Abstract
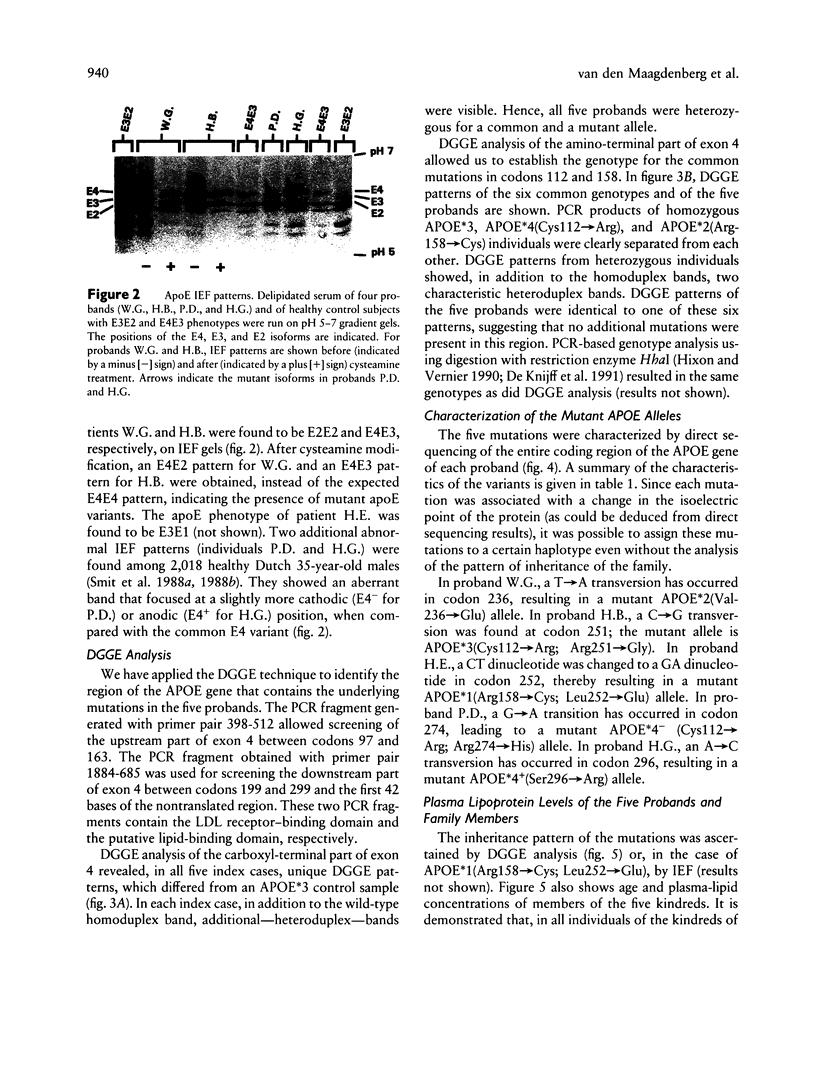
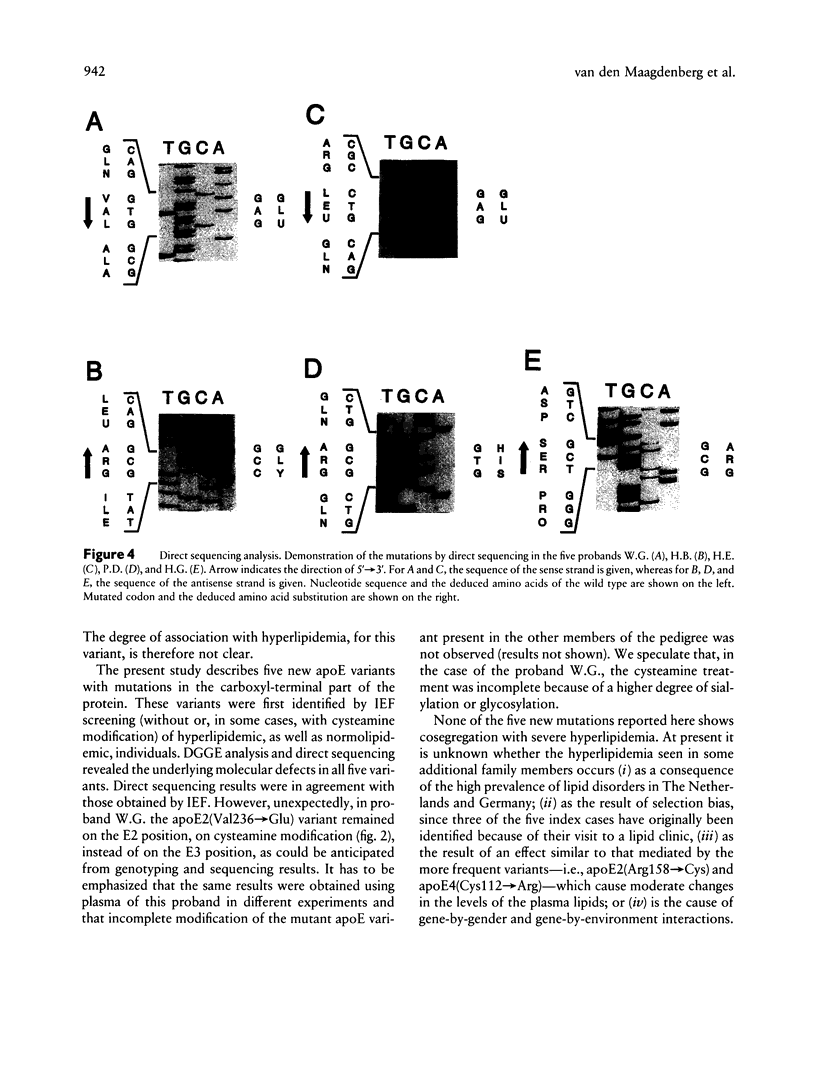
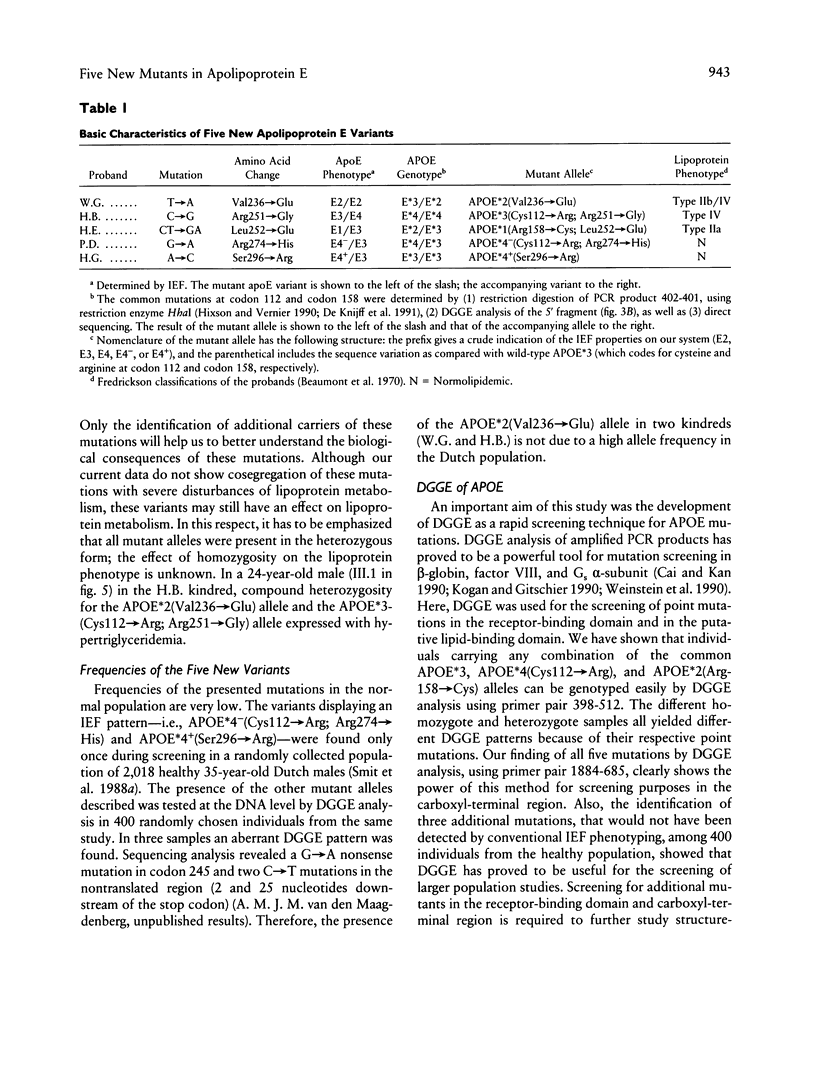
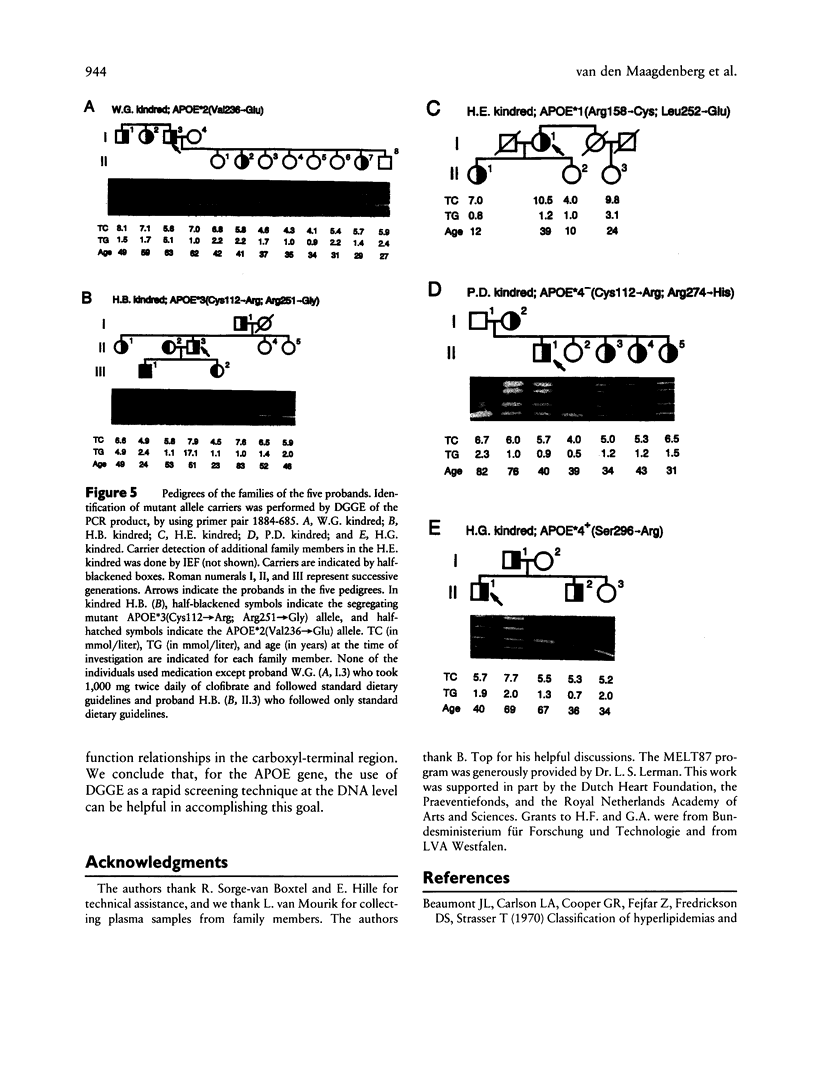
Assessment of the apolipoprotein E (apoE) phenotype by isoelectric focusing of both hyperlipidemic and normolipidemic individuals identified five new variants. All mutations were confined to the downstream part of the APOE gene by using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Sequence analysis revealed five new mutations causing unique amino acid substitutions in the carboxyl-terminal part of the protein containing the putative lipid-binding domain. Three hyperlipoproteinemic probands were carriers of the APOE*2(Val236→Glu) allele, the APOE*3(Cys112→Arg; Arg251→Gly) allele, or the APOE*1(Arg158→Cys; Leu252→Glu) allele. DGGE of the region encoding the receptor-binding domain was useful for haplotyping the mutations at codons 112 and 158. Family studies failed to demonstrate cosegregation between the new mutations and severe hyperlipoproteinemia, although a number of carriers for the APOE*3(Cys112→Arg; Arg251→Gly) allele and the APOE*1(Arg158→Cys; Leu252→Glu) allele expressed hypertriglyceridemia and/or hypercholesterolemia. Two other mutant alleles, APOE*4− (Cys112→Arg; Arg274→His) and APOE*4+(Ser296→Arg), were found in normolipidemic probands. The lack of cosegregation of these new mutations with severe hyperlipoproteinemia suggests that these mutations do not exert a dominant effect on the functioning of apoE.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaumont J. L., Carlson L. A., Cooper G. R., Fejfar Z., Fredrickson D. S., Strasser T. Classification of hyperlipidaemias and hyperlipoproteinaemias. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(6):891–915. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Elshourbagy N., Taylor J. M., Gordon J. I. Comparative analysis of repeated sequences in rat apolipoproteins A-I, A-IV, and E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):992–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai S. P., Kan Y. W. Identification of the multiple beta-thalassemia mutations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):550–553. doi: 10.1172/JCI114471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S. Length-independent