Abstract
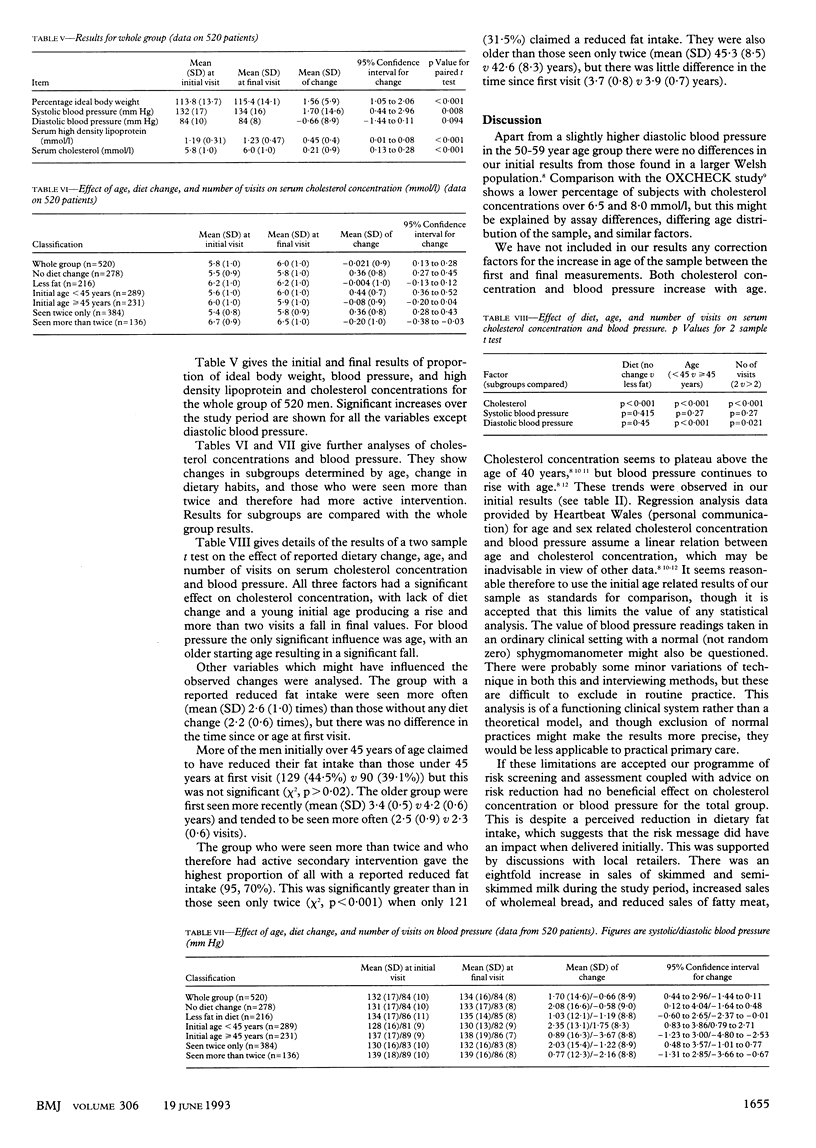
OBJECTIVES--To assess the effectiveness of a programme for reducing cardiovascular risk in men in terms of clinical measurements and perceptions of patients. DESIGN--Collection of paired data on men attending well person clinics over three to five years. Questionnaire to determine changes in risk related habits. SETTING--Well person clinics in rural general practice with five partners in mid-Wales. SUBJECTS--The first 687 men seen in the clinic: analysable data obtained on 520. Initial age range 28-60 years. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Analysis of serum cholesterol concentration (mmol/l) and blood pressure (mm Hg). Changes in diet, exercise, smoking, and drinking. RESULTS--Mean (SD) cholesterol concentration for all subjects increased from 5.8 (1.0) to 6.0 (1.0), p < 0.001. Overall percentage of ideal weight and mean systolic blood pressure also increased. Mean diastolic blood pressure was unchanged at 84 mm Hg. Professed dietary change, age, and number of visits all had significant effects on final cholesterol concentration. Those seen more often showed a significant decrease in cholesterol concentrations (in those seen more than twice mean (SD) initial value 6.7 (0.9) mmol/l v final value 6.5 (1.0) mmol/l, p < 0.001). Those over 45 years at start of study showed a significant decrease in diastolic blood pressure (mean (SD) initial value 89 (9) mm Hg v final value 86 (7) mm Hg, p < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS--These clinics are not effective in achieving a reduction in mean cholesterol concentration or blood pressure, despite evidence that the message of reduction in risk had been successfully transmitted. Success was achieved in older patients and those in whom a definite problem was identified. Identification of high risk groups and clinical case finding with appropriate long term follow up may be more cost effective in reducing cardiovascular risk than non-specific screening of the whole population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmen J., Forsén L., Hjort P. F., Midthjell K., Waaler H. T., Bjørndal A. Detecting hypertension: screening versus case finding in Norway. BMJ. 1991 Jan 26;302(6770):219–222. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6770.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. I., Lewis B., Shepherd J., Winder A. F., Fenster S., Rose L., Morgan B. Blood lipid concentrations and other cardiovascular risk factors: distribution, prevalence, and detection in Britain. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Jun 18;296(6638):1702–1706. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6638.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish R. Breathing life into Wales: progress in the Welsh Heart Programme. Health Trends. 1987 May;19(2):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond W. Preparation and properties of a cholesterol oxidase from Nocardia sp. and its application to the enzymatic assay of total cholesterol in serum. Clin Chem. 1973 Dec;19(12):1350–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Betteridge D. J., Durrington P., Laker M., Lewis B., Mann J., Miller J. P., Reckless J. P., Thompson G. R. Strategies for reducing coronary heart disease and desirable limits for blood lipid concentrations: guidelines of the British Hyperlipidaemia Association. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Nov 14;295(6608):1245–1246. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6608.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



