants react differently to the presence of an elicitor, chitotetraose and xylanase were used. Chitotetraose, a tetramer of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine, is a fungal cell wall component and is closely related to Nod factors because it represents the backbone of the Nod factor (Côte and Hahn, 1994; Boller, 1995). Xylanase is an elicitor protein isolated from the fungus Trichoderma viride (Dean et al., 1989). In suspension-cultured tomato cells, both elicitors activate lipid signaling (Van der Luit et al., 2000; Laxalt et al., 2001; Laxalt and Munnik, 2002).
Alfalfa cells were prelabeled for 3 h with radioactive orthophosphate and were subsequently treated for 15 min with different concentrations of chitotetraose or xylanase. After stimulation, lipids were extracted and separated by TLC. As shown in Figure 2, chitotetraose (Fig. 2A) and xylanase (Fig. 2D) triggered the formation of PA in a dose-dependent manner. Both elicitors stimulated the formation of DGPP (Fig. 2, B and E). However, neither chitotetraose nor xylanase activated the formation of PBut (Fig. 2, C and F), implying that they do not activate PLD in alfalfa cells. In addition, neither elicitor activated PLA2 (data not shown).
Figure 2.
The elicitors chitotetraose and xylanase induce PA and DGPP formation but not PBut formation in suspension-cultured alfalfa cells. A and D, Chitotetraose and xylanase elicit PA formation. Cells were prelabeled with 32Pi for 3 h and stimulated with different concentrations of elicitor for 15 min in the presence of 0.5% (v/v) n-butanol. Treatment was stopped and lipids were extracted and separated by ethyl acetate and alkaline TLC. The amount of radioactive PA was quantified by phosphor imaging and expressed as -fold stimulation compared with the control. Error bars indicate sds. B and E, Chitotetraose and xylanase elicit DGPP formation. The amount of radioactive DGPP was quantified as described above, using alkaline TLC. C and F, PBut formation is not stimulated by chitotetraose or xylanase. The amount of radioactive PBut was quantified as described above.
Nod factor from a non-symbiotic Rhizobium sp. strain (R. leguminosarum bv viciae) also activated the formation of PA in alfalfa cells. The response resembled the reaction to the pathogen elicitors xylanase and chitotetraose. PA was not derived from the PLD pathway, for PBut was not synthesized (data not shown).
PLC in Combination with DGK Contributes to PA Formation
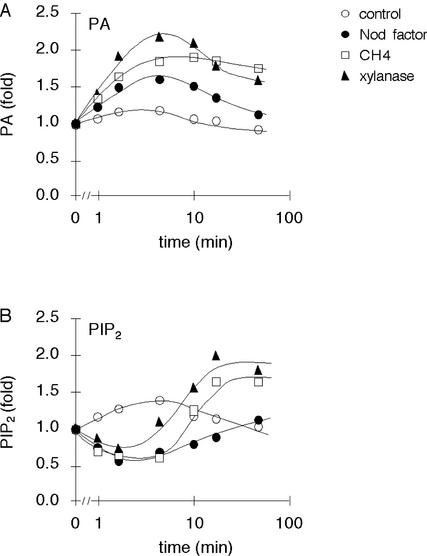
Because chitotetraose and xylanase induced the formation of PA but did not appear to stimulate PLD, this PA may have been derived from PLC and DGK activities (Munnik, 2001). In contrast, Nod factor activated PLD (Fig. 1, A, C, E, and G) but could have activated the PLC pathway as well. To test whether PLC and DGK are activated by these treatments, a differential labeling strategy was used (Munnik et al., 1998b, 2001). The method is based on the principle that radioactive orthophosphate is slowly incorporated into structural lipids, but much faster into the ATP pool. Because PLD hydrolyzes a structural lipid, the PA formed by PLD activity is only radioactive when its substrate is radioactive, which is only after cells have been prelabeled for several hours. On the other hand, the ATP pool that is used to phosphorylate PLC-generated DAG is radioactive within minutes of labeling. Hence, a short labeling period strongly favors the labeling of PA generated via the PLC pathway. Accordingly, alfalfa cells were labeled for only 15 min and then treated with Nod factor, chitotetraose, or xylanase for different periods of time. As shown in Figure 3A, Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase induced the formation of radioactive PA. This increase also correlated with a decrease in the level of PIP2, the substrate of PLC (Fig. 3B). This decrease was soon followed by an increase in synthesis, presumably to replace the PIP2 lost by hydrolysis. These data indicate that Nod factor and the elicitors activate the PLC pathway, even though Nod factor was the least effective of the three.
