Abstract
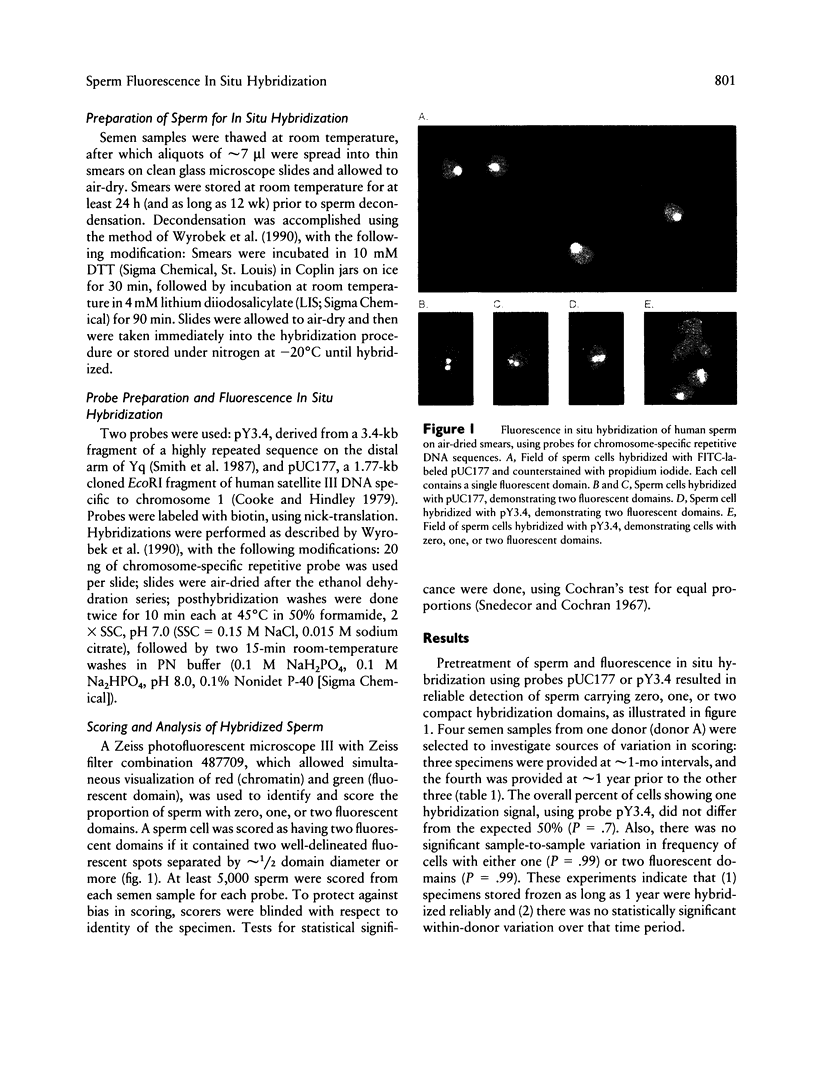
Fluorescence in situ hybridization with repetitive-sequence DNA probes was used to detect human sperm disomic for chromosomes 1 and Y in three healthy men. Data on these same men had been obtained previously, using the human-sperm/hamster-egg cytogenetic technique, providing a cytogenetic reference for validating sperm hybridization measurements. Air-dried smears were prepared from semen samples and treated with DTT and lithium diiodosalicylate to expand sperm chromatin. Hybridization with fluorescently tagged DNA probes for chromosomes 1 (pUC177) or Y (pY3.4) yielded average frequencies of sperm with two fluorescent domains of 14.2 +/- 2.4/10,000 and 5.6 +/- 1.6/10,000 sperm, respectively. These frequencies did not differ statistically from frequencies of hyperploidy observed for these chromosomes with the hamster technique. In addition, frequencies of disomic sperm from one donor were elevated approximately 2.5-fold above those of other donors, for both chromosomes 1 (P = .045) and Y (P = .01), consistent with a trend found with the hamster technique. We conclude that fluorescence in situ hybridization to sperm chromosomes provides a valid and promising measure of the frequency of disomic human sperm.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow P., Vosa C. G. The Y chromosome in human spermatozoa. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):961–962. doi: 10.1038/226961a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Madan K., Pearson P. L. Staining of some specific regions of human chromosomes, particularly the secondary constriction of No. 9. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):122–124. doi: 10.1038/newbio238122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond D. J. Mechanisms of aneuploid induction. Mutat Res. 1987 Dec;181(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(87)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriff B. F., Gordon L. A., Ashworth L. K., Carrano A. V. Chromosomal aberrations induced by in vitro irradiation: comparisons between human sperm and lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1988;12(2):167–177. doi: 10.1002/em.2860120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriff B., Gordon L., Ashworth L. K., Littman V., Watchmaker G., Carrano A. V. Cytogenetics of human sperm: meiotic segregation in two translocation carriers. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonen E., Pieters M. H., Dumoulin J. C., Meyer H., Evers J. L., Ramaekers F. C., Geraedts J. P. Nonisotopic in situ hybridization as a method for nondisjunction studies in human spermatozoa. Mol Reprod Dev. 1991 Jan;28(1):18–22. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080280104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond D. A., Pinkel D. Detection of aneuploidy and aneuploidy-inducing agents in human lymphocytes using fluorescence in situ hybridization with chromosome-specific DNA probes. Mutat Res. 1990 Oct;234(5):303–318. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(90)90041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttenbach M., Schmid M. Determination of Y chromosome aneuploidy in human sperm nuclei by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):553–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. The impact of aneuploidy upon public health: mortality and morbidity associated with human chromosome abnormalities. Basic Life Sci. 1985;36:7–33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2127-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenderny J., Röhrborn G. Chromosome analysis of human sperm. I. First results with a modified method. Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;76(4):385–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00272450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. A., Flook J. P., Hawk H. W. Sex preselection in rabbits: live births from X and Y sperm separated by DNA and cell sorting. Biol Reprod. 1989 Aug;41(2):199–203. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph A. M., Gosden J. R., Chandley A. C. Estimation of aneuploidy levels in human spermatozoa using chromosome specific probes and in situ hybridisation. