Abstract
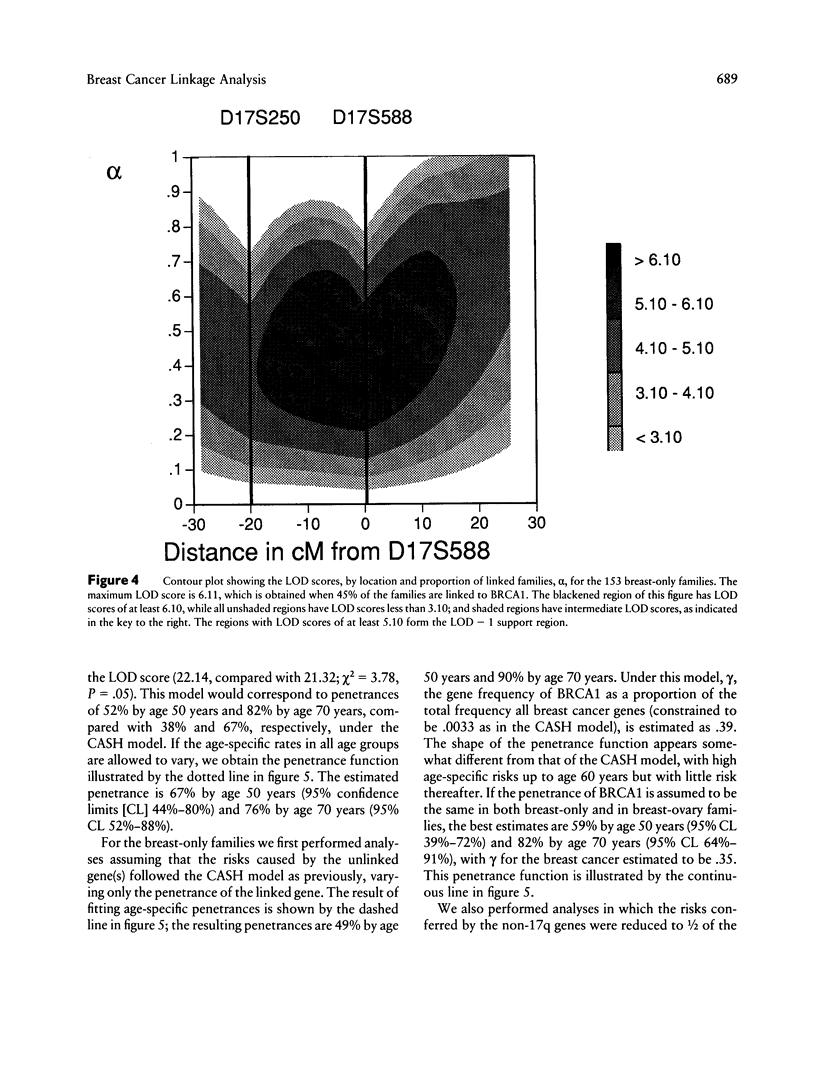
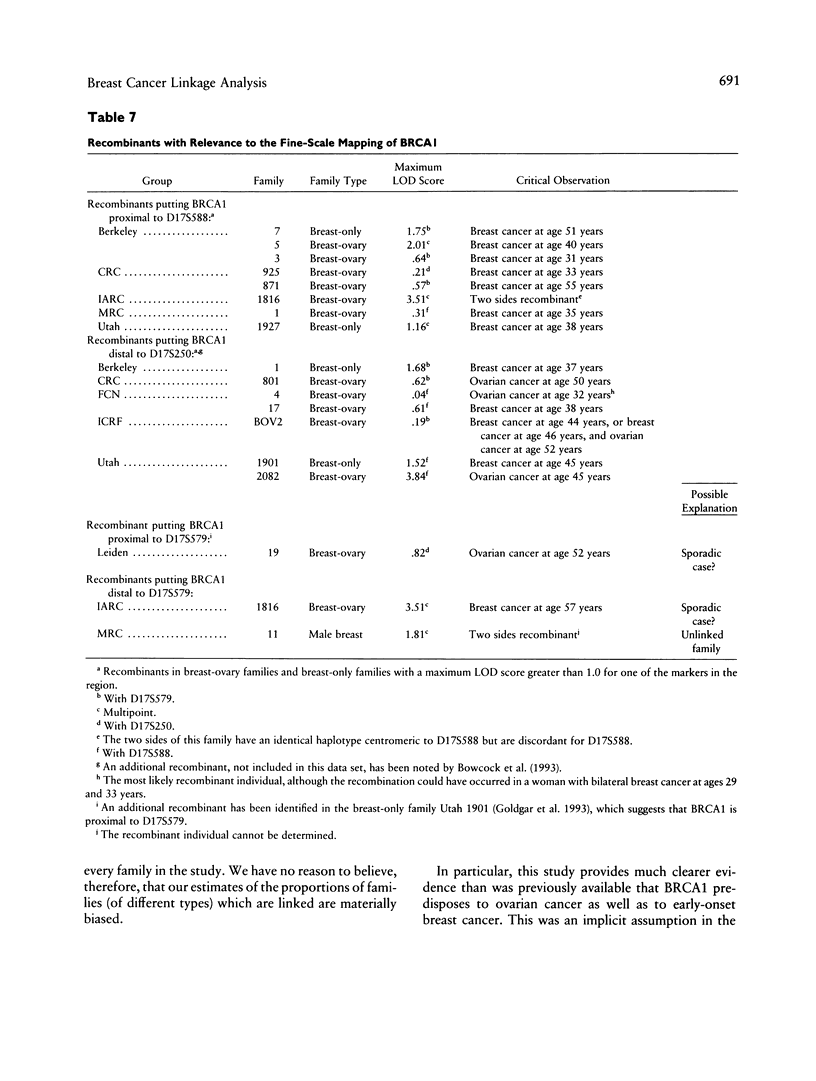
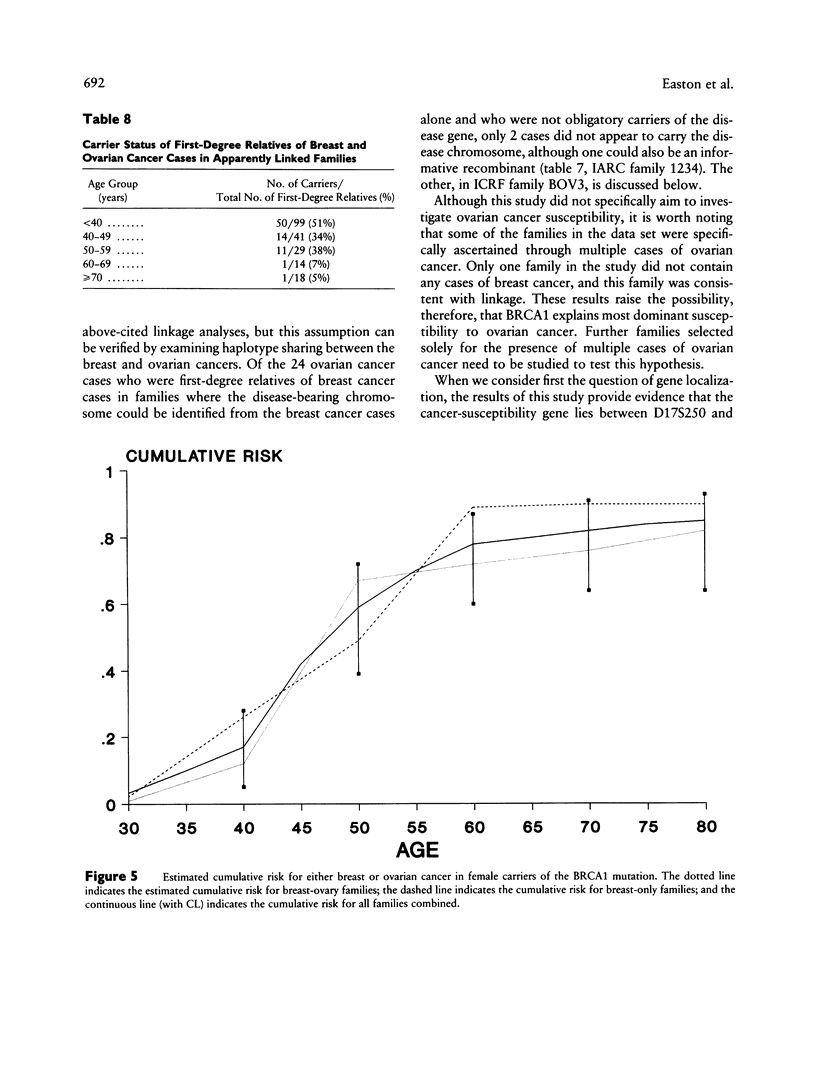
Breast cancer is known to have an inherited component, consistent in some families with autosomal dominant inheritance; in such families the disease often occurs in association with ovarian cancer. Previous genetic linkage studies have established that in some such families disease occurrence is linked to markers on chromosome 17q. This paper reports the results of a collaborative linkage study involving 214 breast cancer families, including 57 breast-ovarian cancer families; this represents almost all the known families with 17q linkage data. Six markers on 17q, spanning approximately 30 cM, were typed in the families. The aims of the study were to define more precisely the localization of the disease gene, the extent of genetic heterogeneity and the characteristics of linked families and to estimate the penetrance of the 17q gene. Under the assumption of no genetic heterogeneity, the strongest linkage evidence was obtained with D17S588 (maximum LOD score [Zmax] = 21.68 at female recombination fraction [theta f] = .13) and D17S579 (Zmax = 13.02 at theta f = .16). Multipoint linkage analysis allowing for genetic heterogeneity provided evidence that the predisposing gene lies between the markers D17S588 and D17S250, an interval whose genetic length is estimated to be 8.3 cM in males and 18.0 cM in females. This position was supported over other intervals by odds of 66:1. The location of the gene with respect to D17S579 could not be determined unequivocally. Under the genetic model used in the analysis, the best estimate of the proportion of linked breast-ovarian cancer families was 1.0 (lower LOD-1 limit 0.79). In contrast, there was significant evidence of genetic heterogeneity among the families without ovarian cancer, with an estimated 45% being linked. These results suggest that a gene(s) on chromosome 17q accounts for the majority of families in which both early-onset breast cancer and ovarian cancer occur but that other genes predisposing to breast cancer exist. By examining the fit of the linkage data to different penetrance functions, the cumulative risk associated with the 17q gene was estimated to be 59% by age 50 years and 82% by age 70 years. The corresponding estimates for the breast-ovary families were 67% and 76%, and those for the families without ovarian cancer were 49% and 90%; these penetrance functions did not differ significantly from one another.