Figure 3.
Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase stimulate PA and PIP2 turnover in suspension-cultured alfalfa cells. A, Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase stimulate PA formation. Cells were prelabeled with 32Pi for just 15 min before stimulating them with 10−9 m Nod factor, 10−9 m chitotetraose, or 200 μg mL−1 xylanase for different periods of time. As a control, cells were treated with conditioned growth medium. Treatment was stopped, and lipids were extracted and then separated by alkaline TLC. The amount of radioactive PA was quantified by phosphor imaging and expressed as -fold stimulation in relation to time 0. B, Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase induce changes in the level of PIP2. Cells were prelabeled with 32Pi for just 15 min before stimulating them with 10−9 m Nod factor, 10−9 m chitotetraose, or 200 μg mL−1 xylanase for different periods of time. As a control, cells were treated with conditioned medium. Treatment was stopped, and the lipids were extracted and separated by alkaline TLC. The amount of radioactive PIP2 was quantified by phosphor imaging and expressed as -fold stimulation in relation to time 0.
DISCUSSION
Root cells are confronted by numerous compounds like Nod factors synthesized by symbiotic Rhizobia as well as a variety of elicitors produced by pathogens. Plants must differentiate between them, welcome the symbiont, and repel the pathogen. It is assumed that Nod factors and elicitors are perceived via diverse receptors that activate different signaling pathways and responses. However, some elements in the signaling pathway and in the response syndrome may be common to both, because they may have evolved from common progenitors. Here, suspension-cultured alfalfa cells were used to investigate whether symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms activate different phospholipid signaling pathways.
Suspension-cultured cells were used because they are more suitable than intact plants for studying phospholipid signaling, because each cell is in direct contact with the medium. This promotes both synchronous labeling of their phospholipids and synchronous perception of the Nod factor or the elicitor, making it possible to visualize rapid changes in phospholipid turnover. For example, using common vetch seedlings, it was not possible to detect Nod factor-induced PIP2 turnover even though PLC was activated (den Hartog et al., 2001). In contrast, when Nod factor was added to alfalfa cell suspensions in this study, the level of PIP2 was readily seen to decrease and subsequently increase as it was hydrolyzed and resynthesized. Responses were also detected at earlier times, for example PA and DGPP increases were detected in seedlings after 9 min, but already after 2 min in cell suspensions.
At first sight, cells did not seem to discriminate between elicitors and Nod factor because they all induced a [32P]PA response within 2 min. However, a clear difference was observed when the origin of the PA was determined. Whereas the PLC pathway contributed to PA formation induced by Nod factor, chitotetraose, and xylanase, only Nod factor activated the PLD pathway. Hence, PLD activation discriminated Nod factor signaling from defense signaling. In plants in general, PLD signals more than just the presence of symbionts. It has been associated with responses to pathogens, wounding, water stress, and the hormones abscisic acid and ethylene (Meijer and Munnik, 2003). Furthermore, its activity is correlated with senescence, germination, and ripening (see Wang, 2001). It is therefore not surprising that plants possess multigene PLD families. In Arabidopsis, 12 different genes can be distinguished (Eliás et al., 2002; Qin and Wang, 2002). They have been categorized into five subgroups (α, β, γ, δ, and ζ) based on their amino acid composition and biochemical properties (Wang, 2001; Qin and Wang, 2002). An important question for the future is which PLDs are involved in signaling as opposed to general phospholipid metabolism, and in particular, which alfalfa PLD signals the presence of Rhizobium sp.