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):234–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00286608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp R. W., Jr, Picciano D. J., Jacobson C. B. Y-chromosomal nondisjunction in dibromochloropropane-exposed workmen. Mutat Res. 1979 Feb;64(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(79)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Barclay L., Hildebrand K., Ko E., Fowlow S. B. Cytogenetic analysis of 400 sperm from three translocation heterozygotes. Hum Genet. 1990 Nov;86(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00205168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Hildebrand K., Yamamoto J., Rademaker A., Barnes M., Douglas G., Arthur K., Ringrose T., Brown I. S. An increased frequency of human sperm chromosomal abnormalities after radiotherapy. Mutat Res. 1986 Jul;174(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Rademaker A. W. The effect of age on the frequency of sperm chromosomal abnormalities in normal men. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):484–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Göhde W., White R. A., Longtin J. L. "Cytogenetic" studies of spermatids of mice carrying Cattanach's translocation by flow cytometry. Chromosoma. 1979;74(2):141–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00292269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Wohlert M. Sex chromosome abnormalities found among 34,910 newborn children: results from a 13-year incidence study in Arhus, Denmark. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1990;26(4):209–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. The use of new staining techniques for human chromosome identification. J Med Genet. 1972 Sep;9(3):264–275. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters M. H., Geraedts J. P., Meyer H., Dumoulin J. C., Evers J. L., Jongbloed R. J., Nederlof P. M., van der Flier S. Human gametes and zygotes studied by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;53(1):15–19. doi: 10.1159/000132886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Gledhill B. L., Van Dilla M. A., Lake S., Wyrobek A. J. Radiation-induced DNA content variability in mouse sperm. Radiat Res. 1983 Sep;95(3):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Lake S., Gledhill B. L., Van Dilla M. A., Stephenson D., Watchmaker G. High resolution DNA content measurements of mammalian sperm. Cytometry. 1982 Jul;3(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudak E., Jacobs P. A., Yanagimachi R. Direct analysis of the chromosome constitution of human spermatozoa. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):911–913. doi: 10.1038/274911a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. D., Young K. E., Talbot C. C., Jr, Schmeckpeper B. J. Repeated DNA of the human Y chromosome. Development. 1987;101 (Suppl):77–92. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.Supplement.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Robinson J. A. A difference in dry mass between the heads of X- and Y-bearing human spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil. 1976 Sep;48(1):9–15. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0480009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt J. L., Templeton A. A., Messinis I., Bell L., Cunningham P., Duncan R. O. Trisomy 1 in an eight cell human pre-embryo. J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;24(1):60–64. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrobek A. J., Alhborn T., Balhorn R., Stanker L., Pinkel D. Fluorescence in situ hybridization to Y chromosomes in decondensed human sperm nuclei. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Nov;27(3):200–208. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080270304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrobek A. J., Gordon L. A., Burkhart J. G., Francis M. W., Kapp R. W., Jr, Letz G., Malling H. V., Topham J. C., Whorton M. D. An evaluation of human sperm as indicators of chemically induced alterations of spermatogenic function. A report of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Gene-Tox Program. Mutat Res. 1983 May;115(1):73–148. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(83)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]