separation of DNA restriction fragments in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Hwang S. L., Karlin J. B., Lin A. H., Prasad S. C., Bradley W. A. Apolipoprotein E mediates uptake of Sf 100-400 hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins by the low density lipoprotein receptor pathway in normal human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4526–4533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L. M., de Knijff P., Beisiegel U., Havinga J., Smit M., Klasen E. A rapid micromethod for apolipoprotein E phenotyping directly in serum. J Lipid Res. 1987 Apr;28(4):455–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L., de Wit E., Leuven J. G., Klasen E., Utermann G., Weber W., Beisiegel U. Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden. A new variant of human apolipoprotein E associated with familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;73(2):157–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00291607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S., Gitschier J. Mutations and a polymorphism in the factor VIII gene discovered by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2092–2096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalazar A., Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Giladi H., Innerarity T. L., Levanon A. Z., Boyles J. K., Amit B., Gorecki M., Mahley R. W. Site-specific mutagenesis of human apolipoprotein E. Receptor binding activity of variants with single amino acid substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3542–3545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Silverstein K. Computational simulation of DNA melting and its application to denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:482–501. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Tanimura M., Luo C. C., Datta S., Chan L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J Lipid Res. 1988 Mar;29(3):245–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann W. A., Gregg R. E., Sprecher D. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein E-1Harrisburg: a new variant of apolipoprotein E dominantly associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 17;1005(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Maniatis T., Lerman L. S. Detection and localization of single base changes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:501–527. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik Y. K., Chang D. J., Reardon C. A., Davies G. E., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the human apolipoprotein E gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Newhouse Y. M., Clarke H. R., Weisgraber K. H., McCarthy B. J., Mahley R. W., Bersot T. P. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E phenotype E3/3. Structure and genetics of an apolipoprotein E3 variant. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI113988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Blum C. B. Identification of a new structural variant of human apolipoprotein E, E2(Lys146 leads to Gln), in a type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject with the E3/2 phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1288–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI111085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4696–4700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., Rosseneu M., Bury J., Klasen E., Frants R., Havekes L. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in The Netherlands and its effect on plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):287–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01790099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., Sijts A., Klasen E. C., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Rare apolipoprotein E variant cosegregating with a unique APOE-C1-C2 haplotype in a normolipidemic family. Hum Hered. 1988;38(5):277–282. doi: 10.1159/000153799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., van der Kooij-Meijs E., Groenendijk C., van den Maagdenberg A. M., Gevers Leuven J. A., Stalenhoef A. F., Stuyt P. M., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Genetic heterogeneity in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. The E2(lys146----gln) variant results in a dominant mode of inheritance. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima S., Yamamura T., Menju M., Yamamoto A. Analysis of apolipoprotein E7 (apolipoprotein E-Suita) gene from a patient with hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biochem. 1989 Feb;105(2):249–253. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Langenbeck U., Beisiegel U., Weber W. Genetics of the apolipoprotein E system in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):339–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell M. R., Brennan S. O., Janus E. D., Fraser R., Carrell R. W. Apolipoprotein E2-Christchurch (136 Arg----Ser). New variant of human apolipoprotein E in a patient with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):483–490. doi: 10.1172/JCI113096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell M. R., Rall S. C., Jr, Brennan S. O., Nye E. R., George P. M., Janus E. D., Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E2-Dunedin (228 Arg replaced by Cys): an apolipoprotein E2 variant with normal receptor-binding activity. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Havekes L. M., Rall S. C., Jr Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden contains a seven-amino acid insertion that is a tandem repeat of residues 121-127. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21205–21210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Gejman P. V., Friedman E., Kadowaki T., Collins R. M., Gershon E. S., Spiegel A. M. Mutations of the Gs alpha-subunit gene in Albright hereditary osteodystrophy detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8287–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E distribution among human plasma lipoproteins: role of the cysteine-arginine interchange at residue 112. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Agard D. A. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1817–1822. doi: 10.1126/science.2063194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Yamamoto A., Sumiyoshi T., Hiramori K., Nishioeda Y., Nambu S. New mutants of apolipoprotein E associated with atherosclerotic diseases but not to type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1229–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Knijff P., van den Maagdenberg A. M., Stalenhoef A. F., Leuven J. A., Demacker P. N., Kuyt L. P., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E3-Leiden in an extended multigeneration pedigree. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):643–655. doi: 10.1172/JCI115349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]