The product of PLD is PA, which is becoming acknowledged as a general intracellular signal in plants (Munnik, 2001; Munnik and Musgrave, 2001). PA also seems to act as a second messenger downstream from Nod factor, because if PA synthesis is inhibited, downstream responses such as root hair deformation (den Hartog et al., 2001), ENOD12 expression (Pingret et al., 1998; M. den Hartog and T. Munnik, unpublished data), and Ca2+ spiking (Engstrom et al., 2002) are also inhibited. But how can a cell distinguish between different PA signals? First, PA generated by PLC/DGK activity is not the same as that generated by PLD. PAPLD originates from a structural lipid, whereas PAPLC/DGK is derived from PIP2, which has a very different fatty acid composition (Arisz et al., 2000, 2003). Downstream signaling components can discriminate between them, as shown for mammalian cells (Pettitt et al., 1997). In addition, PLC can be activated at a different location in the cell compared with PLD, i.e. plasma membrane and Golgi. Although it is not yet clear how PA works, several proteins specifically bind this lipid and/or are activated by it (see Munnik, 2001; Munnik and Musgrave, 2001). In plants for example, a CDPK (Farmer and Choi, 1999) and a MAPK cascade (Lee et al., 2001) can be activated. Finally, PA could play an important role in vesicular trafficking and secretion, because it is known to affect the physical properties of the membrane, thereby influencing membrane curvature and the ability to form vesicles (Scales and Scheller, 1999).
Nod factor and elicitors stimulated the production of DGPP from PA. Similar effects were found on adding Nod factor to common vetch roots (den Hartog et al., 2001), on eliciting tomato cells (Van der Luit et al., 2000), and on osmotically stressing alfalfa, tomato, Arabidopsis, tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), and Craterostigma plantageneum (Frank et al., 2000; Munnik et al., 2000; Meijer et al., 2001, 2002; Munnik and Meijer, 2001). Originally, DGPP was discovered as an in vitro product of PA kinase when ATP was added to plant microsomes (Wissing and Behrbohm, 1993) and later as an in vivo product when cells were stimulated with the G-protein activator mastoparan (Munnik et al., 1996). Whether the formation of DGPP represents a PA attenuation mechanism or a second signal pathway remains to be established (Munnik, 2001).
The primary response to Nod factor is an influx of Ca2+ that opens plasma membrane anion channels (Felle et al., 1998, 1999). This Ca2+ influx seems to be specific, because it is not detected in root hairs or cell suspensions treated with elicitors such as chitotetraose (Ehrhardt et al., 1992; Gehring et al., 1997; Cardenas et al., 1999; Felle et al., 1999; Yokoyama et al., 2000). Because some PLDs are activated by Ca2+ (Munnik et al., 1998a; Wang, 2001), Nod factor-induced PLD activation could be downstream from the initial Ca2+ influx.
A successful symbiosis may depend on Rhizobium sp. bacteria escaping or suppressing the defense response of the plant (Niehaus et al., 1993). In this perspective, the activation of PLC by Nod factor may represent vestigial defense signaling, whereas PLD activity attenuates or modifies that reaction. For example, PLD could block the extracellular alkalinization thought to be involved in the onset of plant defense (Felix et al., 1993, 1999; Baier et al., 1999). PLC activity seems to be necessary for this response because it is inhibited by PLC inhibitors (C.F. de Jong, A.M. Laxalt, B.O.R. Bargmann, P.J.G.M. de Wit, M.H.A.J. Jooslen, and T. Munnik, unpublished data). Also, Rhizobium sp. components other than Nod factor itself could attenuate the defense response. For instance, Sinorhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to synthesize the exopolysaccharide EPSI do not invade the host plant but instead activate its defense system (Niehaus et al., 1993). Lipopolysaccharides are also important for symbiosis (Niehaus et al., 1998), because they can suppress pathogen-induced alkalinization and the oxidative burst (Albus et al., 2001). It will therefore be interesting to see whether such components can modify the Nod factor-induced lipid signaling described here.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Material
Suspension-cultured alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cells were kindly provided by Dr. K. Niehaus (University Bielefeld, Germany). They were grown in Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with Gamborg vitamins, 5.4 μm naphthylacetic acid, and 1.0 μm 6-benzyladenine (Duchefa, Haarlem, The Netherlands). Cells were continuously rotated at 125 rpm in the dark at 25°C and used 4 to 6 d after subculturing.
