Abstract
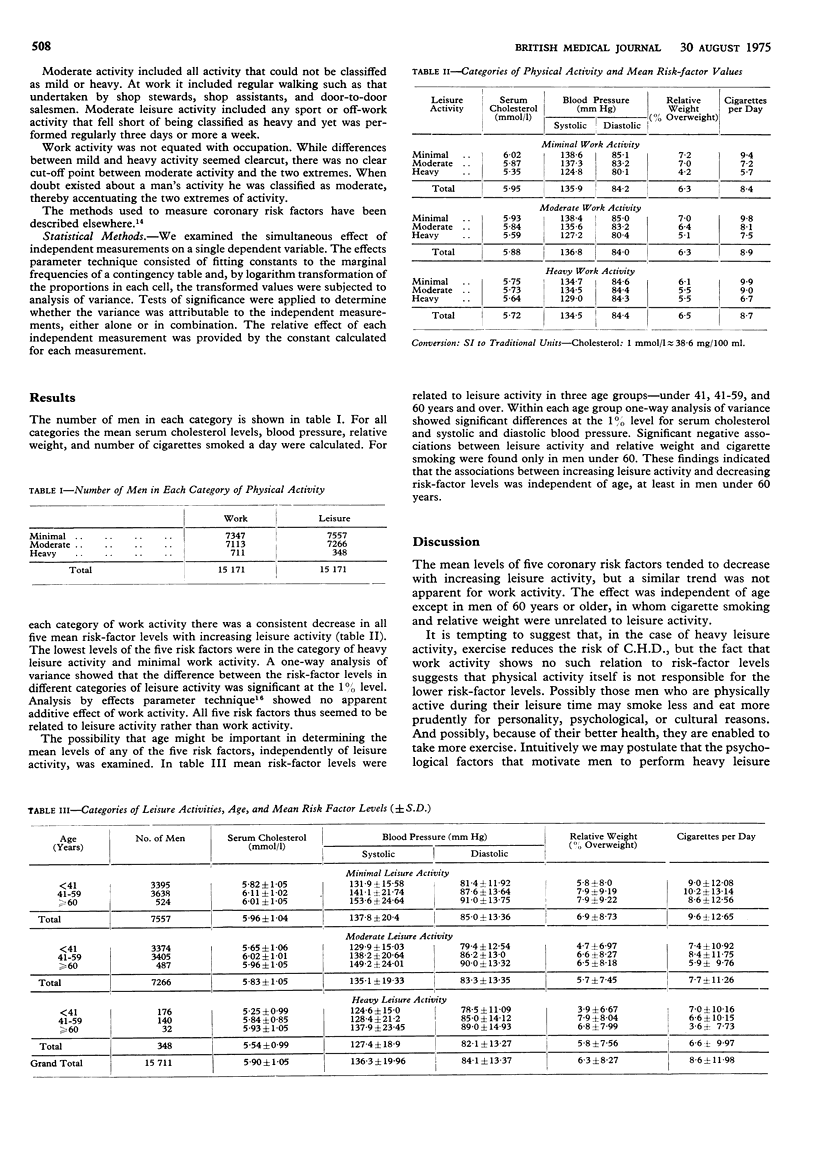
Physical activity, both at work and during leisure, was assessed in 15 171 men aged 25-74 years. Heavy leisure activity was associated with lower mean serum cholesterol levels and blood pressure. In men under 60 years the same negative association was also noted between leisure activity and relative weight and cigarette smoking. Different degrees of physical activity at work were not associated with any differences in these risk factors, nor did the level of exercise at work seem to influence the negative association between leisure activity and risk factors. Heavy leisure activity in young and middle-aged men is associated with lower levels of certain coronary risk factors and, therefore, a lower risk of coronary heart disease. The often-reported reduction in coronary morbidity and mortality with physical exercise may not be the direct effect of the exercise itself.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAHL L. K. Salt intake and salt need. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jun 5;258(23):1152–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195806052582305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOSZY J. O., SKINNER J. S., TORO G., CURETON T. K. EFFECTS OF A SIX MONTH PROGRAM OF ENDURANCE EXERCISE ON THE SERUM LIPIDS OF MIDDLE-AGED MAN. Am J Cardiol. 1964 Dec;14:753–760. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey N., Bourke G. J., Gearty G., Mulcahy R. Mediscan: a population screening programme for the detection of coronary heart disease risk factors. J Ir Med Assoc. 1971 Mar 18;64(408):155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. N., Chave S. P., Adam C., Sirey C., Epstein L., Sheehan D. J. Vigorous exercise in leisure-time and the incidence of coronary heart-disease. Lancet. 1973 Feb 17;1(7799):333–339. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. N., Kagan A., Pattison D. C., Gardner M. J. Incidence and prediction of ischaemic heart-disease in London busmen. Lancet. 1966 Sep 10;2(7463):553–559. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)93034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL O., LEPPER M. H., PHELAN W. H., DUPERTUIS G. W., MACMILLAN A., McKEAN H., PARK H. A longitudinal study of coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1963 Jul;28:20–31. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.28.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paffenbarger R. S., Jr, Laughlin M. E., Gima A. S., Black R. A. Work activity of longshoremen as related to death from coronary heart disease and stroke. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1109–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPIRO S., WEINBLATT E., FRANK C. W., SAGER R. V. THE H.I.P. STUDY OF INCIDENCE AND PROGNOSIS OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE; PRELIMINARY FINDINGS ON INCIDENCE OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND ANGINA. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Jun;18:527–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMLER J., LINDBERG H. A., BERKSON D. M., SHAFFER A., MILLER W., POINDEXTER A. Prevalence and incidence of coronary heart disease in strata of the labor force of a Chicago industrial corporation. J Chronic Dis. 1960 Apr;11:405–420. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(60)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. L., Buskirk E. R., Remington R. D. Exercise in controlled trials of the prevention of coronary heart disease. Fed Proc. 1973 May;32(5):1623–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



