Abstract
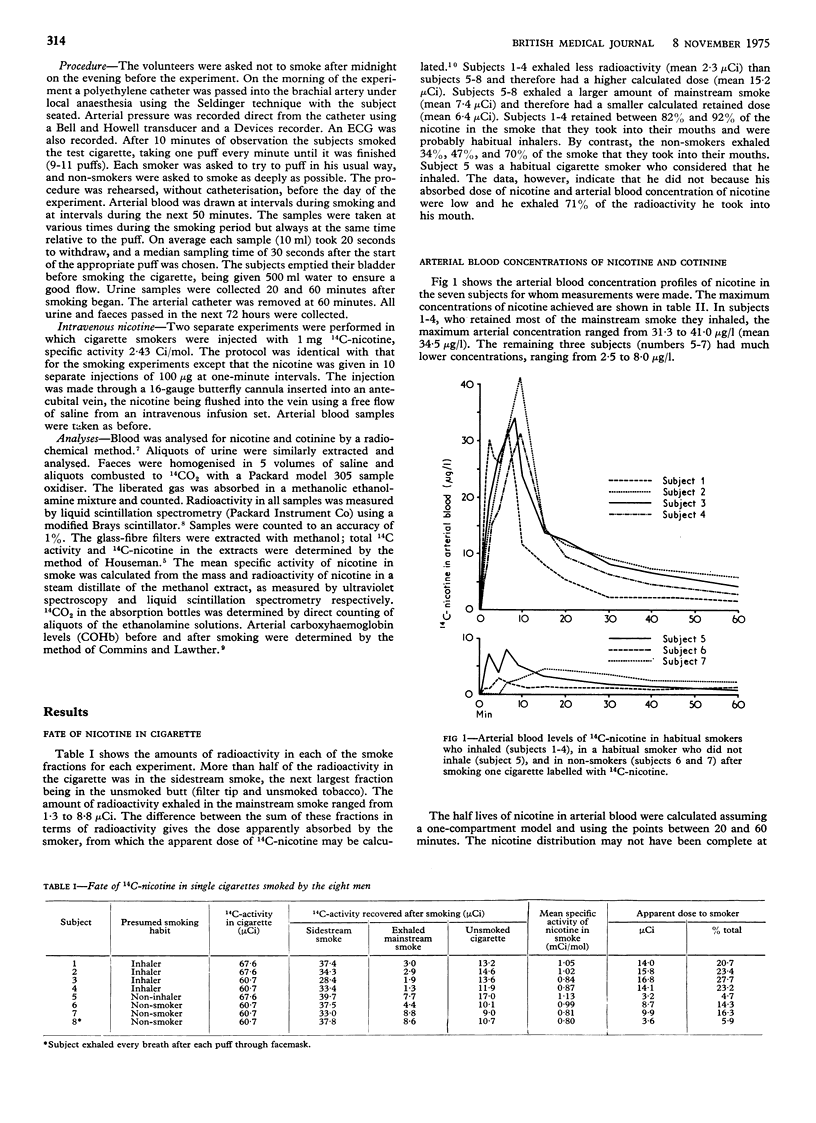
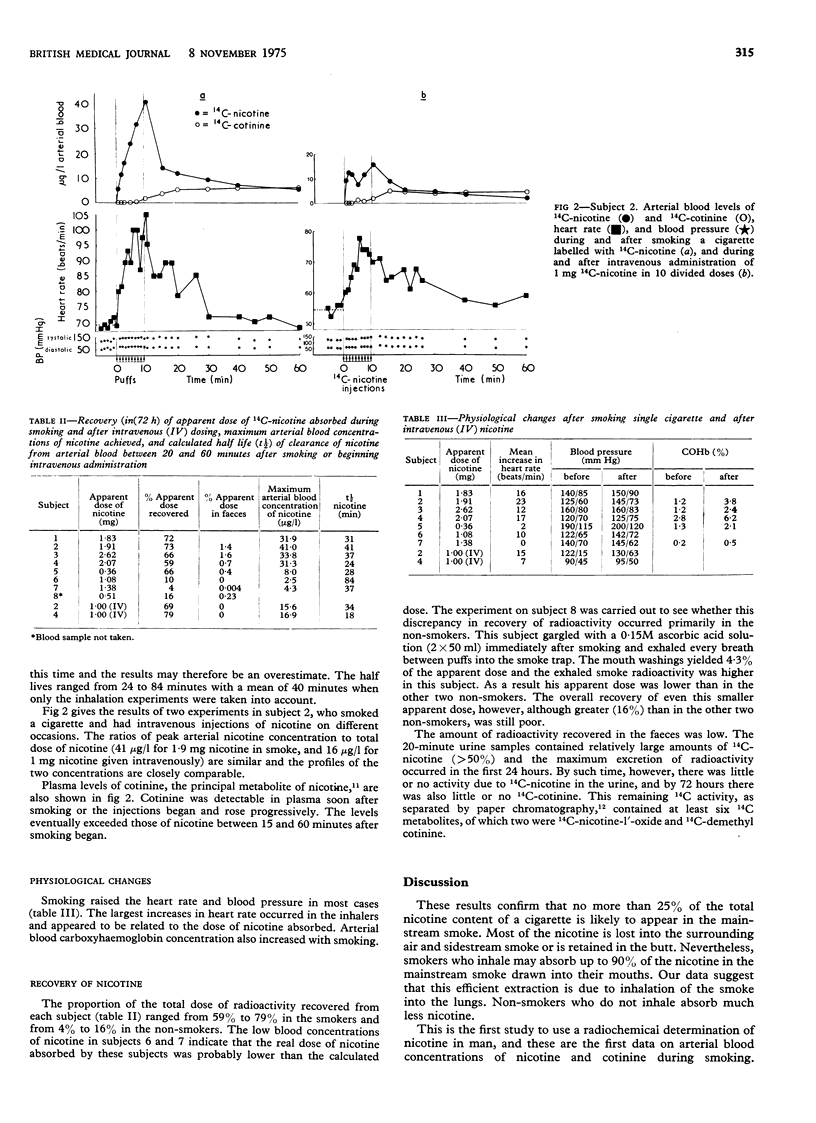
Eight men volunteers each smoked a single cirgarette containing 14C-nicotine and gave arterial blood samples during and for 50 minutes after smoking. The maximum concentration of nicotine in the arterial blood ranged from 31 to 41 mug/l in four regular cigarette smokers who inhaled. Two non-smokers achieved maximum levels of 2 and 4 mug/l. On a separate occasion two of the inhalers received 1 mg. 14C-nicotine in 10 divided doses injected intravenously. In both cases the peak arterial nicotine concentrations bore a similar relationship to the intravenous dose, as did the peak nicotine concentrations to the retained doses during smoking.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage A. K., Hall G. H., Morrison C. F. Pharmacological basis for the tobacco smoking habit. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):331–334. doi: 10.1038/217331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMMINS B. T., LAWTHER P. J. A SENSITIVE METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF CARBOXYHAEMOGLOBIN IN A FINGER PRICK SAMPLE OF BLOOD. Br J Ind Med. 1965 Apr;22:139–143. doi: 10.1136/oem.22.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines C. F., Jr, Mahajan D. K., Miljkovć D., Miljković M., Vesell E. S. Radioimmunoassay of plasma nicotine in habituated and naive smokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Dec;16(6):1083–1089. doi: 10.1002/cpt19741661083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac P. F., Rand M. J. Cigarette smoking and plasma levels of nicotine. Nature. 1972 Apr 7;236(5345):308–310. doi: 10.1038/236308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Gjika H. B., Van Vunakis H. Nicotine and its metabolites. Radioimmunoassays for nicotine and cotinine. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):5025–5030. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPADOPOULOS N. M., KINTZIOS J. A. Formation of metabolites from nicotine by a rabbit liver preparation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jun;140:269–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. A., Feyerabend C. Blood and Urinary nicotine in non-smokers. Lancet. 1975 Jan 25;1(7900):179–181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. M. Metabolism of small multiple doses of (14C) nicotine in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;41(3):521–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb08050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