[32P]Phospholipid Labeling, Extraction, and Analysis
Alfalfa cell suspension was prelabeled with 0.18 Mbq carrier-free 32Pi (Amersham International, Roosendaal, The Netherlands) per 100 μL of cells. Subsequently, they were treated with Nod factor or the elicitors for the times indicated. Conditioned sterile growth medium was used for control treatments. Incubations were stopped by adding perchloric acid (5% [v/v] final concentration) and snap-freezing in liquid nitrogen. Lipid extraction was initiated by adding 3.75 volumes of CHCl3:MeOH:HCl (50:100:1, v/v). The samples were then vigorously shaken for 15 min. A two-phase system was induced by adding of 3.75 volumes of CHCl3 and 1 volume of 0.9% (w/v) NaCl. After vortexing and centrifugation, the upper phase was removed, and the lower phase washed with 3.75 volumes of CHCl3:MeOH:1 m HCl (3:48:47, v/v). Lipid extracts were dried by vacuum centrifugation, dissolved in 20 μL of CHCl3, and stored under N2 at −20°C, or immediately used for TLC analysis.
Lipids were chromatographed using two different solvents in combination with silica 60 TLC plates (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). An alkaline solvent (CHCl3:MeOH:25% [w/v] NH4OH:H2O [45:35:2:8, v/v]) was used to separate the different phospholipids, and an ethyl acetate solvent system (the organic upper phase of ethyl acetate:iso-octane:formic acid:H2O [13:2:3:10, v/v]) was used to separate PBut and PA from the other phospholipids as described earlier (den Hartog et al., 2001). Radiolabeled lipids were visualized by autoradiography (X-Omat S, Kodak, Amsterdam) and were quantified by phosphor imaging (Storm, Molecular Dynamics, Sunnyvale, CA).
PLD activity was measured as the production of PBut, essentially as described by Munnik et al. (1995). After prelabeling with 32Pi, the cells were treated with Nod factor, elicitor, or conditioned growth medium in the presence of 0.5% (v/v) n-butanol. Reactions were stopped, and lipids were extracted and analyzed by ethyl acetate TLC.
Materials
Xylanase (Trichoderma viride) was purchased from Fluka BioChemika (Buchs, Switzerland), and chitin fragment CH4 (chitotetraose) was purchased from Seikagaku (Tokyo). Stock solutions were prepared in water and stored at −20°C. Purified NodSm-IV (C16:2, Ac, S) factor from Sinorhizobium meliloti was a gift from Dr. J. Goedhart (University of Amsterdam). Reagents for lipid extraction were from Merck.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank our colleagues in the lab for many stimulating discussions and in particular Alan Musgrave for his help during writing and Herman van den Ende for critically reading the manuscript.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research and the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/doi/10.1104/pp.102.017954.