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami H. O., Hansen J., Jung B., Rimsten A. Familiality in breast cancer: a case-control study in a Sweden population. Br J Cancer. 1980 Jul;42(1):71–77. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arason A., Barkardóttir R. B., Egilsson V. Linkage analysis of chromosome 17q markers and breast-ovarian cancer in Icelandic families, and possible relationship to prostatic cancer. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):711–717. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Green P., Knowlton R., Schumm J., Lander E., Oliphant A., Willard H., Akots G., Brown V., Gravius T. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 7 with 63 DNA markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8006–8010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. T., Cannon-Albright L., McLellan T., Gardner E. J., Skolnick M. H. Segregation and linkage analysis of nine Utah breast cancer pedigrees. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(3):151–169. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. M., Nicolai H., Borrow J., Solomon E. A somatic cell hybrid map of the long arm of human chromosome 17, containing the familial breast cancer locus (BRCA1). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):702–710. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Anderson L. A., Friedman L. S., Black D. M., Osborne-Lawrence S., Rowell S. E., Hall J. M., Solomon E., King M. C. THRA1 and D17S183 flank an interval of < 4 cM for the breast-ovarian cancer gene (BRCA1) on chromosome 17q21. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):718–722. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Boehnke M., Frank T. S., Kiousis S., Xu J., Guo S. W., Hauser E. R., Norum R. A., Helmbold E. A., Markel D. S. BRCA1 maps proximal to D17S579 on chromosome 17q21 by genetic analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):792–798. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus E. B., Risch N. J., Thompson W. D. Age at onset as an indicator of familial risk of breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jun;131(6):961–972. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. B., Porter D. E., Wallace M. R., Carothers A., Steel C. M. Linkage of a major breast cancer gene to chromosome 17q12-21: results from 15 Edinburgh families. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):723–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C. Ascertainment and age of onset in pedigree analysis. Hum Hered. 1973;23(2):105–112. doi: 10.1159/000152561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Solomon E., Ledbetter D. H. Second international workshop on human chromosome 17. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;57(2-3):66–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Narod S. A., Lynch H. T., Watson P., Conway T., Lynch J., Parboosingh J., O'Connell P., White R., Lenoir G. M. A breast-ovarian cancer susceptibility gene maps to chromosome 17q21. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):736–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Grundy G. W., Creagan E. T., Everson R. B. Six families prone to ovarian cancer. Cancer. 1975 Aug;36(2):364–369. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197508)36:2<364::aid-cncr2820360211>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J., STEPHENS F. E. Breast cancer in one family group. Am J Hum Genet. 1950 Mar;2(1):30–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgar D. E., Cannon-Albright L. A., Oliphant A., Ward J. H., Linker G., Swensen J., Tran T. D., Fields P., Uharriet P., Skolnick M. H. Chromosome 17q linkage studies of 18 Utah breast cancer kindreds. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):743–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Friedman L., Guenther C., Lee M. K., Weber J. L., Black D. M., King M. C. Closing in on a breast cancer gene on chromosome 17q. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;50(6):1235–1242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Lee M. K., Newman B., Morrow J. E., Anderson L. A., Huey B., King M. C. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1684–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2270482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iselius L., Slack J., Littler M., Morton N. E. Genetic epidemiology of breast cancer in Britain. Ann Hum Genet. 1991 May;55(Pt 2):151–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1991.tb00408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey J. L. A review of the epidemiology of human breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1979;1:74–109. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Harris R. E., Guirgis H. A., Maloney K., Carmody L. L., Lynch J. F. Familial association of breast/ovarian carcinoma. Cancer. 1978 Apr;41(4):1543–1549. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197804)41:4<1543::aid-cncr2820410444>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay K., Hawkins J. R., Superti-Furga A., Steinmann B., Dalgleish R. A HaeIII RFLP in COL1A1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5926–5926. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margaritte P., Bonaiti-Pellie C., King M. C., Clerget-Darpoux F. Linkage of familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21 may not be restricted to early-onset disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;50(6):1231–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettlin C., Croghan I., Natarajan N., Lane W. The association of age and familial risk in a case-control study of breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jun;131(6):973–983. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mérette C., King M. C., Ott J. Heterogeneity analysis of breast cancer families by using age at onset as a covariate. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):515–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narod S. A., Feunteun J., Lynch H. T., Watson P., Conway T., Lynch J., Lenoir G. M. Familial breast-ovarian cancer locus on chromosome 17q12-q23. Lancet. 1991 Jul 13;338(8759):82–83. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B., Austin M. A., Lee M., King M. C. Inheritance of human breast cancer: evidence for autosomal dominant transmission in high-risk families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3044–3048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A simple scheme for the analysis of HLA linkages in pedigrees. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Oct;42(2):255–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. A simple sequence repeat polymorphism at the human growth hormone locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):689–689. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Segregation analysis incorporating linkage markers. I. Single-locus models with an application to type I diabetes. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):363–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. M., Risch N., Thompson W. D. Evaluating genetic association among ovarian, breast, and endometrial cancer: evidence for a breast/ovarian cancer relationship. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):521–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. M., Thompson W. D. Familial ovarian cancer: a population-based case-control study. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Sep;128(3):456–466. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Easton D. F., Ford D., Peto J., Anderson K., Averill D., Stratton M., Ponder M., Pye C., Ponder B. A. Genetic heterogeneity and localization of a familial breast-ovarian cancer gene on chromosome 17q12-q21. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):767–776. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr N. K., Kelsell D. P., Black D. M., Murday V. A., Turner G., Crockford G. P., Solomon E., Cartwright R. A., Bishop D. T. Linkage analysis of early-onset breast and ovarian cancer families, with markers on the long arm of chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):777–785. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Caligo M. A., Simi P., Black D. M., Nardini V., Casarino L., Rocchi M., Ferrara G., Solomon E., Bevilacqua G. The NM23 gene maps to human chromosome band 17q22 and shows a restriction fragment length polymorphism with BglII. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):84–88. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. R., Anderson D. E. Genetic epidemiology of breast cancer: segregation analysis of 200 Danish pedigrees. Genet Epidemiol. 1984;1(1):7–20. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


