Abstract
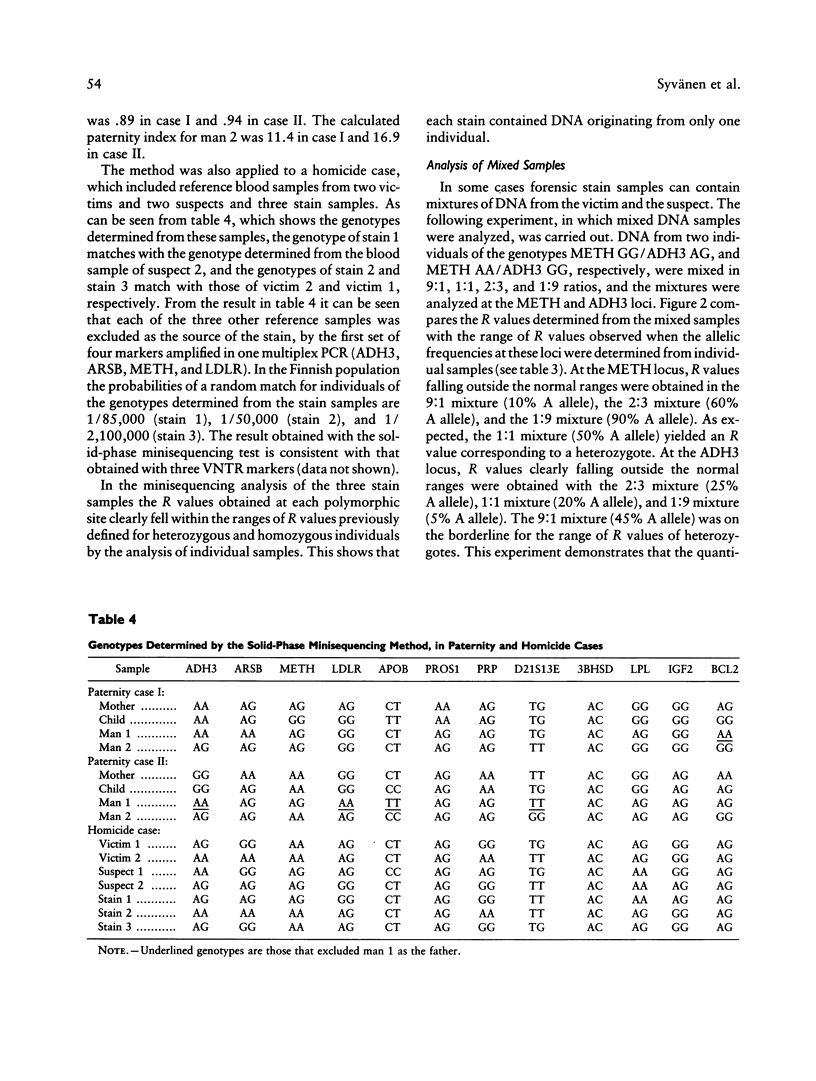
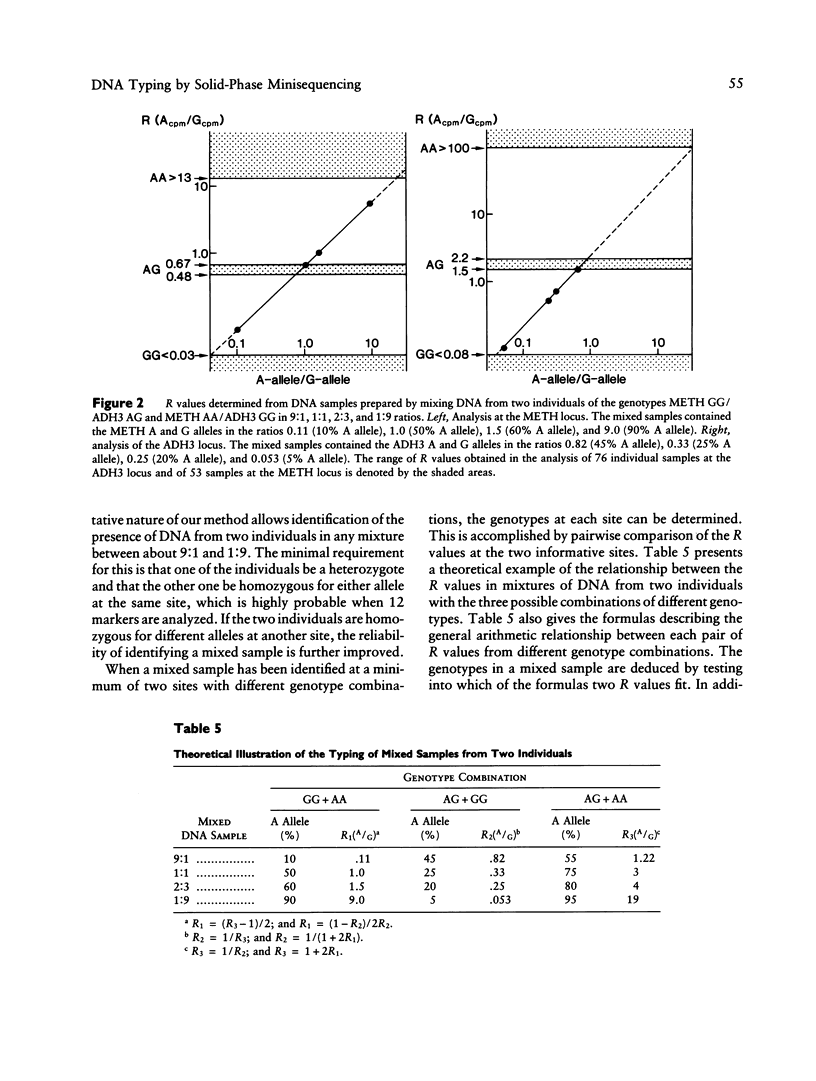
We have developed a new method for forensic identification of individuals, in which a panel of biallelic DNA markers are amplified by the PCR, and the variable nucleotides are detected in the amplified DNA fragments by the solid-phase minisequencing method. A panel of 12 common polymorphic nucleotides located on different chromosomes with reported allele frequencies close to .5 were chosen for the test. The allele frequencies for most of the markers were found to be similar in the Finnish and other Caucasian populations. We also introduce a novel approach for rapid determination of the population frequencies of biallelic markers. By this approach we were able to determine the allele frequencies of the markers in the Finnish population, by quantitative analysis of three pooled DNA samples representing 3,000 individuals. The power of discrimination and exclusion of the solid-phase minisequencing typing test with 12 markers was similar to that of three VNTR markers that are routinely used in forensic analyses at our institute. The solid-phase minisequencing method was successfully applied to type paternity and forensic case samples. We also show that the quantitative nature of our method allows typing of mixed samples.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto-Setälä K., Viikari J., Akerblom H. K., Kuusela V., Kontula K. DNA polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein B and A-I/C-III genes are associated with variations of serum low density lipoprotein cholesterol level in childhood. J Lipid Res. 1991 Sep;32(9):1477–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Graves G., Budowle B. Polymerase chain reaction amplification products separated on rehydratable polyacrylamide gels and stained with silver. Biotechniques. 1989 Jul-Aug;7(7):736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. J., Webb C. E., Peake I. R., Bloom A. L. AatII polymorphism in von Willebrand factor gene at codon 471. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3159–3159. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowle B., Chakraborty R., Giusti A. M., Eisenberg A. J., Allen R. C. Analysis of the VNTR locus D1S80 by the PCR followed by high-resolution PAGE. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):137–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Hirvonen S., Kauppinen H. L., Myllylä G. Production of interferon in human leukocytes from normal donors with the use of Sendai virus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov P. M., Jenkins J. R. BstNI/NciI polymorphism of the human p53 gene (TP53). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6969–6969. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6969-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Palmer M. S., Dryden A. J. Genetic predisposition to iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1991 Jun 15;337(8755):1441–1442. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93128-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diepstraten C. M., van Amstel J. K., Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M. A CCA/CCG neutral dimorphism in the codon for Pro 626 of the human protein S gene PS alpha (PROS1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5091–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Civitello A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T. DNA typing and genetic mapping with trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeats. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):746–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K. L., FitzGerald G. A., Lawn R. M. Two polymorphisms in the human lipoprotein lipase (LPL) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7657–7657. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURTLER H. Principles of blood-group statistical evaluation of paternity cases at the University Institute of Forensic Medicine, Copenhagen. Acta Med Leg Soc (Liege) 1956;9(Spec No):83–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. D., Newbold J. E., Sugino A. Intraspecific nucleotide sequence variability surrounding the origin of replication in human mitochondrial DNA. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helminen P., Sajantila A., Johnsson V., Lukka M., Ehnholm C., Peltonen L. Amplification of three hypervariable DNA regions by polymerase chain reaction for paternity determinations: comparison with conventional methods and DNA fingerprinting. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Feb;6(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Richards B., Merrill J. J., Klinger K. W. Characterization and rapid diagnostic analysis of DNA polymorphisms closely linked to the cystic fibrosis locus. Clin Chem. 1990 Sep;36(9):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög J. O., Hedén L. O., Larsson K., Jörnvall H., von Bahr-Lindström H. The gamma 1 and gamma 2 subunits of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. cDNA structures, two amino acid replacements, and compatibility with changes in the enzymatic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):215–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., MacLeod A., Tamaki K., Neil D. L., Monckton D. G. Minisatellite repeat coding as a digital approach to DNA typing. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):204–209. doi: 10.1038/354204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin W. D., Desnick R. J., Schuchman E. H. A common polymorphism in the human arylsulfatase B (ARSB) gene at 5q13-q14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4305–4305. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4305-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A. Blood samples: probability of discrimination. J Forensic Sci Soc. 1972 Apr;12(2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/s0015-7368(72)70695-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai K., Nakamura Y., White R. Amplification of a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) locus (pMCT118) by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and its application to forensic science. J Forensic Sci. 1990 Sep;35(5):1196–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Rall S. C., Jr, Innerarity T. L., Blackhart B., Taylor W. H., Marcel Y., Milne R. Complete protein sequence and identification of structural domains of human apolipoprotein B. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):734–738. doi: 10.1038/323734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar H. A., Stowring L. E., Westaway D., Stubblebine W. H., Prusiner S. B., Dearmond S. J. Molecular cloning of a human prion protein cDNA. DNA. 1986 Aug;5(4):315–324. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachance Y., Luu-The V., Labrie C., Simard J., Dumont M., de Launoit Y., Guérin S., Leblanc G., Labrie F. Characterization of human 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5-delta 4-isomerase gene and its expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20469–20475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Hobbs H. H. Human LDL receptor gene: HincII polymorphism detected by gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7215–7215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukka M., Ehnholm C., Kuusi T. Phosphoglucomutase (PGM1) subtypes in a Finnish population determined by isoelectric focusing in agarose gel. Hum Hered. 1985;35(2):95–100. doi: 10.1159/000153523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukka M., Turunen P., Kataja M., Ehnholm C. Group-specific component (Gc): subtypes in the Finnish population. Description of a new allele and an apparent mother-child incompatibility. Hum Hered. 1986;36(5):299–303. doi: 10.1159/000153646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiura K., Durrant I., Evans M. R., Gait M. J. Biotinyl and phosphotyrosinyl phosphoramidite derivatives useful in the incorporation of multiple reporter groups on synthetic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4345–4354. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevanlinna H. R. The Finnish population structure. A genetic and genealogical study. Hereditas. 1972;71(2):195–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1972.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. A., Kaiser R., Lappin S., Stewart J., Hood L., Landegren U. Automated DNA diagnostics using an ELISA-based oligonucleotide ligation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8923–8927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Tkalcevic G. T., Stocks J., Galton D. J., Brown W. V. Nucleotide sequence of PvuII polymorphic site at the human lipoprotein lipase gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6752–6752. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C., Schmidt B., Rommerskirch W., Rupp K., Zühlsdorf M., Vingron M., Meyer H. E., Pohlmann R., von Figura K. Phylogenetic conservation of arylsulfatases. cDNA cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3374–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploos van Amstel H. K., Reitsma P. H., van der Logt C. P., Bertina R. M. Intron-exon organization of the active human protein S gene PS alpha and its pseudogene PS beta: duplication and silencing during primate evolution. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7853–7861. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhéaume E., Sirois I., Labrie F., Simard J. Codon 367 polymorphism of the human type I 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/isomerase gene (HS5DB3). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):6060–6060. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Walsh P. S., Levenson C. H., Erlich H. A. Genetic analysis of amplified DNA with immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajantila A., Budowle B., Ström M., Johnsson V., Lukka M., Peltonen L., Ehnholm C. PCR amplification of alleles at the DIS80 locus: comparison of a Finnish and a North American Caucasian population sample, and forensic casework evaluation. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):816–825. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajantila A., Puomilahti S., Johnsson V., Ehnholm C. Amplification of reproducible allele markers for amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis. Biotechniques. 1992 Jan;12(1):16, 18, 20-2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria L. F., Ludwig E. H., Clarke H. R., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., McCarthy B. J. Association between a specific apolipoprotein B mutation and familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):587–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinissen P., Van Broeckhoven C. PCR detection of the frequent TaqI RFLP at locus D21S13E. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2516–2516. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2516-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Hopgood R., Lang B., Gill P. Automated amplification and sequencing of human mitochondrial DNA. Electrophoresis. 1991 Jan;12(1):17–21. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150120105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Aalto-Setälä K., Harju L., Kontula K., Söderlund H. A primer-guided nucleotide incorporation assay in the genotyping of apolipoprotein E. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):684–692. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90255-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Söderlund H., Laaksonen E., Bengtström M., Turunen M., Palotie A. N-ras gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: accurate detection by solid-phase minisequencing. Int J Cancer. 1992 Mar 12;50(5):713–718. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro K., Fujii H., Inoue T., Yamada M. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of ApaI polymorphism at the insulin like growth factor II gene (IGF2). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6967–6967. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Kant J., Reed J. C. G to A polymorphism in the second exon of the BCL2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1964–1964. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1964-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. S., Erlich H. A., Higuchi R. Preferential PCR amplification of alleles: mechanisms and solutions. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 May;1(4):241–250. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. L., Carr L. G., Bosron W. F., Li T. K., Edenberg H. J. Genotyping of human alcohol dehydrogenases at the ADH2 and ADH3 loci following DNA sequence amplification. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter-Holthuizen P., Jansen M., van der Kammen R. A., van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Differential expression of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene. Characterization of the IGF-II mRNAs and an mRNA encoding a putative IGF-II-associated protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