LITERATURE CITED
- Albus U, Baier R, Holst O, Pühler A, Niehaus K. Suppression of an elicitor-induced oxidative burst reaction in Medicago sativa cell cultures by Sinorhizobium meliloti lipopolysaccharides. New Phytol. 2001;151:597–606. doi: 10.1046/j.0028-646x.2001.00214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arisz SA, Valianpour F, van Gennip AH, Munnik T (2003) Substrate preference of stress-activated phospholipase D in Chlamydomonas and its contribution to PA formation. Plant J (in press) [DOI] [PubMed]
- Arisz SA, Van Himbergen JAJ, Musgrave A, Van den Ende H, Munnik T. Polar glycerolipids of Chlamydomonas moewusii. Phytochemistry. 2000;53:265–270. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(99)00505-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier R, Schiene K, Kohring B, Flaschel E, Niehaus K. Alfalfa and tobacco cells react differently to chitin oligosaccharides and Sinorhizobium meliloti nodulation factors. Planta. 1999;210:157–164. doi: 10.1007/s004250050665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller T. Chemoperception of microbial signals in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1995;46:189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas L, Feijo JA, Kunkel JG, Sanchez F, Holdaway-Clarke T, Hepler PK, Quinto C. Rhizobium Nod factor induces increases in intracellular free calcium and extracellular calcium influxes in bean root hairs. Plant J. 1999;19:347–352. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.00517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côte F, Hahn MG. Oligosaccharins: structures and signal transduction. Plant Mol Biol. 1994;26:1379–1411. doi: 10.1007/BF00016481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullimore JV, Ranjeva R, Bono J-J. Perception of lipo-chitooligosaccharidic Nod factors in legumes. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:24–30. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01810-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean JFD, Gamble HR, Anderson JD. The ethylene biosynthesis inducing xylanase: its induction in Trichoderma viride and certain plant pathogens. Phytopathology. 1989;79:1071–1078. [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog M, Musgrave A, Munnik T. Nod factor-induced phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate formation: a role for phospholipase C and D in root hair deformation. Plant J. 2001;25:55–65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt DW, Atkinson EM, Long SR. Depolarization of alfalfa root hair membrane potential by Rhizobium Nod factors. Science. 1992;256:998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.10744524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliás M, Potocky M, Cvrcková F, Zársky V. Molecular diversity of phospholipase D in angiosperms. BioMed Central Genomics. 2002;3:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-3-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom EM, Ehrhardt DW, Mitra RM, Long SR. Pharmacological analysis of Nod factor-induced calcium spiking in Medicago truncatula: evidence for the requirement of type IIA calcium pumps and phosphoinositide signaling. Plant Physiol. 2002;128:1390–1401. doi: 10.1104/pp.010691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer PK, Choi JH. Calcium and phospholipid activation of a recombinant calcium-dependent protein kinase (DcCPK1) from carrot (Daucus carota L.) Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1434:6–17. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(99)00166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G, Duran JD, Volko S, Boller T. Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J. 1999;18:265–276. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.00265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G, Regenass M, Boller T. Specific perception of sub-nanomolar concentration of chitin fragments by tomato cells: induction of extracellular alkalinisation, changes in protein phosphorylation, and establishment of refractory state. Plant J. 1993;4:307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Felle HH, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A, Schultze M. The role of ion fluxes in Nod factor signaling in Medicago sativa. Plant J. 1998;13:455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Felle HH, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A, Schultze M. Elevation of the cytosolic free [Ca2+] is indispensable for the transduction of the Nod factor signal in alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1999;121:273–279. doi: 10.1104/pp.121.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank W, Munnik T, Kerkmann K, Salamini F, Bartels D. Water deficit triggers phospholipase D activity in the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum. Plant Cell. 2000;12:111–123. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring CA, Irving HR, Kabbara AA, Parish RW, Boukli NM, Broughton WJ. Rapid, plateau-like increases in intracellular free calcium are associated with Nod-factor-induced root-hair deformation. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 1997;10:791–802. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts R, Bisseling T. Rhizobium Nod factor perception and signaling. Plant Cell. 2002;14:S239–S249. doi: 10.1105/tpc.002451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M, Mansfield J. Early events in host-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1999;2:312–319. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(99)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxalt AM, Munnik T. Phospholipid signaling in plant defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;5:332–338. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxalt AM, Ter Riet B, Verdonk JC, Parigi L, Tameling WIL, Vossen J, Haring M, Musgrave A, Munnik T. Characterization of five tomato phospholipase D cDNAs: rapid and specific expression of LePLDβ1 on elicitation with xylanase. Plant J. 2001;26:237–247. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S, Hirt H, Lee Y. Phosphatidic acid activates a wound-activated MAPK in Glycine max. Plant J. 2001;26:479–486. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer HJG, Arisz SA, Van Himbergen JAJ, Musgrave A, Munnik T. Hyperosmotic stress rapidly generates lyso-phosphatidic acid in Chlamydomonas. Plant J. 2001;25:541–548. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer HJG, Munnik T (2003) Phospholipid-based signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54: (in press) [DOI] [PubMed]
