Abstract
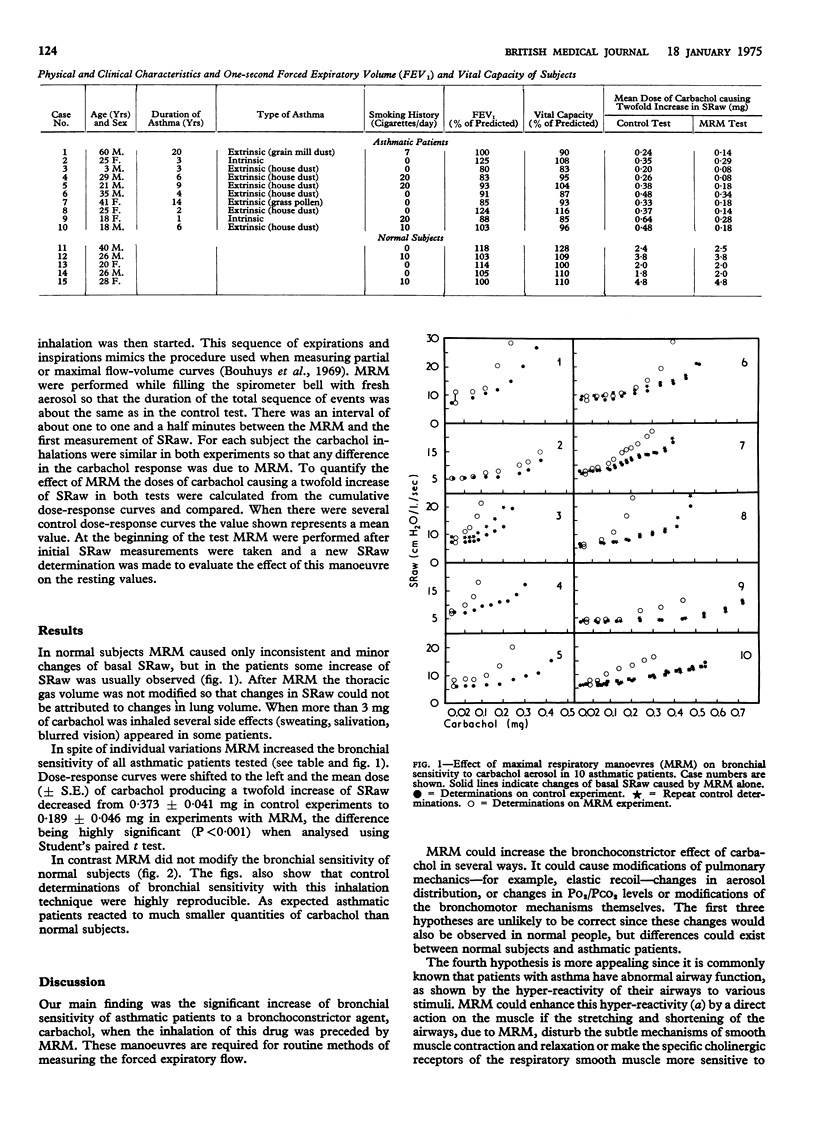
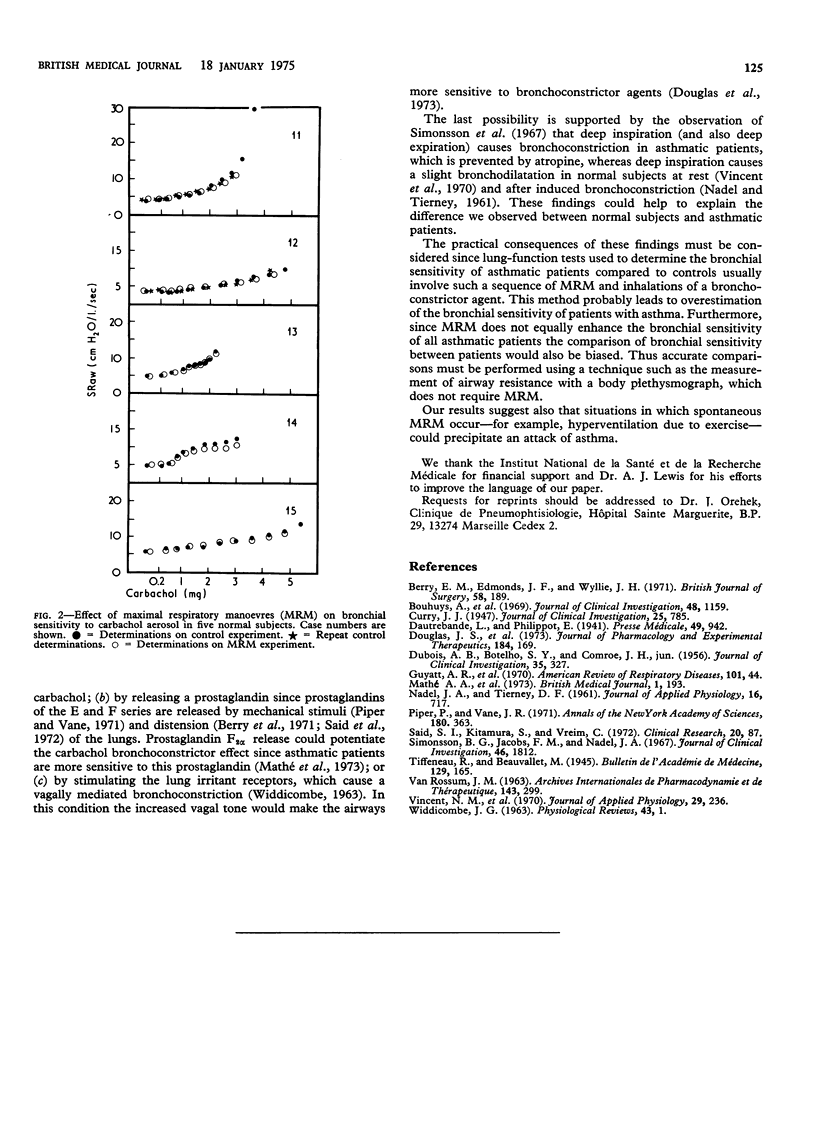
Cumulative dose-response curves to carbachol given by aerosol were established using plethysmographic measurements of specific airways resistance (SRaw) in 10 patients with asthma and five healthy subjects. Two experiments were performed--a control test and one in which maximal respiratory manoeuvres (MRM) (two maximal inspirations and two maximal expirations) were made before each carbachol inhalation. MRM did not modify the dose-response curves in the normal subjects. In the patients these manoeuvres enhanced the bronchoconstrictor effect of carbachol: curves were shifted to the left and the mean dose of carbachol producing a twofold increase in initial SRaw was decreased from 0.373 mg to 0.189 mg (P less than 0.001). Bronchial provocation tests using methods which require MRM--for example, forced expiratory volume at one second--could overestimate the bronchial sensitivity of patients with asthma.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry E. M., Edmonds J. F., Wyllie H. Release of prostaglandin E2 and unidentified factors from ventilated lungs. Br J Surg. 1971 Mar;58(3):189–192. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry J. J. THE ACTION OF HISTAMINE ON THE RESPIRATORY TRACT IN NORMAL AND ASTHMATIC SUBJECTS. J Clin Invest. 1946 Nov;25(6):785–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI101764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. S., Dennis M. W., Ridgway P., Bouhuys A. Airway constriction in guinea pigs: interaction of histamine and autonomic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jan;184(1):169–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt A. R., Berry G., Alpers J. H., Bramley A. C., Fletcher C. M. Relationship of airway conductance and its immediate change on smoking to smoking habits and symptoms of chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Jan;101(1):44–54. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADEL J. A., TIERNEY D. F. Effect of a previous deep inspiration on airway resistance in man. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Jul;16:717–719. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P., Vane J. The release of prostaglandins from lung and other tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:363–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson B. G., Jacobs F. M., Nadel J. A. Role of autonomic nervous system and the cough reflex in the increased responsiveness of airways in patients with obstructive airway disease. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1812–1818. doi: 10.1172/JCI105671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent N. J., Knudson R., Leith D. E., Macklem P. T., Mead J. Factors influencing pulmonary resistance. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Aug;29(2):236–243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. Regulation of tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jan;43:1–37. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