- Meijer HJG, Ter Riet B, Van Himbergen JAJ, Musgrave A, Munnik T. KCl activates phospholipase D at two different concentration ranges: distinguishing between hyperosmotic stress and membrane depolarization. Plant J. 2002;31:51–59. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T. Phosphatidic acid: an emerging plant lipid second messenger. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:227–233. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(01)01918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Arisz SA, De Vrije T, Musgrave A. G protein activation stimulates phospholipase D signaling in plants. Plant Cell. 1995;7:2197–2210. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.12.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, De Vrije T, Irvine RF, Musgrave A. Identification of diacylglycerol pyrophosphate as a novel metabolic product of phosphatidic acid during G-protein activation in plants. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15708–15715. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.26.15708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Irvine RF, Musgrave A. Phospholipid signalling in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998a;1389:222–272. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(97)00158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Meijer HJG. Osmotic stress activates distinct lipid- and MAPK signalling pathways in plants. FEBS Lett. 2001;498:172–178. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Meijer HJG, Ter Riet B, Hirt H, Frank W, Bartels D, Musgrave A. Hyperosmotic stress stimulates phospholipase D activity and elevates the levels of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant J. 2000;22:147–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Musgrave A. Phospholipid signaling in plants: holding on to phospholipase D. Sci STKE. 2001;111:PE42. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.111.pe42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnik T, Van Himbergen JAJ, Ter Riet B, Braun FJ, Irvine RF, Van den Ende H, Musgrave A. Detailed analysis of the turnover of polyphosphoinositides and phosphatidic acid upon activation of phospholipase C and D in Chlamydomonas cells treated with non-permeabilizing concentrations of mastoparan. Planta. 1998b;207:133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus K, Kapp D, Pühler A. Plant defense and delayed infection of alfalfa pseudonodules induced by an exopolysaccharide (EPS I)-deficient Rhizobium meliloti mutant. Planta. 1993;190:415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus K, Lagares A, Pühler A. A Sinorhizobium meliloti lipopolysaccharide mutant induces effective nodules on the host plant Medicago sativa (alfalfa) but fails to establish a symbiosis with Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 1998;11:906–914. [Google Scholar]
- Pettitt TR, Martin A, Horton T, Liossis C, Lord JM, Wakelam MJ. Diacylglycerol and phosphatidate generated by phospholipases C and D, respectively, have distinct fatty acid compositions and functions: Phospholipase D-derived diacylglycerol does not activate protein kinase C in porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;11:17354–17359. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.28.17354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingret JL, Journet EP, Barker DG. Rhizobium Nod factor signaling: evidence for a G protein-mediated mechanism. Plant Cell. 1998;10:659–671. doi: 10.1105/tpc.10.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin C, Wang X. The Arabidopsis phospholipase D family: characterization of a calcium-independent and phosphatidylcholine-selective PLDζ1 with distinct regulatory domains. Plant Physiol. 2002;128:1057–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.010928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales SJ, Scheller RH. Lipid membranes shape up. Nature. 1999;401:123–124. doi: 10.1038/43582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Luit AH, Piatti T, Van Doorn A, Musgrave A, Felix G, Boller T, Munnik T. Elicitation of suspension-cultured tomato cells triggers the formation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant Physiol. 2000;123:1507–1524. doi: 10.1104/pp.123.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. Plant phospholipases. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2001;52:211–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissing JB, Behrbohm H. Phosphatidate kinase, a novel enzyme in phospholipid metabolism: purification, subcellular localization and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Plant Physiol. 1993;102:1243–1249. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T, Kobayashi N, Kouchi H, Minamisawa K, Kaku H, Tsuchiya K. A lipochito-oligosaccharide, Nod factor, induces transient calcium influx in soybean suspension-cultured cells. Plant J. 2000;22:71–78. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]